Question: Please see below for data from Example 22.7-1, but only answer 2.7-1 Please see formula 22.5-15 below 2.7-1. Liquid Film Coefficients and Design of an
 Please see below for data from Example 22.7-1, but only answer 2.7-1
Please see below for data from Example 22.7-1, but only answer 2.7-1

Please see formula 22.5-15 below
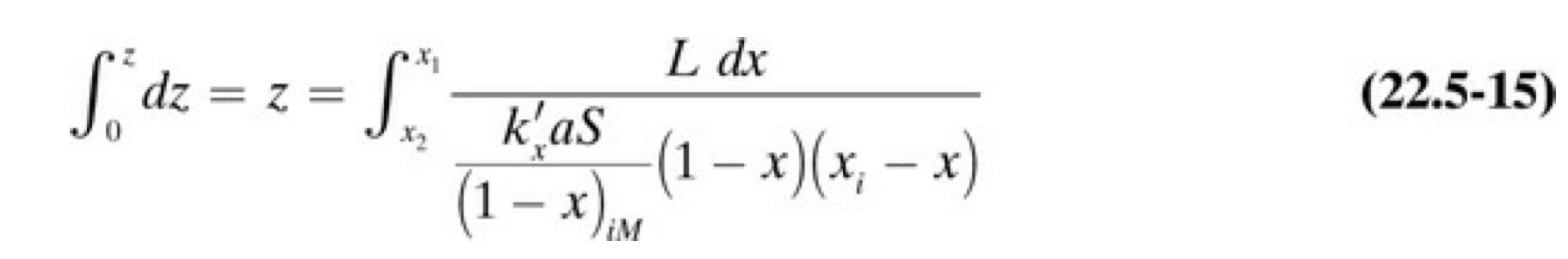
2.7-1. Liquid Film Coefficients and Design of an SO2 Tower. Using the data for Example 22.7-1, calculate the height of the tower using Eq. (22.5-15), which is based on the liquid film mass-transfer coefficient kxa. (Note: The interface values xi have already been obtained.) EXAMPLE 22.7-1. Design of an Absorption Tower with a Concentrated Gas Mixture A tower packed with 25.4-mm ceramic rings is to be designed to absorb SO2 from air by using pure water at 293K and 1.013105Pa abs pressure. The entering gas contains 20mol%SO2 and that leaving contains 2mol%. The inert air flow is 6.53104kg mol air/s and the inert water flow is 4.20102kg mol water/s. The tower cross-sectional area is 0.0929m2. For dilute SO2, the film mass-transfer coefficients at 293K are, for 25.4-mm (1-in.) rings (W1) kya=0.0594Gy0.7Gx0.25kxa=0.152Gx0.82 where kya is kgmol/sm3mol frac, kxa is kgmol/sm3mol frac, and GX and Gy are kg total liquid or gas, respectively, per sec per m2 tower cross section. Calculate the tower height. 0zdz=z=x2x1(1x)iMkxaS(1x)(xix)Ldx
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


