Question: Please in Python code :) To find the LU decomposition of a matrix M, we use the function call la.lu(M). This will return three matrices

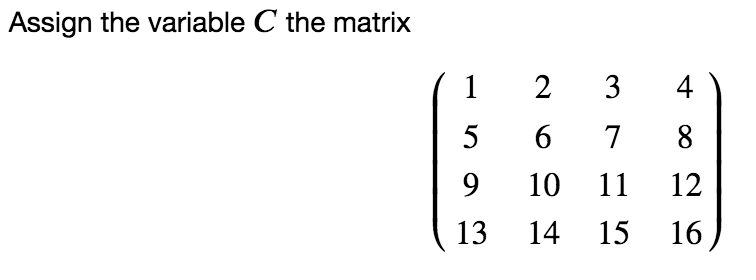
Please in Python code :)
To find the LU decomposition of a matrix M, we use the function call la.lu(M). This will return three matrices (arrays), a permutation array P, a lower triangular matrix L, and an upper triangular matrix U such that M PLU. To compute the LU decomposition of a matrix M, we simply can run the code: P,L,U = la.lu(M). This will assign the variables P,L,U the values described above. Note that in class, we considered matrices that can be reduced to row echelon form without partial pivoting (i.e., without swapping rows). In that case, the matrix P above ends up being the identity matrix. In the more general case where we have to swap rows, we need a non-trivial permutation matrix. Find the LU decomposition of the matrix C as in Exercise 3. Precisely, assign variables P,L,U the matrix values such that PC = LU. Be careful: the P in PC = LU is is still a permutation matrix, but it is not the same as the P returned by la.lu. Assign the variable C the matrix 1 2 3 4 6 7 8 5 9 10 11 12 15 16 13 14
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


