Question: PLEASE HELP WITH D AND E! In an electrophoresis experiment a charged biomolecule is placed in an electric field E. At steady state the electric
 PLEASE HELP WITH D AND E!
PLEASE HELP WITH D AND E!
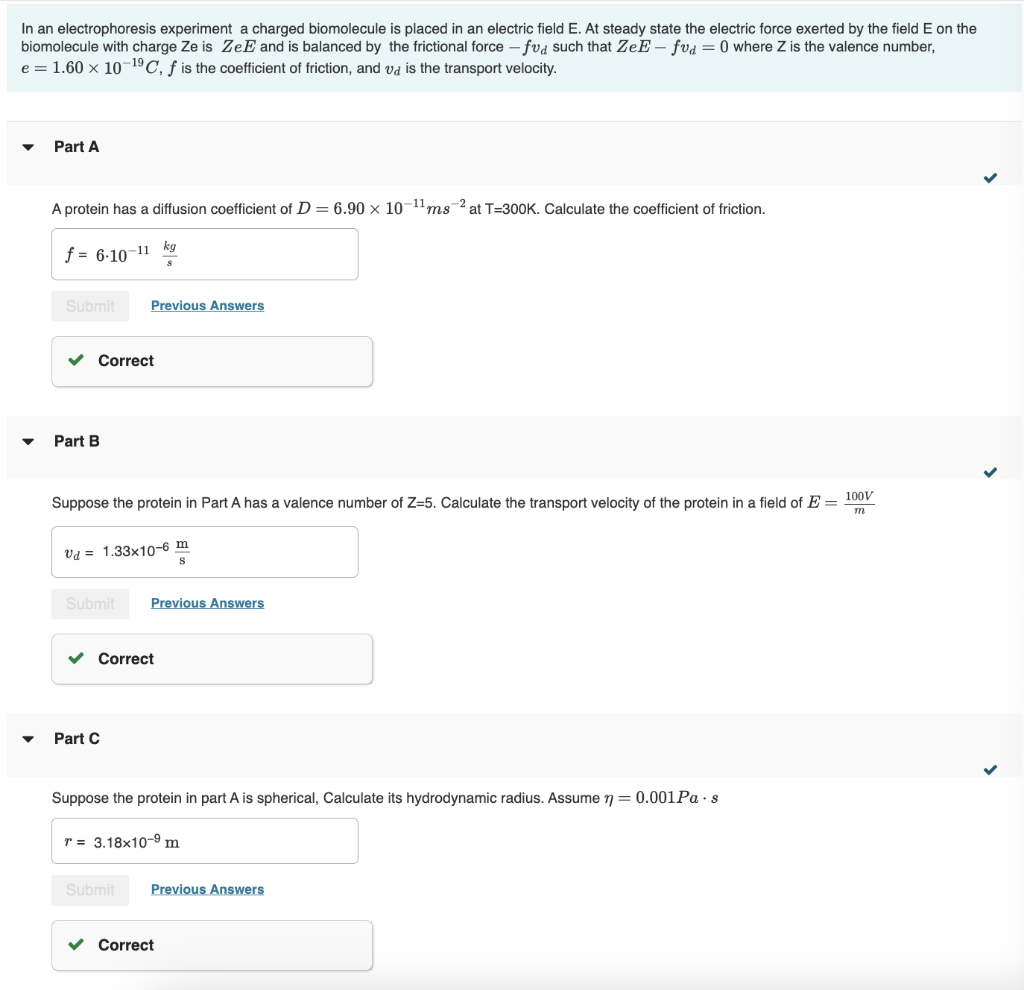
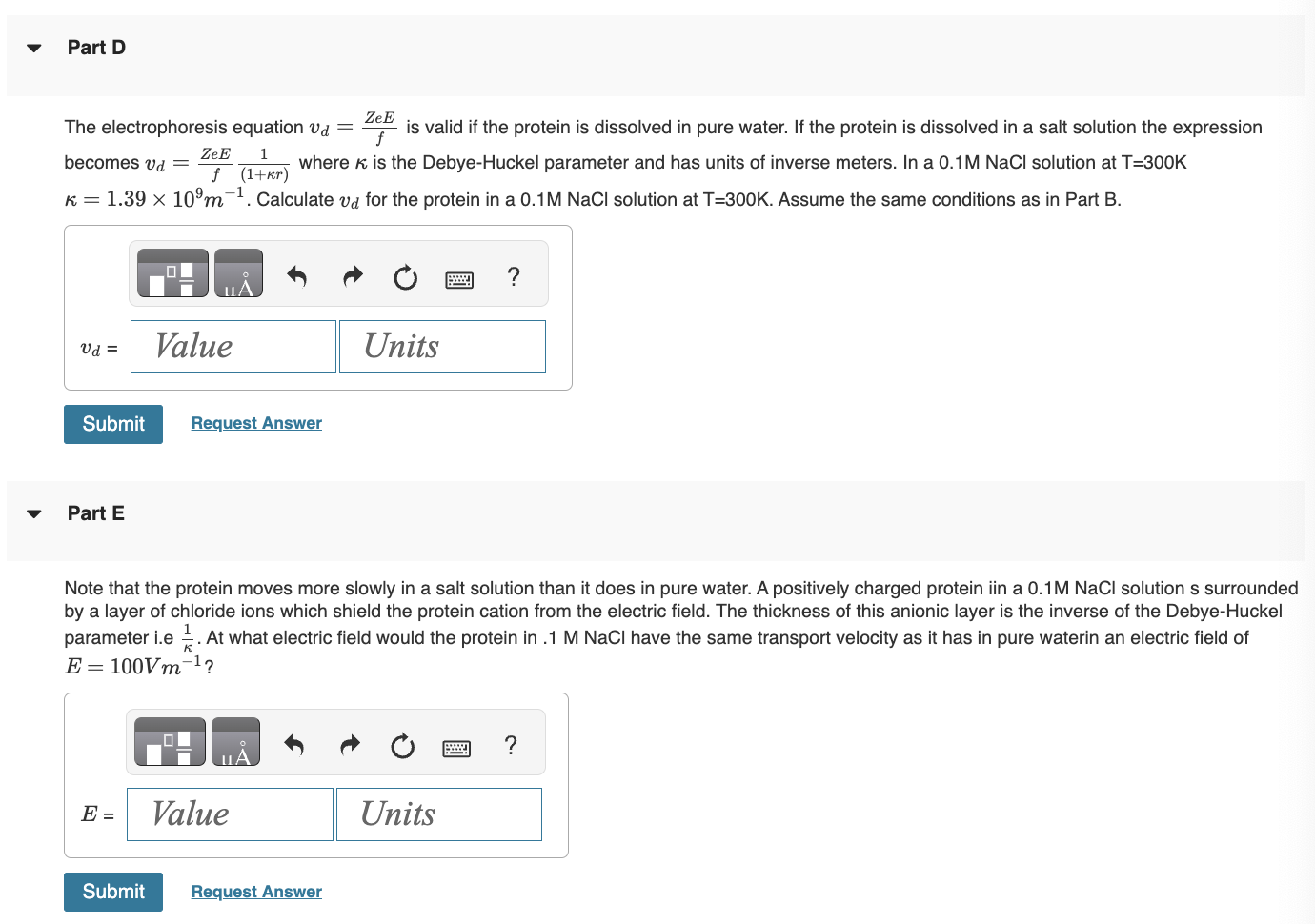
In an electrophoresis experiment a charged biomolecule is placed in an electric field E. At steady state the electric force exerted by the field E on the biomolecule with charge Ze is ZeE and is balanced by the frictional force fvd such that ZeEfvd=0 where Z is the valence number, e=1.601019C,f is the coefficient of friction, and vd is the transport velocity. Part A A protein has a diffusion coefficient of D=6.901011ms2 at T=300K. Calculate the coefficient of friction. Part B Suppose the protein in Part A has a valence number of Z=5. Calculate the transport velocity of the protein in a field of E=m100V Part C Suppose the protein in part A is spherical, Calculate its hydrodynamic radius. Assume =0.001Pas The electrophoresis equation vd=fZeE is valid if the protein is dissolved in pure water. If the protein is dissolved in a salt solution the expression becomes vd=fZeE(1+r)1 where is the Debye-Huckel parameter and has units of inverse meters. In a 0.1MNaCl solution at T=300K =1.39109m1. Calculate vd for the protein in a 0.1MNaCl solution at T=300K. Assume the same conditions as in Part B. Part E Note that the protein moves more slowly in a salt solution than it does in pure water. A positively charged protein iin a 0.1MNaCl solution s surroundec by a layer of chloride ions which shield the protein cation from the electric field. The thickness of this anionic layer is the inverse of the Debye-Huckel parameter i.e 1. At what electric field would the protein in .1 MNaCl have the same transport velocity as it has in pure waterin an electric field of E=100Vm1
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


