Question: Solve the the data table to fill it Table 1. Raw and Processed Data for the Determination of the Dissociation Constant of Acetic Acid Molarity
Solve the the data table to fill it
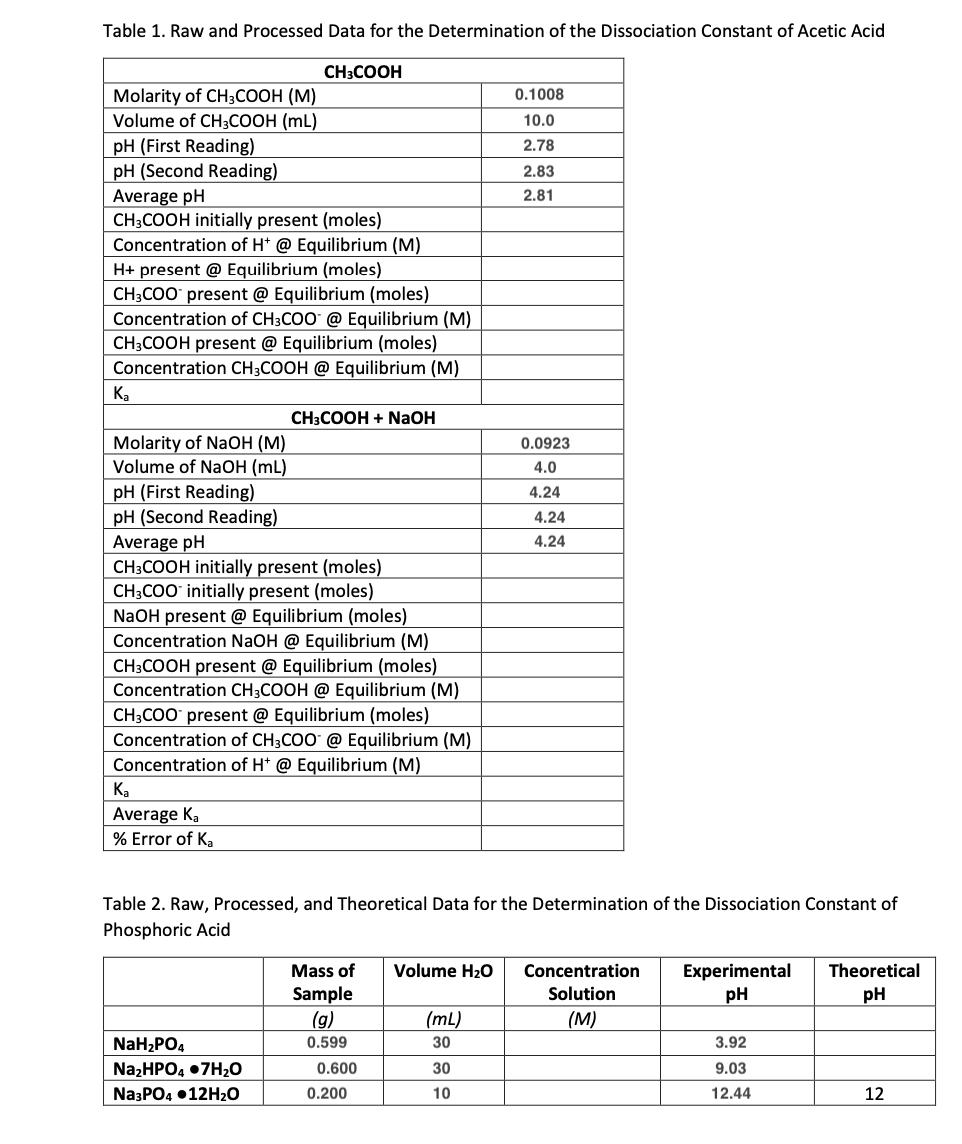

Table 1. Raw and Processed Data for the Determination of the Dissociation Constant of Acetic Acid Molarity of CH3COOH (M) Volume of CH3COOH (ML) pH (First Reading) pH (Second Reading) Average pH CH3COOH initially present (moles) Concentration of H+ @ Equilibrium (M) H+ present @ Equilibrium (moles) CH3COO present @ Equilibrium (moles) Concentration of CH3COO @ Equilibrium (M) CH3COOH present @ Equilibrium (moles) Concentration CH3COOH @ Equilibrium (M) Ka Molarity of NaOH (M) Volume of NaOH (mL) Ka Average Ka % Error of Ka CH3COOH pH (First Reading) pH (Second Reading) Average pH CH3COOH initially present (moles) CH3COO initially present (moles) NaOH present @ Equilibrium (moles) Concentration NaOH @ Equilibrium (M) CH3COOH present @ Equilibrium (moles) Concentration CH3COOH @ Equilibrium (M) CH3COO present @ Equilibrium (moles) Concentration of CH3COO @ Equilibrium (M) Concentration of H+ @ Equilibrium (M) NaHPO4 NaHPO4.7HO CH3COOH + NaOH Na3PO4 12HO Table 2. Raw, Processed, and Theoretical Data for the Determination of the Dissociation Constant of Phosphoric Acid Sample (g) 0.599 0.600 0.200 0.1008 10.0 2.78 Mass of Volume HO Concentration Experimental Theoretical pH pH Solution (M) (mL) 30 2.83 2.81 30 10 0.0923 4.0 4.24 4.24 4.24 3.92 9.03 12.44 12
Step by Step Solution
3.51 Rating (154 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Answer Total answers posted by the expert is 1183 Acetic acid is a weak acid and ionizes as follows ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


