Question: Please Modify TestPart2 to test the correctness and efficiency of FasterDefaultList. Thanks import java.util.List; import java.util.AbstractList; import java.util.Map; import java.util.HashMap; public class DumbDefaultList extends AbstractList
Please Modify TestPart2 to test the correctness and efficiency of FasterDefaultList. Thanks

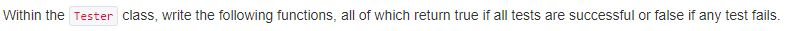

import java.util.List; import java.util.AbstractList; import java.util.Map; import java.util.HashMap; public class DumbDefaultList extends AbstractList { Map map; public DumbDefaultList() { map = new HashMap(); } public int size() { return Integer.MAX_VALUE; } public T get(int i) { return map.get(i); } public T set(int i, T x) { return map.put(i, x); } public void add(int i, T x) { Map map2 = new HashMap(); for (Integer k : map.keySet()) { if (k >= i) { map2.put(k, map.get(k)); } } for (Integer k : map2.keySet()) { map.remove(k); } for (Map.Entry e : map2.entrySet()) { map.put(e.getKey()+1, e.getValue()); } map.put(i, x); } public T remove(int i) { Map map2 = new HashMap(); for (Integer k : map.keySet()) { if (k >= i) { map2.put(k, map.get(k)); } } for (Integer k : map2.keySet()) { map.remove(k); } T retval = map2.remove(i); for (Map.Entry e : map2.entrySet()) { map.put(e.getKey()-1, e.getValue()); } return retval; } public static void main(String[] args) { Tester.testDefaultList(new DumbDefaultList()); } } -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
import java.lang.reflect.Array; import java.lang.IllegalStateException; import java.util.AbstractList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.List; import java.util.NoSuchElementException; import java.util.Random; /** * Implements the List interface as a skiplist so that all the * standard operations take O(log n) time * * TODO: Modify this so that it creates a DefaultList, which is basically * an infinitely long list whose values start out as null * */ public class FastDefaultList extends AbstractList { class Node { T x; Node[] next; int[] length; @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public Node(T ix, int h) { x = ix; next = (Node[])Array.newInstance(Node.class, h+1); length = new int[h+1]; } public int height() { return next.length - 1; } } /** * This node sits on the left side of the skiplist */ protected Node sentinel; /** * The maximum height of any element */ int h; /** * The number of elements stored in the skiplist */ int n; // Hint: You don't need this anymore! /** * A source of random numbers */ Random rand; public FastDefaultList() { n = 0; sentinel = new Node(null, 32); h = 0; rand = new Random(0); } /** * Find the node that precedes list index i in the skiplist. * * @param x - the value to search for * @return the predecessor of the node at index i or the final * node if i exceeds size() - 1. */ protected Node findPred(int i) { // Hint: It's not enough to know u, you also need the value j, // maybe return the pair (u,j) Node u = sentinel; int r = h; int j = -1; // index of the current node in list 0 while (r >= 0) { while (u.next[r] != null && j + u.length[r] return u; } public T get(int i) { // Hint: this is too restrictive any non-negative i is allowed if (i n-1) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(); // Hint: Are you sure findPred(i).next is the node you're looking for? return findPred(i).next[0].x; } public T set(int i, T x) { // Hint: this is too restrictive any non-negative i is allowed if (i n-1) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(); // Hint: Are you sure findPred(i).next is the node you're looking for? // If it's not, you'd better add a new node, maybe get everything // else working and come back to this later. Node u = findPred(i).next[0]; T y = u.x; u.x = x; return y; } /** * Insert a new node into the skiplist * @param i the index of the new node * @param w the node to insert * @return the node u that precedes v in the skiplist */ protected Node add(int i, Node w) { Node u = sentinel; int k = w.height(); int r = h; int j = -1; // index of u while (r >= 0) { while (u.next[r] != null && j+u.length[r] // accounts for new node in list 0 if (r return u; } /** * Simulate repeatedly tossing a coin until it comes up tails. * Note, this code will never generate a height greater than 32 * @return the number of coin tosses - 1 */ protected int pickHeight() { int z = rand.nextInt(); int k = 0; int m = 1; while ((z & m) != 0) { k++; m return k; } public void add(int i, T x) { // Hint: bounds checking again! if (i n) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(); Node w = new Node(x, pickHeight()); if (w.height() > h) h = w.height(); add(i, w); } public T remove(int i) { // Hint: bounds checking again! if (i n-1) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(); T x = null; Node u = sentinel; int r = h; int j = -1; // index of node u while (r >= 0) { while (u.next[r] != null && j+u.length[r] // for the node we are removing if (j + u.length[r] + 1 == i && u.next[r] != null) { x = u.next[r].x; u.length[r] += u.next[r].length[r]; u.next[r] = u.next[r].next[r]; if (u == sentinel && u.next[r] == null) h--; } r--; } n--; return x; } public int size() { return Integer.MAX_VALUE; } public String toString() { // This is just here to help you a bit with debugging StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); int i = -1; Node u = sentinel; while (u.next[0] != null) { i += u.length[0]; u = u.next[0]; sb.append(" " + i + "=>" + u.x); } return sb.toString(); } public static void main(String[] args) { Tester.testDefaultList(new FastDefaultList()); } } ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This needs to be modified
import java.util.Random; import java.util.List; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; public class Tester { public static boolean testPart2(List ell) { // put your testing code here return true; } public static void testDefaultList(List ell) { long start = System.nanoTime(); boolean result = Tester.testPart2(ell); long stop = System.nanoTime(); double elapsed = (stop-start)/1e9; System.out.println("testPart1 returns " + result + " in " + elapsed + "s" + " when testing a " + ell.getClass().getName()); } } Note: A DumbDefaultList class has already been implemented for you. You can use it to help test correctness of your implementation
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


