Question: please solve using Matlab Boundary Value Problem #2: 9.27 The radial distribution of temperature in a current-caming bare wire is described by: To where T
please solve using Matlab
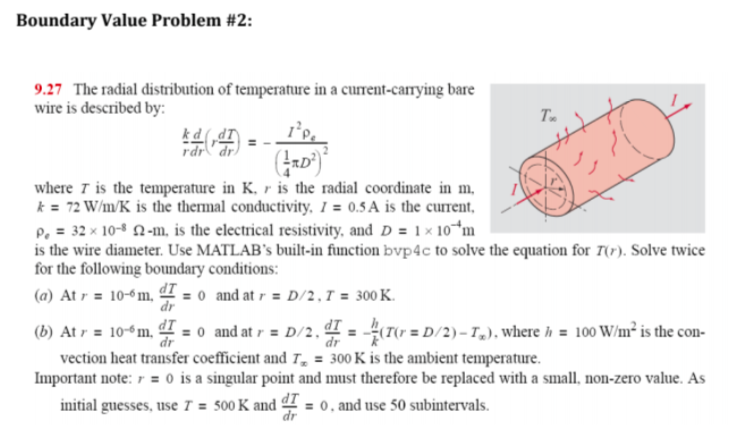
Boundary Value Problem #2: 9.27 The radial distribution of temperature in a current-caming bare wire is described by: To where T is the temperature in K. r is the radial coordinate in m k 72 winK is the thermal conductivity. 1 0.5 A is the current, ?.-32 10-8 ?-m. is the electrical resistivity, and D-1x 10.4m is the wire diameter. Use MATLAB's built-in function bvp4c to solve the equation for T). Solve twice for the following boundary conditions: (a) At r = 10-6 m. d, o and at r . D/2, ? = 300 K. (b) Atr 10-6 m. d, o and at r D/2.? -h( rr = D/2 ) _ T.). where h 100 W/mr is the con- vection heat transfer coefficient and T300 K is the ambient temperature Important note: 0 is a singular point and must therefore be replaced with a small, non-zero value. As initial guesses, use T 50o K and o, and use 50 subintervals Boundary Value Problem #2: 9.27 The radial distribution of temperature in a current-caming bare wire is described by: To where T is the temperature in K. r is the radial coordinate in m k 72 winK is the thermal conductivity. 1 0.5 A is the current, ?.-32 10-8 ?-m. is the electrical resistivity, and D-1x 10.4m is the wire diameter. Use MATLAB's built-in function bvp4c to solve the equation for T). Solve twice for the following boundary conditions: (a) At r = 10-6 m. d, o and at r . D/2, ? = 300 K. (b) Atr 10-6 m. d, o and at r D/2.? -h( rr = D/2 ) _ T.). where h 100 W/mr is the con- vection heat transfer coefficient and T300 K is the ambient temperature Important note: 0 is a singular point and must therefore be replaced with a small, non-zero value. As initial guesses, use T 50o K and o, and use 50 subintervals
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


