Question: Please solve with OCaml programing and I will give you like. 1. Tree Higher-order functions arent just for lists! Recall the algebraic data type of
Please solve with OCaml programing and I will give you like.
1.Tree
Higher-order functions arent just for lists! Recall the algebraic data type of binary trees from lecture:
type a tree = Leaf | Node of a * a tree * a tree
In this section, youll implement and use higher-order functions over trees.
As an example, we implemented the function tree_fold : a tree -> b -> (a -> b -> b -> b) that folds over trees like List.fold_right folds over lists. For example, tree_fold (Node (v1, Node (v2, Leaf, Leaf), Leaf)) u f is f v1 (f v2 u u) u. Note that our implementation isnt tail-recursive.
The Cornell book (linked from the course website) gives a tail-recursive version.
Task 1.
Base Code :
(** Trees **)
type 'a tree = Leaf | Node of 'a * 'a tree * 'a tree ;;
let rec tree_fold (t: 'a tree) (u: 'b) (f: 'a -> 'b -> 'b -> 'b) = match t with | Leaf -> u | Node (v, l, r) -> f v (tree_fold l u f) (tree_fold r u f)
(*>* Problem Task 1 *>*) let tree_map (t: 'a tree) (f: 'a -> 'b) : 'b tree = raise ImplementMe
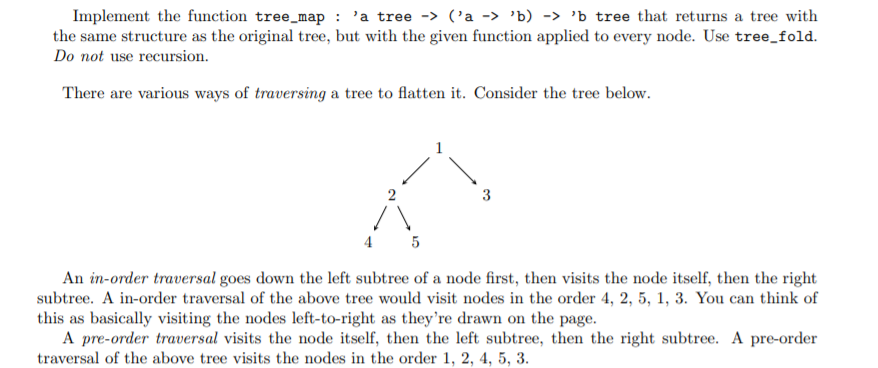
Implement the function tree_map : 'a tree -> ('a -> 'b) -> 'b tree that returns a tree with the same structure as the original tree, but with the given function applied to every node. Use tree_fold. Do not use recursion. There are various ways of traversing a tree to flatten it. Consider the tree below. 1 2 3 4 5 An in-order traversal goes down the left subtree of a node first, then visits the node itself, then the right subtree. A in-order traversal of the above tree would visit nodes in the order 4, 2, 5, 1, 3. You can think of this as basically visiting the nodes left-to-right as they're drawn on the page. A pre-order traversal visits the node itself, then the left subtree, then the right subtree. A pre-order traversal of the above tree visits the nodes in the order 1, 2, 4, 5, 3. Implement the function tree_map : 'a tree -> ('a -> 'b) -> 'b tree that returns a tree with the same structure as the original tree, but with the given function applied to every node. Use tree_fold. Do not use recursion. There are various ways of traversing a tree to flatten it. Consider the tree below. 1 2 3 4 5 An in-order traversal goes down the left subtree of a node first, then visits the node itself, then the right subtree. A in-order traversal of the above tree would visit nodes in the order 4, 2, 5, 1, 3. You can think of this as basically visiting the nodes left-to-right as they're drawn on the page. A pre-order traversal visits the node itself, then the left subtree, then the right subtree. A pre-order traversal of the above tree visits the nodes in the order 1, 2, 4, 5, 3
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


