Question: >> Please read the below background information of a simple blockchain data structure. Background Information. A simple blockchain is a linked list of blocks as
>>
Please read the below background information of a simple blockchain data structure.
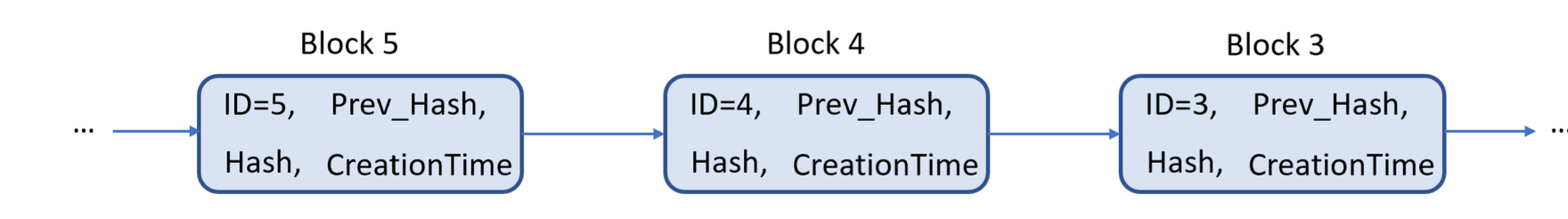
Background Information. A simple blockchain is a linked list of blocks as shown in the below figure, where each block contains a unique block ID, a hash (a unique string of characters), a hash of the previous block, and a creation time of the block. Each block is used to store transaction data, which are records of transferring digital currency. A unit of the digital currency is called a token. Each token can be uniquely identified by a token ID and has a market value.
Please read the below users requirements, and answer questions (a) and (b).
User Requirements. A DBMS team is building a transaction system by using blockchain.
- The main purpose of the system is to manage transactions of tokens between accounts. - Each user in the system is identified by a unique username. Each user has a profile attribute, which consists of a name, an email address, and the date the user joined the system.
- A user owns one or more accounts. Each account in the system is identified by a unique account number, and an account must be owned by a user.
- There are two specifications of accounts, including token account and virtual account. An account is either a token account or a virtual account.
- Token account is an account that keeps tokens in the system. Each token can be uniquely identified by a token ID and has its market value.
- A token mush be owned by only one token account. A token account may or may not have one or more tokens.
- Virtual account has no token by itself. Instead, it must be linked to one or more token accounts. A token account may or may not have multiple virtual accounts.
- A transaction is initiated by specifying a total amount to be transferred from one account to another account, for example, either from a token account to a virtual account or from a virtual account to a token account. Each transaction is uniquely identified by a transaction ID. It is possible to leave (attach) several messages along with the transaction.
- A transaction must be kept in only one block. Each block has a unique block ID and a creation time, and each block may or may not have multiple transactions. A hash value is calculated and recorded in each block.
- A block is always linked to only one previous block (except for the very first block in the system), in order to form a blockchain. The hash value of the previous block is also explicitly recorded in a block. It is possible that multiple blocks have the same previous block at the same time.
- In fact, each transaction is completed by using one or more internal transactions. An internal transaction has an internal ID, which can only uniquely identify each internal transaction when combining with the corresponding transaction ID.
- Each internal transaction is used to transfer one token from one token account to another token account.
(a) Please model the above users requirements by drawing the corresponding E-R Diagram. If a requirement is unclear, a reasonable assumption could be made. You must clearly state all such assumptions.
(b) Please reduce your E-R Diagram into relational table schemas. For each relation, underline the primary key and identify all foreign key(s), if any.
Block 5 Block 4 Block 3 ID=4, Prev_Hash, ID=3, Prev_Hash, ID=5, Prev_Hash, Hash, Creation Time Hash, Creation Time Hash, Creation Time
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


