Question: Please solve the calculation part which are : A B &C Mass Transfer and Diffusion Coefficients 1. Objectives: - Direct measurement of mass transfer rates



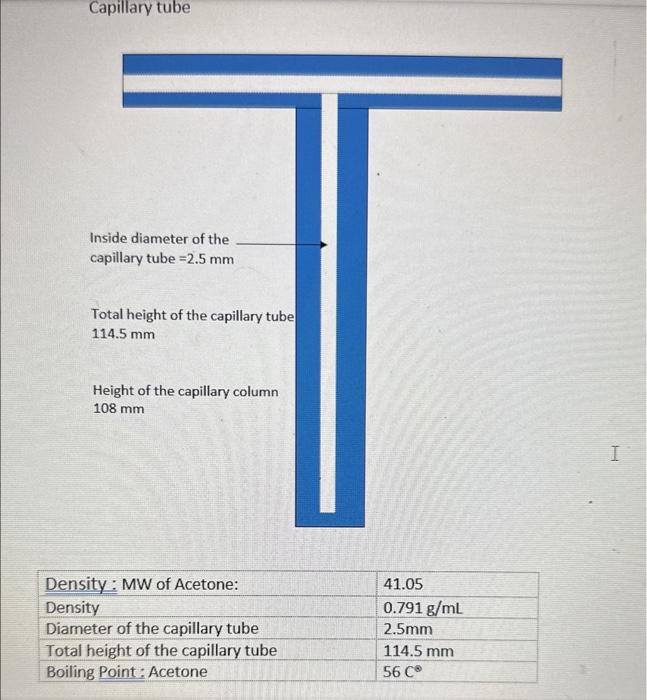
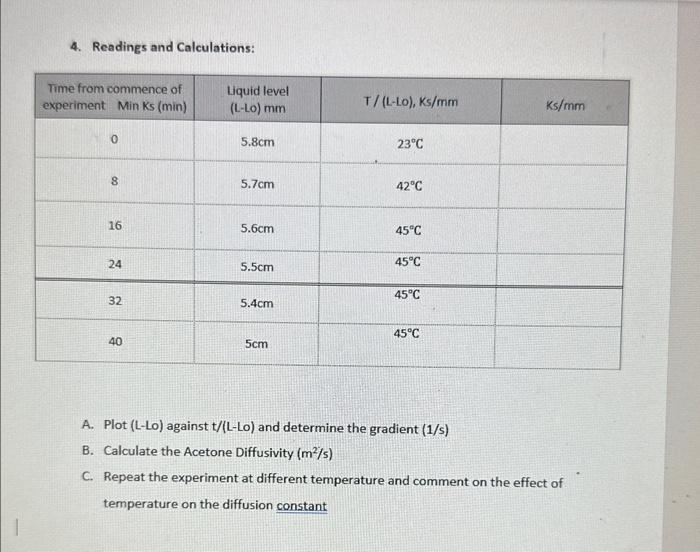
Mass Transfer and Diffusion Coefficients 1. Objectives: - Direct measurement of mass transfer rates in the absence of convective effects * Use of gas laws to calculate concentration differences in terms of partial - Use of Elcks slaw to measure diffusion coefficient in the presence of a stationary gas - Measurement of the effect of temperature on diffusion coefficients - Gaining familiarity with the use of laboratory instruments to achieve accurate measurements of data required for industrial process. 2. Theory: Formula The rate of diffusion is given by: NA=RBMT(z2z1)pBMDABP=(pA1pA2) The flux NA in kmol/sm2 is equal to the rate of evaporation of the acetone. The rate of evaporation =[(LL0)r2]/MW,t (2) Where: r.=radiusoftesttube=densityofacetone=liquidacetonedensity=790kg/m3MW=molecularweightofacetone=58.08kg/kmolt=timefromthestartofexperiment.pA1=vaporpressureofacetone=73kN/m2at321K pB1=PpA1p62=PpA2Ru=8.314m3Pa/molKT=temperaturez2z1=heightoftubedepthofliquid+heightduetoliquidevaporation=h+(L-Lo) By equating Equations (1) \& (2) MWt(r2)(LL0)r2=RuT(z2z1)pBMDABP(pA1pA2)(LL0)t=MWPDAB(pA1pA2)()RsiTpBM(z2z1)=s(h+(LL)))(LL0)=s(LL0)th Plot (L - Lo) versus (t/(LLo)) with slope equal (1/s) Where S=MWPDAB(PA1PA2)RuTpBM, and h= height of tube - initial depth of liquid Inside diameter of the capillary tube =2.5mm Total height of the capillary tube 114.5mm Height of the capillary column 108mm 4. Readings and Calculations: A. Plot (L-Lo) against t/(LLo) and determine the gradient (1/s) B. Calculate the Acetone Diffusivity (m2/s) C. Repeat the experiment at different temperature and comment on the effect of temperature on the diffusion constant Mass Transfer and Diffusion Coefficients 1. Objectives: - Direct measurement of mass transfer rates in the absence of convective effects * Use of gas laws to calculate concentration differences in terms of partial - Use of Elcks slaw to measure diffusion coefficient in the presence of a stationary gas - Measurement of the effect of temperature on diffusion coefficients - Gaining familiarity with the use of laboratory instruments to achieve accurate measurements of data required for industrial process. 2. Theory: Formula The rate of diffusion is given by: NA=RBMT(z2z1)pBMDABP=(pA1pA2) The flux NA in kmol/sm2 is equal to the rate of evaporation of the acetone. The rate of evaporation =[(LL0)r2]/MW,t (2) Where: r.=radiusoftesttube=densityofacetone=liquidacetonedensity=790kg/m3MW=molecularweightofacetone=58.08kg/kmolt=timefromthestartofexperiment.pA1=vaporpressureofacetone=73kN/m2at321K pB1=PpA1p62=PpA2Ru=8.314m3Pa/molKT=temperaturez2z1=heightoftubedepthofliquid+heightduetoliquidevaporation=h+(L-Lo) By equating Equations (1) \& (2) MWt(r2)(LL0)r2=RuT(z2z1)pBMDABP(pA1pA2)(LL0)t=MWPDAB(pA1pA2)()RsiTpBM(z2z1)=s(h+(LL)))(LL0)=s(LL0)th Plot (L - Lo) versus (t/(LLo)) with slope equal (1/s) Where S=MWPDAB(PA1PA2)RuTpBM, and h= height of tube - initial depth of liquid Inside diameter of the capillary tube =2.5mm Total height of the capillary tube 114.5mm Height of the capillary column 108mm 4. Readings and Calculations: A. Plot (L-Lo) against t/(LLo) and determine the gradient (1/s) B. Calculate the Acetone Diffusivity (m2/s) C. Repeat the experiment at different temperature and comment on the effect of temperature on the diffusion constant
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


