Question: please just do problem 8 problem 7: 8*. Now, consider a firm in question 7, using the cost function you have derived in part (c)

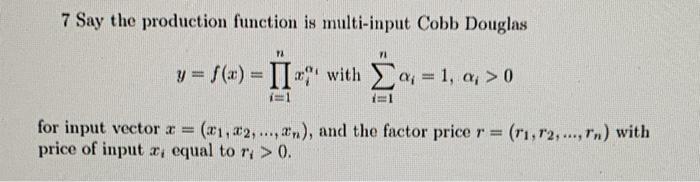
8*. Now, consider a firm in question 7, using the cost function you have derived in part (c) of Q7, derive a "two step" theory of profit maximization Approach 1: first construct the cost function by solving a cost minimization problem (which generates factor demands as a function of vector of factor prices r>>0 and some fixed level of output y); second, define a profit function in y, and then solve for the optimal level of y") Approach 2: given output price p, factor prices r, just define a profit function over input choices x, and maximize profits choosing r. (a). In approach 1: (i) construct the cost minimization problem for this general technology using a Lagrangian approach. Apply the envelope theorem to compute all the partials of the "value function" (i.e., the cost function). In particular, what is the marginal cost function? (ii) Now use the cost function that you have derived to define a profit max- imization problem (over choosing the level of output y) if the price of output good y is p > 0. What is the FOC for that profit max problem? (b) In approach 2: (i) redo this problem using a standard profit maximization approach (i.e., choosing the inputs x, not doing first cost minimization, and then using that cost function to do profit max). (ii) what are all the partials of the profit function in the parameters (i.e., compute all the partials of the value function using the envelope theorem) (c). Prove the answer you get doing the two methods are exactly the same for r*(p, r) and output y(p,r). 7 Say the production function is multi-input Cobb Douglas 12 9 = f(x) = with = 1, a; > 0 Q;= for input vector x = (x1,x2,...,x), and the factor price r = (r1,r2, ..., r.) with price of input x, equal to ry > 0. 8*. Now, consider a firm in question 7, using the cost function you have derived in part (c) of Q7, derive a "two step" theory of profit maximization Approach 1: first construct the cost function by solving a cost minimization problem (which generates factor demands as a function of vector of factor prices r>>0 and some fixed level of output y); second, define a profit function in y, and then solve for the optimal level of y") Approach 2: given output price p, factor prices r, just define a profit function over input choices x, and maximize profits choosing r. (a). In approach 1: (i) construct the cost minimization problem for this general technology using a Lagrangian approach. Apply the envelope theorem to compute all the partials of the "value function" (i.e., the cost function). In particular, what is the marginal cost function? (ii) Now use the cost function that you have derived to define a profit max- imization problem (over choosing the level of output y) if the price of output good y is p > 0. What is the FOC for that profit max problem? (b) In approach 2: (i) redo this problem using a standard profit maximization approach (i.e., choosing the inputs x, not doing first cost minimization, and then using that cost function to do profit max). (ii) what are all the partials of the profit function in the parameters (i.e., compute all the partials of the value function using the envelope theorem) (c). Prove the answer you get doing the two methods are exactly the same for r*(p, r) and output y(p,r). 7 Say the production function is multi-input Cobb Douglas 12 9 = f(x) = with = 1, a; > 0 Q;= for input vector x = (x1,x2,...,x), and the factor price r = (r1,r2, ..., r.) with price of input x, equal to ry > 0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


