Question: Please show all required work. Thank you! 2. Use the attached example as work template to do S-AES a) The plain text is the first
Please show all required work. Thank you!


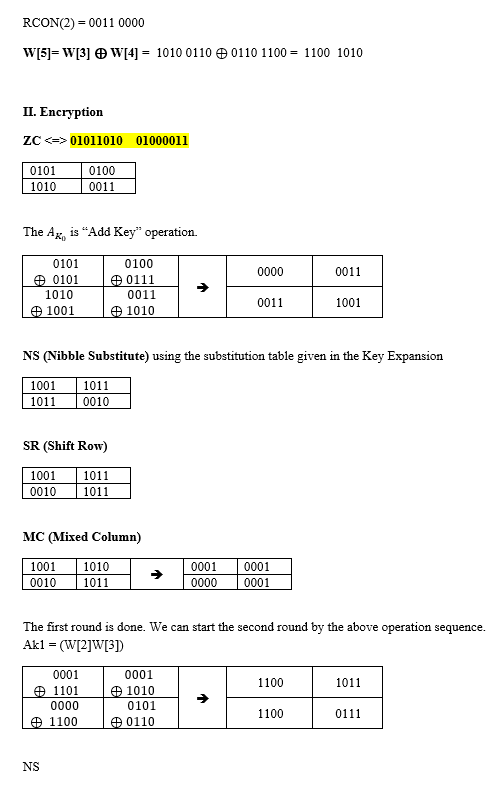
2. Use the attached example as work template to do S-AES a) The plain text is the first letter of students' first name and the first letter of the last. For example, John Dole is JD. For Chinese names, use pinyin. Find the HEX value of the letters in the ASCII code table, and translate it into 16 bit string. b) The key is generated from their student ID like 1620106. Take the ID as a decimal integer, translate it into a binary number, and take the last 16 bits as the key. If the length is less than 16, add 0 in front of the bit stream. For example, if John Dole's WID is 214348990, then its binary is 11001100 0110101101 0010111110. The last 16 bits is 1011010010111110. c) Using the above info to get the ciphertext. d) Using the above ciphertext and key to get the plaintext (challenging) Simple AES Examples Students can follow the steps to do s-AES encryption. Refer detailed explanation to the slides S-AES. The example is using the following. Students can replace them with theirs plaintext: ZC input key 0101 1001 0111 1010 1. Keys (Key Expansion) W[0] =0101 1001 (from the original fist 8 bit) W[1]=0111 1010 (from the original last 8 bit) W[2] = W[0] RCON[1] SubNib(RotNib(W[1])) RotNib(W[1]) = RotNib(0111 1010) = 1010 0111 Substitution using the table below: 1010 from the table is 0000 and 0111 is 0101. Therefore SubNib(1010 0111) = 0000 0101 Follows the formula RC(i) = xi+ GF16 ** +x+1 RC(1) = x RC(1) =1000. +x+1 RCON(1) = 1000 0000. g(wi) = 1000 0000 0000 0101 = 1000 0101, and W[2] = 0101 1001 1000 0101 = 1101 1100 W[3] = w[1] W[2] So W[3] = w[1] W[2] == 0111 1010 1101 1100 = 1010 0110 W[4] = W[2] e RCON[2] SubNib(RotNib(W[3])) RotNib(1010 0110) = 0110 1010, SubNib(0110 1010) = 1000 0000 RC(2) = x +1. We can see it by intuitively the following ** = x* +x+1-x-1=-x- 1 mod (x* +x+1) = x + 1 mod(2). So by the mapping, x+1 0011. RC(2) = 0011 ** +3+1 RCON(2) = 0011 0000 W[5]=W[3] W[4] = 1010 0110 0110 1100 = 1100 1010 II. Encryption ZC01011010 01000011 0101 1010 0100 0011 The Ax, is "Add Key" operation. 0000 0011 0101 O 0101 1010 1001 0100 90111 0011 1010 > 0011 1001 NS (Nibble Substitute) using the substitution table given in the Key Expansion 1001 1011 1011 0010 SR (Shift Row) 1001 0010 1011 1011 MC (Mixed Column) 1001 0010 1010 1011 0001 0000 0001 0001 The first round is done. We can start the second round by the above operation sequence. Ak1 = (W[2][3] 0001 0001 1010 1101 1100 1011 0000 0101 1100 0111 1100 0110 NS 2. Use the attached example as work template to do S-AES a) The plain text is the first letter of students' first name and the first letter of the last. For example, John Dole is JD. For Chinese names, use pinyin. Find the HEX value of the letters in the ASCII code table, and translate it into 16 bit string. b) The key is generated from their student ID like 1620106. Take the ID as a decimal integer, translate it into a binary number, and take the last 16 bits as the key. If the length is less than 16, add 0 in front of the bit stream. For example, if John Dole's WID is 214348990, then its binary is 11001100 0110101101 0010111110. The last 16 bits is 1011010010111110. c) Using the above info to get the ciphertext. d) Using the above ciphertext and key to get the plaintext (challenging) Simple AES Examples Students can follow the steps to do s-AES encryption. Refer detailed explanation to the slides S-AES. The example is using the following. Students can replace them with theirs plaintext: ZC input key 0101 1001 0111 1010 1. Keys (Key Expansion) W[0] =0101 1001 (from the original fist 8 bit) W[1]=0111 1010 (from the original last 8 bit) W[2] = W[0] RCON[1] SubNib(RotNib(W[1])) RotNib(W[1]) = RotNib(0111 1010) = 1010 0111 Substitution using the table below: 1010 from the table is 0000 and 0111 is 0101. Therefore SubNib(1010 0111) = 0000 0101 Follows the formula RC(i) = xi+ GF16 ** +x+1 RC(1) = x RC(1) =1000. +x+1 RCON(1) = 1000 0000. g(wi) = 1000 0000 0000 0101 = 1000 0101, and W[2] = 0101 1001 1000 0101 = 1101 1100 W[3] = w[1] W[2] So W[3] = w[1] W[2] == 0111 1010 1101 1100 = 1010 0110 W[4] = W[2] e RCON[2] SubNib(RotNib(W[3])) RotNib(1010 0110) = 0110 1010, SubNib(0110 1010) = 1000 0000 RC(2) = x +1. We can see it by intuitively the following ** = x* +x+1-x-1=-x- 1 mod (x* +x+1) = x + 1 mod(2). So by the mapping, x+1 0011. RC(2) = 0011 ** +3+1 RCON(2) = 0011 0000 W[5]=W[3] W[4] = 1010 0110 0110 1100 = 1100 1010 II. Encryption ZC01011010 01000011 0101 1010 0100 0011 The Ax, is "Add Key" operation. 0000 0011 0101 O 0101 1010 1001 0100 90111 0011 1010 > 0011 1001 NS (Nibble Substitute) using the substitution table given in the Key Expansion 1001 1011 1011 0010 SR (Shift Row) 1001 0010 1011 1011 MC (Mixed Column) 1001 0010 1010 1011 0001 0000 0001 0001 The first round is done. We can start the second round by the above operation sequence. Ak1 = (W[2][3] 0001 0001 1010 1101 1100 1011 0000 0101 1100 0111 1100 0110 NS
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


