Question: please i need help with this Time dilation, Length contraction and Relativistic velocity-addition Time dilation is the phenomenon predicted by the theory of special relativity
please i need help with this
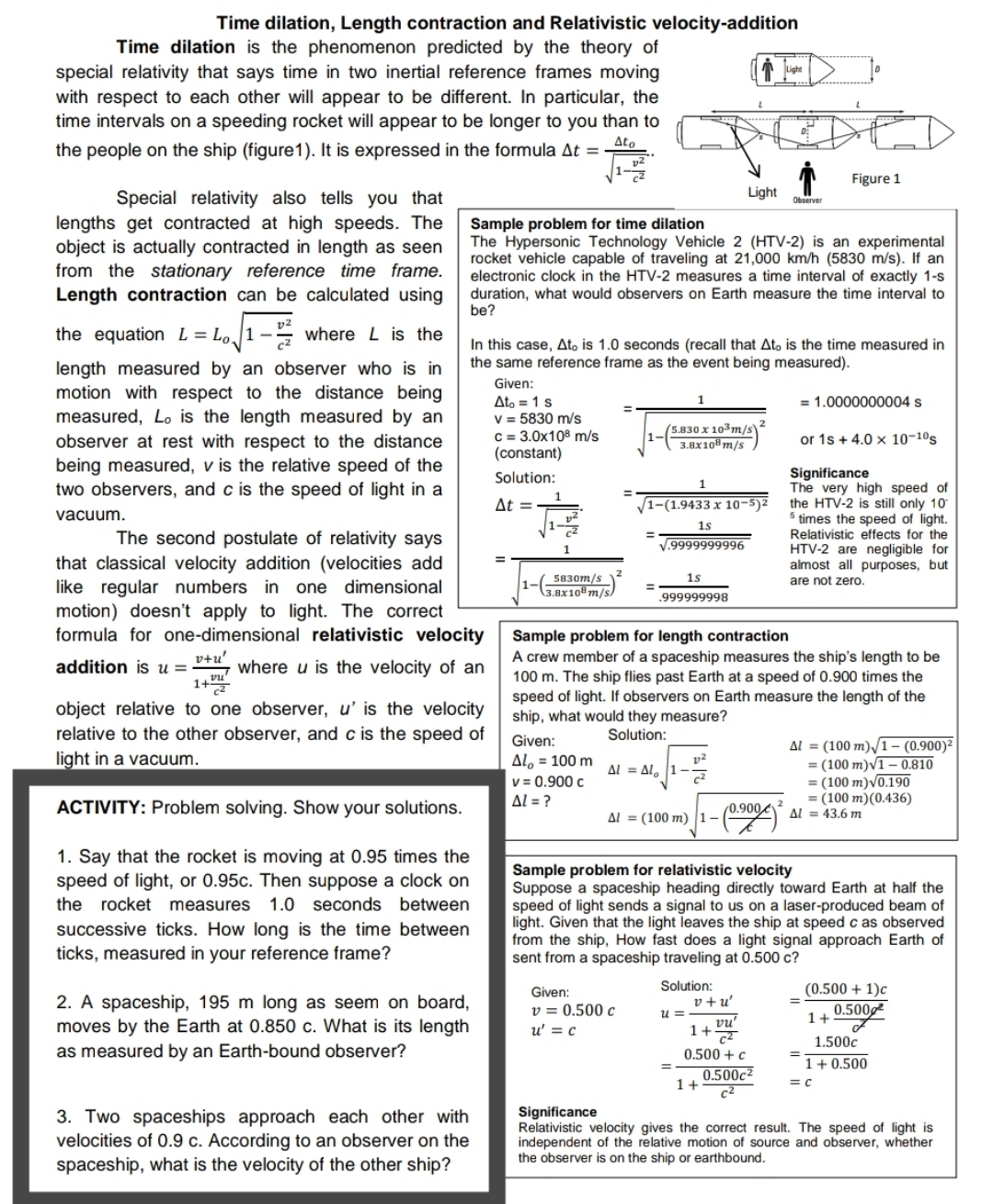
Time dilation, Length contraction and Relativistic velocity-addition Time dilation is the phenomenon predicted by the theory of special relativity that says time in two inertial reference frames moving with respect to each other will appear to be different. In particular. the time intervals on a speeding rocket will appear to be longer to you than to the people on the ship {figure1). It is expressed in the formula tit = a\" . Special relativity also tells you that lengths get contracted at high speeds- The object is actually contracted in length as seen from the stationary reference time frame. Length contraction can be calculated using the equation L = Lo 1 :: where l. is the length measured by an observer who is in motion with respect to the distance being measured. Lo is the length measured by an observer at rest with respect to the distance being measured. v is the relative speed of the two observers, and c is the speed of light in a vacuum. The second postulate of relativity says that classical velocity addition (velocities add like regular numbers in one dimensional motion) doesn't apply to light. The correct formula for one-dimensional relativistic velocity addition is u = L"; where u is the velocity of an V" 1+? object relative to one observer. 0' is the velocity relative to the other observer. and c is the speed of l' ht in a vacuum. ACTIVI'I'Y: Problem solving. Show your solutions. 1. Say that the rocket is moving at 0.95 times the speed of light. or 0.95c. Then suppose a clock on the rocket measures 1.0 seconds between successive ticks. How long is the time between ticks. measured in your reference frame? 2. A spaceship, 195 m long as seem on board. moves by the Earth at 0.850 c. What is its length as measured by an Earth-bound observer? 3. Two spaceships approach each other with velocities of 0.9 c. According to an observer on the spacech'p. what is the velocity of the other ship? Sample problem for the dilation The Hypersonic Technology Vehicle 2 [lint-2) is an experimental rocket vehicle capable of traveling at 21.000 itrnlh (5830 mfs}. If an electronic clock in the HTVZ measures a time interval of exactly 1s duration. what would observers on Earth measure the time interval to ba? In this case. bin is 1.0 seconds (recall that die is the time measured in the same reference frame as the event being measured}. Given: Mo = 1 S v = 5830 mfs c - 3.0x109 mls (dormant) 1 e1.00000000045 3 Z "3\"" m\") or ta + 4.0 3-: arms :uxm nus Significance The very high speed of the HTV-2 is still only 10' 5 times the speed of rm. Relativistt: effects for the HIV-2 are neigible for chest all purposes. but are not zero. _ 1 '- .l1-(1.9433: 10-5)? A 4.9999999st _ 1: 899999998 1 _ )1(..::::"'.:,.)' Sample problem for length contraction A crew member of a spaceship mares the ship's length to be 100 m. The ship flies past Earth at a speed of 0.900 times the speed of light. If observers on Earth measure the length of the shin. what would they measure? Gm": 50mm 2 tit = (100 m) 'i - (c900)! Alo=100m M g\" 1-" =(Im) 14.910 0 a v=0.900c t =(lun l'll)\\|llu.190 at = ? = (mu muons) = 43.6": at =(100m)1(%)2 M Sample problem for relativistic velocity Suppose a spaceship heading directly toward Earth at half the speed at light sends a signal to us on a laser-produced beam of light. Given that the light leaves the ship at speed c as observed from the sh'p. How fast does a lig'rt signal approach Earth of sent from a spaceship traveling at 0.500 c? _ (0.500 + 1):: 1 + 0.500 1.500: Relativistic velocity gives the correct resul. The speed of ght is independerr of the relative motim of source and cbsenrer, whether 'Ih observer IS on the slip OI eanhbound
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


