Question: please solve with work! Virginia's Department Store faces a purchasing decision for a seasonal product for which demand can be high, medium, or low. The
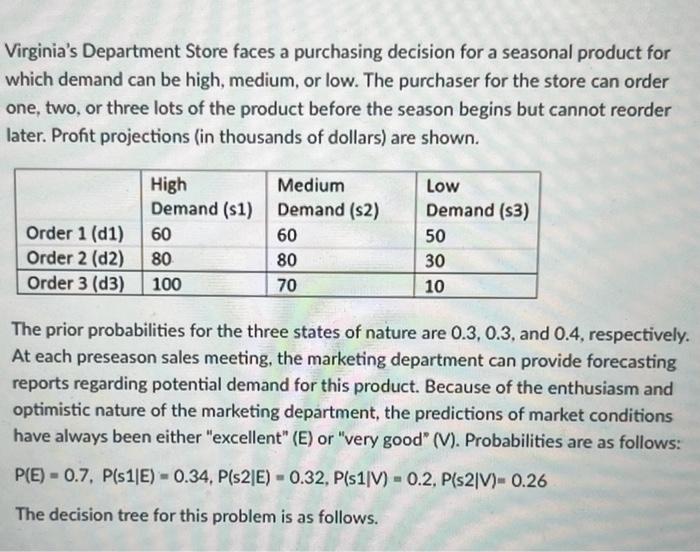
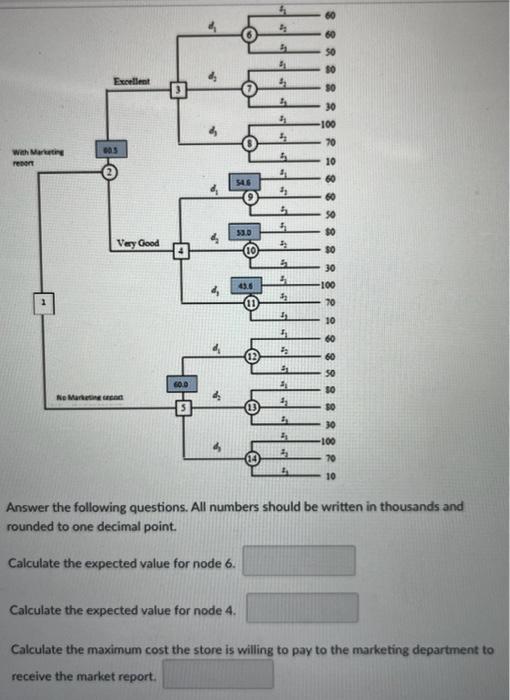
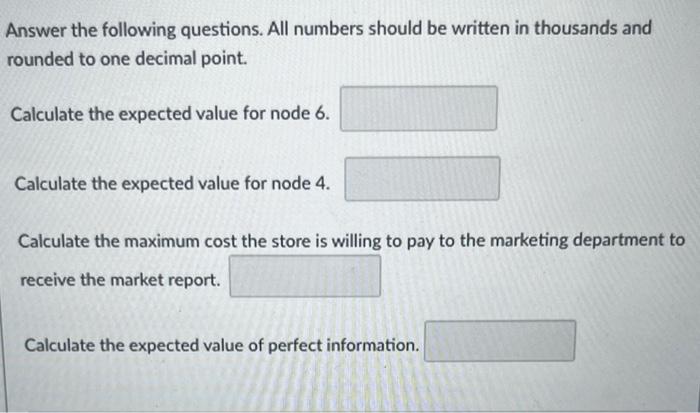

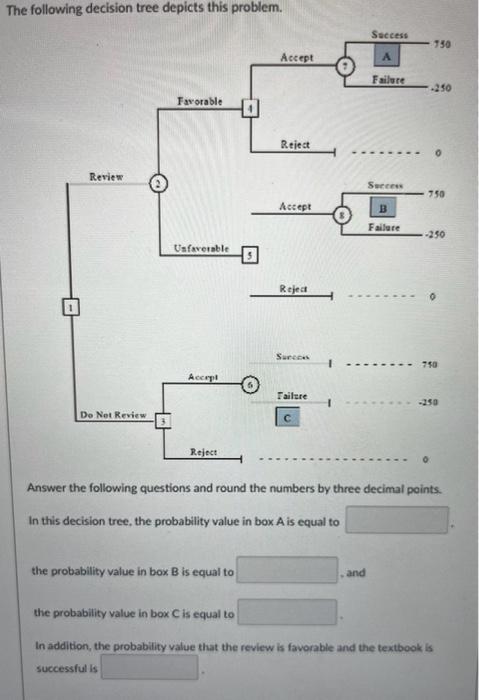

Virginia's Department Store faces a purchasing decision for a seasonal product for which demand can be high, medium, or low. The purchaser for the store can order one, two, or three lots of the product before the season begins but cannot reorder later. Profit projections (in thousands of dollars) are shown. The prior probabilities for the three states of nature are 0.3,0.3, and 0.4 , respectively. At each preseason sales meeting, the marketing department can provide forecasting reports regarding potential demand for this product. Because of the enthusiasm and optimistic nature of the marketing department, the predictions of market conditions have always been either "excellent" (E) or "very good" (V). Probabilities are as follows: P(E)=0.7,P(s1E)=0.34,P(s2E)=0.32,P(s1V)=0.2,P(s2V)=0.26 The decision tree for this problem is as follows. Answer the following questions. All numbers should be written in thousands and rounded to one decimal point. Calculate the expected value for node 6. Calculate the expected value for node 4. Calculate the maximum cost the store is willing to pay to the marketing department to receive the market report. Answer the following questions. All numbers should be written in thousands and rounded to one decimal point. Calculate the expected value for node 6. Calculate the expected value for node 4. Calculate the maximum cost the store is willing to pay to the marketing department to receive the market report. Calculate the expected value of perfect information. Virginia Publishing Company received a manuscript for a new college textbook. The editor of the college division is familiar with the manuscript and estimated a 0.65 probability that the textbook will be successful. If successful, a profit of $750,000 will be realized. If the company decides to publish the textbook and it is unsuccessful, a loss of $250,000 will occur. Before making the decision to accept or reject the manuscript, the editor is considering sending the manuscript out for review. A review process provides either a favorable (F) or unfavorable (U) evaluation of the manuscript. Past experience with the review process suggests that probabilities Let s1= the textbook is successful, and s2= the textbook is unsuccessful. The editor's initial probabilities of s1 and s2 will be revised based on whether the review is favorable or unfavorable. Currently, the reviewer claims that if the textbook is successful, with a 90% possibility the review will be favorable. In addition, if the textbook is not successful, with an 80% possibility the review will be unfavorable. The following decision tree depicts this problem. The following decision tree depicts this problem. Answer the following questions and round the numbers by three decimal points. In this decision tree, the probability value in box A is equal to the probability value in box B is equal to . and the probability value in box C is equal to In addition, the probability yalue that the review is favorable and the textbook is successful is From industry statistics, a credit card company knows that 0.85 of its potential card holders are good credit risks and 0.15 are bad credit risks. The company uses discriminant analysis to screen credit card applicants and determine which ones should receive credit cards. The company awards credit cards to 75% of those who apply. The company has found that of those awarded credit cards, 98% turn out to be good credit risks. What is the probability that an applicant who is a bad credit risk will be denied a credit card? Round the answer to two decimal point. Virginia's Department Store faces a purchasing decision for a seasonal product for which demand can be high, medium, or low. The purchaser for the store can order one, two, or three lots of the product before the season begins but cannot reorder later. Profit projections (in thousands of dollars) are shown. The prior probabilities for the three states of nature are 0.3,0.3, and 0.4 , respectively. At each preseason sales meeting, the marketing department can provide forecasting reports regarding potential demand for this product. Because of the enthusiasm and optimistic nature of the marketing department, the predictions of market conditions have always been either "excellent" (E) or "very good" (V). Probabilities are as follows: P(E)=0.7,P(s1E)=0.34,P(s2E)=0.32,P(s1V)=0.2,P(s2V)=0.26 The decision tree for this problem is as follows. Answer the following questions. All numbers should be written in thousands and rounded to one decimal point. Calculate the expected value for node 6. Calculate the expected value for node 4. Calculate the maximum cost the store is willing to pay to the marketing department to receive the market report. Answer the following questions. All numbers should be written in thousands and rounded to one decimal point. Calculate the expected value for node 6. Calculate the expected value for node 4. Calculate the maximum cost the store is willing to pay to the marketing department to receive the market report. Calculate the expected value of perfect information. Virginia Publishing Company received a manuscript for a new college textbook. The editor of the college division is familiar with the manuscript and estimated a 0.65 probability that the textbook will be successful. If successful, a profit of $750,000 will be realized. If the company decides to publish the textbook and it is unsuccessful, a loss of $250,000 will occur. Before making the decision to accept or reject the manuscript, the editor is considering sending the manuscript out for review. A review process provides either a favorable (F) or unfavorable (U) evaluation of the manuscript. Past experience with the review process suggests that probabilities Let s1= the textbook is successful, and s2= the textbook is unsuccessful. The editor's initial probabilities of s1 and s2 will be revised based on whether the review is favorable or unfavorable. Currently, the reviewer claims that if the textbook is successful, with a 90% possibility the review will be favorable. In addition, if the textbook is not successful, with an 80% possibility the review will be unfavorable. The following decision tree depicts this problem. The following decision tree depicts this problem. Answer the following questions and round the numbers by three decimal points. In this decision tree, the probability value in box A is equal to the probability value in box B is equal to . and the probability value in box C is equal to In addition, the probability yalue that the review is favorable and the textbook is successful is From industry statistics, a credit card company knows that 0.85 of its potential card holders are good credit risks and 0.15 are bad credit risks. The company uses discriminant analysis to screen credit card applicants and determine which ones should receive credit cards. The company awards credit cards to 75% of those who apply. The company has found that of those awarded credit cards, 98% turn out to be good credit risks. What is the probability that an applicant who is a bad credit risk will be denied a credit card? Round the answer to two decimal point
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


