Question: Please help with basic 'awk' programming You don't need advanced features of AWK for these scripts. Do not use 'getline' or 'next', and stick to
Please help with basic 'awk' programming
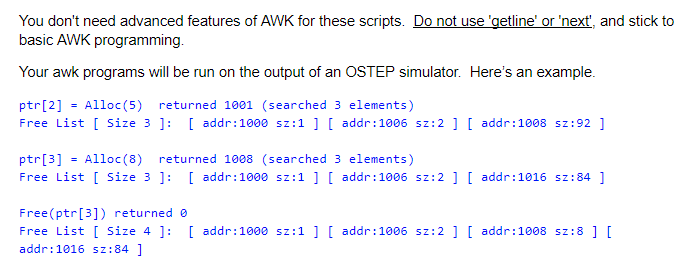

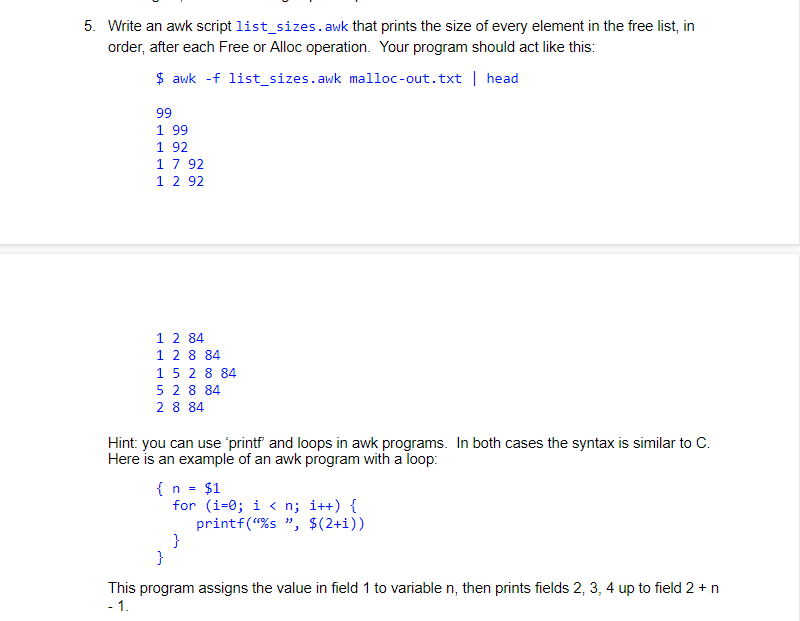
You don't need advanced features of AWK for these scripts. Do not use 'getline' or 'next', and stick to basic AWK programming. Your awk programs will be run on the output of an OSTEP simulator. Here's an example. ptr [2] = Alloc(5) returned 1001 (searched 3 elements) Free List [ Size 3 ]: [ addr:1000 sz:1 ] [ addr:1006 sz:2 ] [ addr:1008 sz:92] ptr [3] Alloc(8) returned 1008 (searched 3 elements) Free List [ Size 3 ]: [ addr:1000 sz:1 ] [ addr:1006 sz:2 ] [ addr:1016 sz:84 ] Free (ptr [3]) returned a Free List [ Size 4 ]: [ addr:1000 addr: 1016 sz: 84 ] 2:1 ] [ addr:1006 sz:2 ] [ addr:1008 sz:8 ] [ 1. Write an awk script freesize. awk that gets the size of the free list after every "Free" or "Alloc" operation. Your program should act like this: $ awk -f freesize. awk malloc-out.txt | wc -1 991 $ awk -f freesize. awk malloc-out.txt tail -5 45 44 45 45 44 Hint: this can easily be done with a one-line awk script. 2. Write an awk script count_allocs.awk that counts the number of successful allocs and the number of failed alloc calls. Your program should act like this: $ awk -f count_allocs. awk malloc-out.txt num successes: 444; num failures: 104 Hint consider writing one pattern for the failure case and another pattern for the success case. 3. Write an awk script num_bytes.awk that records the number of bytes requested in each alloc call. Your program should act like this: $ awk -f num_bytes. awk malloc-out.txt | WC -1 548 $ awk -f num_bytes.awk malloc-out.txt | head -200 tail -5 1 10 10 6 Hint: This can be done in one line. Consider using the awk 'substr' function. 4. Write an awk script succ_reqs.awk that prints the number of bytes requested, and then a 1 or a 0 depending on whether the request was successful (1 means success). Your program should act like this: $ awk -f succ_reqs. awk malloc-out.txt | tail -5 5 1 7 1 1 1 10 0 6 1 Hint: Again, consider writing separate patterns for the success and failure cases. 5. Write an awk script list_sizes.awk that prints the size of every element in the free list, in order, after each Free or Alloc operation. Your program should act like this: $ awk -f list_sizes.awk malloc-out.txt | head 99 1 99 1 92 1 7 92 1 292 1 2 84 1 2 8 84 15 2 8 84 5 2 8 84 2 8 84 Hint: you can use 'printf and loops in awk programs. In both cases the syntax is similar to C. Here is an example of an awk program with a loop { n = $1 for (i=0; i
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


