Question: Please provide Excel formula. Information is provided. Veighted Moving Average Data Sheet-Each column holds information you may find helpful in your analysis. The lowing is
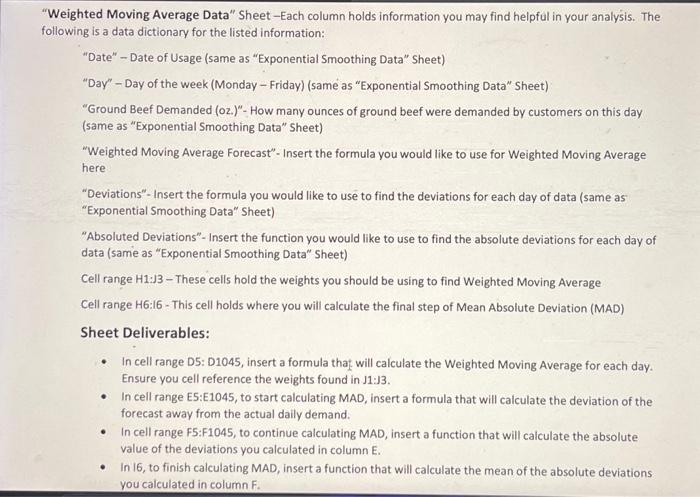
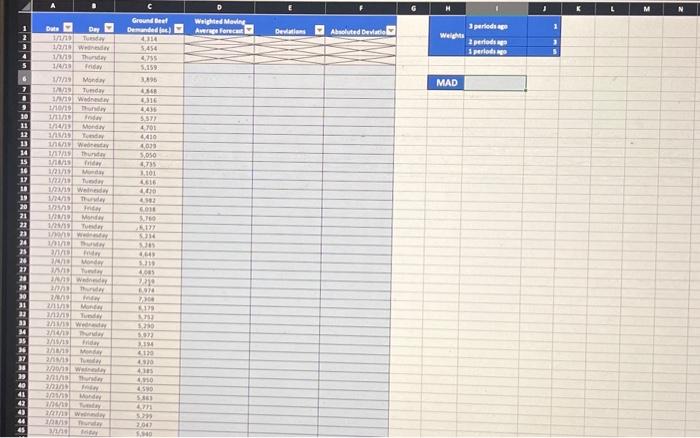
Veighted Moving Average Data" Sheet-Each column holds information you may find helpful in your analysis. The lowing is a data dictionary for the listed information: "Date" - Date of Usage (same as "Exponential Smoothing Data" Sheet) "Day" - Day of the week (Monday - Friday) (same as "Exponential Smoothing Data" Sheet) "Ground Beef Demanded (oz.)"- How many ounces of ground beef were demanded by customers on this day (same as "Exponential Smoothing Data" Sheet) "Weighted Moving Average Forecast" - Insert the formula you would like to use for Weighted Moving Average here "Deviations"- Insert the formula you would like to use to find the deviations for each day of data (same as "Exponential Smoothing Data" Sheet) "Absoluted Deviations"- Insert the function you would like to use to find the absolute deviations for each day of data (same as "Exponential Smoothing Data" Sheet) Cell range H1:J3 - These cells hold the weights you should be using to find Weighted Moving Average Cell range H6:16 - This cell holds where you will calculate the final step of Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD) Sheet Deliverables: - In cell range D5: D1045, insert a formula that will calculate the Weighted Moving Average for each day. Ensure you cell reference the weights found in J1:J3. - In cell range E5:E1045, to start calculating MAD, insert a formula that will calculate the deviation of the forecast away from the actual daily demand. - In cell range F5:F1045, to continue calculating MAD, insert a function that will calculate the absolute value of the deviations you calculated in column E. - In 16, to finish calculating MAD, insert a function that will calculate the mean of the absolute deviations you calculated in column F
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


