Question: please show all the working and formulas used..... Valuing a Business Sangria is a U.S.-based company whose products aim to promote happy, low-stress lifestyles. The

please show all the working and formulas used.....
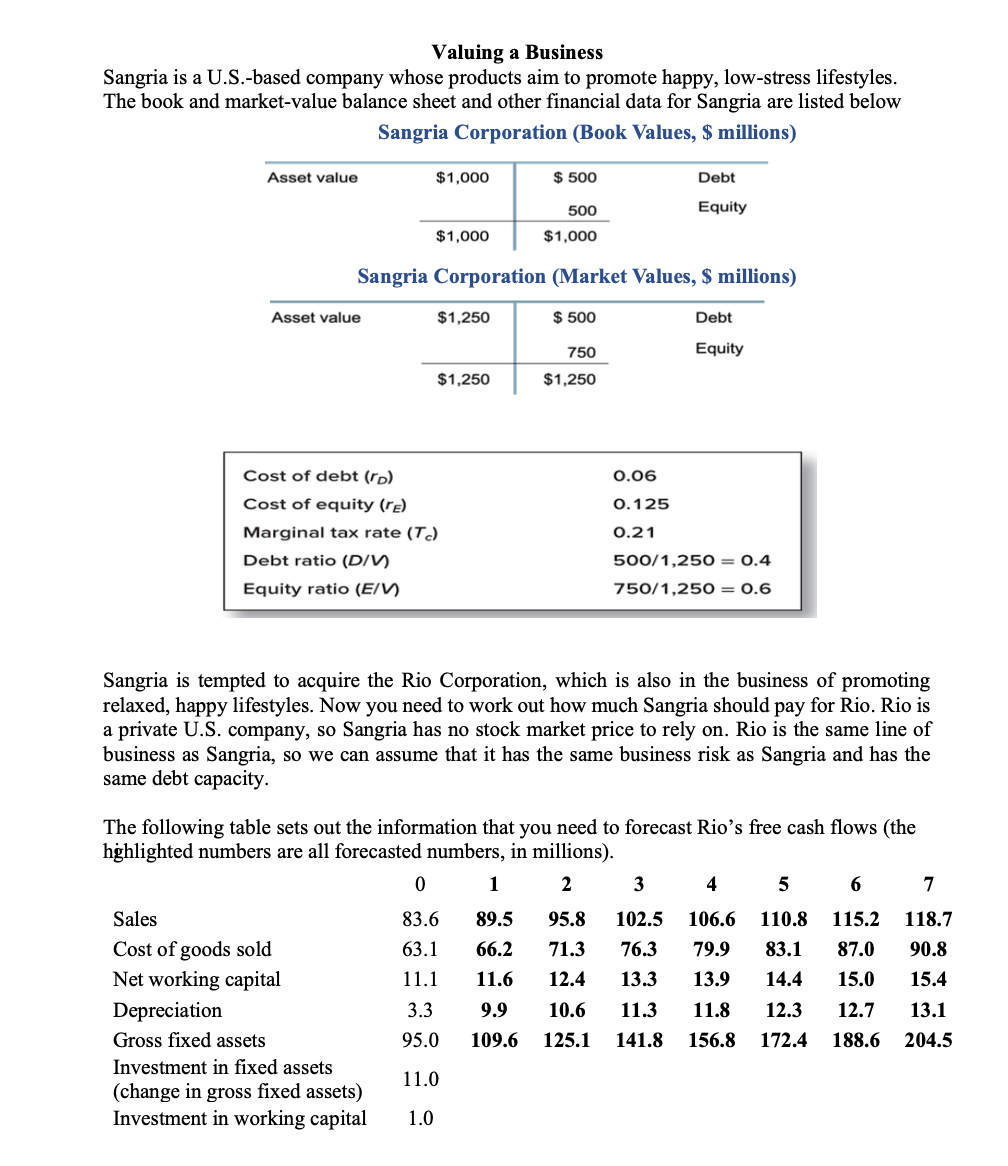
Valuing a Business Sangria is a U.S.-based company whose products aim to promote happy, low-stress lifestyles. The book and market value balance sheet and other financial data for Sangria are listed below Sangria Corporation (Book Values, $ millions) Asset value $1,000 $ 500 Debt 500 Equity $1,000 $1,000 Sangria Corporation (Market Values, $ millions) Asset value $1,250 $ 500 Debt 750 Equity $1,250 $1,250 0.06 0.125 Cost of debt (ro) Cost of equity (re) Marginal tax rate (T) Debt ratio (DIV Equity ratio (E/V) 0.21 500/1,250 = 0.4 750/1,250 = 0.6 Sangria is tempted to acquire the Rio Corporation, which is also in the business of promoting relaxed, happy lifestyles. Now you need to work out how much Sangria should pay for Rio. Rio is a private U.S. company, so Sangria has no stock market price to rely on. Rio is the same line of business as Sangria, so we can assume that it has the same business risk as Sangria and has the same debt capacity. The following table sets out the information that you need to forecast Rio's free cash flows (the highlighted numbers are all forecasted numbers, in millions). 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 83.6 89.5 66.2 95.8 71.3 12.4 102.5 76.3 106.6 79.9 63.1 11.1 110.8 83.1 14.4 115.2 87.0 15.0 118.7 90.8 15.4 11.6 13.3 13.9 10.6 12.3 12.7 Sales Cost of goods sold Net working capital Depreciation Gross fixed assets Investment in fixed assets (change in gross fixed assets) Investment in working capital 3.3 95.0 9.9 109.6 11.3 141.8 11.8 156.8 13.1 204.5 125.1 172.4 188.6 11.0 1.0 3 7 74.5 u 76.5 Assumptions: Sales growth, % Costs (% of sales) Working capital (% of sales) Net fixed assets (% of sales) Depreciation (% of net fixed assets) Tax rate, % 6.7 75.5 13.3 79.0 7 74 13 79 7 74.5 13 79 4 75 13 79 4 75 13 79 4 75.5 13 79 13 13 79 79 s 5 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 21 Long-term growth forecast, % 3 (a). Forecast Rio's free cash flow over the next 7 years, assuming value horizon is 6 years. From year 7 onward, we assume a long-term growth rate of 3% each. (b). What's the discount rate to calculate PV? (c). What's the PV of the company? (d). What's the stock price per share, assume Rio has 1.5 million shares outstanding? (e). Review your calculation, do you have anything to recheck? (f). Now assume Sangria plans to finance the purchase with $62 million of debt. It intends to pay down the debt to $53 million in year 6 so that the debt ratio at the horizon is 40%, the normal debt ratio of the company. The debt balance is listed below. The free cash flows remain the same from Q1. 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Debt 62 60 60 58 56 54 53 (i). Use the APV approach to calculate the value of Rio. (ii). What's the difference between the values in (c) and (f)? What are the factors leading to such difference? Valuing a Business Sangria is a U.S.-based company whose products aim to promote happy, low-stress lifestyles. The book and market value balance sheet and other financial data for Sangria are listed below Sangria Corporation (Book Values, $ millions) Asset value $1,000 $ 500 Debt 500 Equity $1,000 $1,000 Sangria Corporation (Market Values, $ millions) Asset value $1,250 $ 500 Debt 750 Equity $1,250 $1,250 0.06 0.125 Cost of debt (ro) Cost of equity (re) Marginal tax rate (T) Debt ratio (DIV Equity ratio (E/V) 0.21 500/1,250 = 0.4 750/1,250 = 0.6 Sangria is tempted to acquire the Rio Corporation, which is also in the business of promoting relaxed, happy lifestyles. Now you need to work out how much Sangria should pay for Rio. Rio is a private U.S. company, so Sangria has no stock market price to rely on. Rio is the same line of business as Sangria, so we can assume that it has the same business risk as Sangria and has the same debt capacity. The following table sets out the information that you need to forecast Rio's free cash flows (the highlighted numbers are all forecasted numbers, in millions). 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 83.6 89.5 66.2 95.8 71.3 12.4 102.5 76.3 106.6 79.9 63.1 11.1 110.8 83.1 14.4 115.2 87.0 15.0 118.7 90.8 15.4 11.6 13.3 13.9 10.6 12.3 12.7 Sales Cost of goods sold Net working capital Depreciation Gross fixed assets Investment in fixed assets (change in gross fixed assets) Investment in working capital 3.3 95.0 9.9 109.6 11.3 141.8 11.8 156.8 13.1 204.5 125.1 172.4 188.6 11.0 1.0 3 7 74.5 u 76.5 Assumptions: Sales growth, % Costs (% of sales) Working capital (% of sales) Net fixed assets (% of sales) Depreciation (% of net fixed assets) Tax rate, % 6.7 75.5 13.3 79.0 7 74 13 79 7 74.5 13 79 4 75 13 79 4 75 13 79 4 75.5 13 79 13 13 79 79 s 5 14 14 14 14 14 14 14 21 Long-term growth forecast, % 3 (a). Forecast Rio's free cash flow over the next 7 years, assuming value horizon is 6 years. From year 7 onward, we assume a long-term growth rate of 3% each. (b). What's the discount rate to calculate PV? (c). What's the PV of the company? (d). What's the stock price per share, assume Rio has 1.5 million shares outstanding? (e). Review your calculation, do you have anything to recheck? (f). Now assume Sangria plans to finance the purchase with $62 million of debt. It intends to pay down the debt to $53 million in year 6 so that the debt ratio at the horizon is 40%, the normal debt ratio of the company. The debt balance is listed below. The free cash flows remain the same from Q1. 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Debt 62 60 60 58 56 54 53 (i). Use the APV approach to calculate the value of Rio. (ii). What's the difference between the values in (c) and (f)? What are the factors leading to such difference
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


