Question: please use C programming language. 7.2.1 Problem You must create a struct for holding calculation operations and data, then write functions to load and run

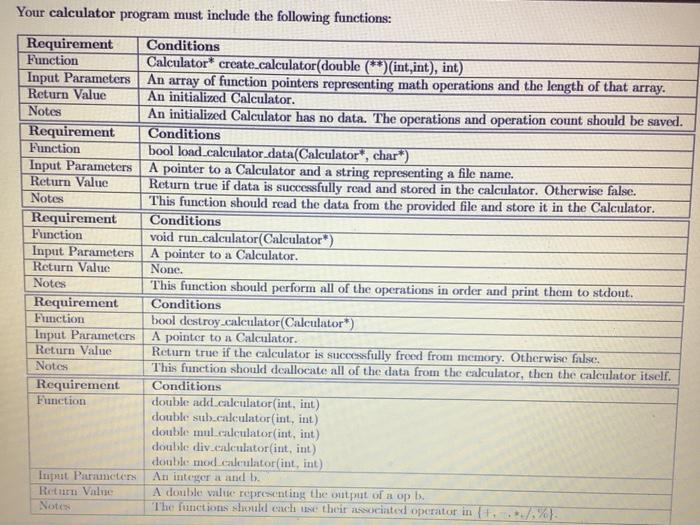
7.2.1 Problem You must create a struct for holding calculation operations and data, then write functions to load and run the calculation process. 7.2.2 Preconditions You are required to write an arithmetic calculator for handling add, subtract, multiply, divide, and mod (remainder) operations across a simple data set. You will create a struct for holding the math functions (as an array of function pointers), a selection of operation inputs (an array of integer arrays), as well as the lengths of those arrays. You will then write a series of functions for creating a calculator, loading the operation inputs, and then executing those inputs. The input files must be read into your program via file 1/0, where each file contains 100 lines of integers, with 3 integers on cach line. Each line's integers are represented as op a b, where op represents an index in the function pointer list (to select the math function to use), while a and b are the inputs to those functions, in order. Once your program reads in the input, it should also have the capability of performing all of the operations in order and printing them to stdout. Your calculator.h header file will contain forward definitions, struct definitions and typedefs, and any necessary library imports to ensure the proper operation of your functions. You must also write an accompanying calculator.c file containing all of the matching function implementations. When you compile, you will need to include the source file in your command in order to ensure the functions exist during the linking process. You may include any additional helper functions as you see fit, although they will likely not be necessary. Since you are dealing with pointers, you will need to check all of your pointers to crostire they are not null. Trying to perform operations on mill will lead to segmentation faults or other program crashes at run-time. Your calculator program must include the following structs (typedef-ed appropriately): Structure Name Fields Functionality Calculator double (operations) (int,int) Holds a list of function pointers to math operations, (typedef Calenator) int **data Holds the operational data from an input file. int operation Count Holes the total number of operations in the Caleulator int dataLength Holds the total number of data points from the input file. Your calculator program must include the following functions: Requirement Conditions Function Calculator* create calculator(double (*)(int,int), int) Input Parameters An array of function pointers representing math operations and the length of that array. Return Value An initialized Calculator. Notes An initialized Calculator has no data. The operations and operation count should be saved. Requirement Conditions Function bool load calculator data(Calculator*, char*) Input Parameters A pointer to a Calculator and a string representing a file name. Return value Return true if data is successfully read and stored in the calculator. Otherwise false. Notes This function should read the data from the provided file and store it in the Calculator. Requirement Conditions Function void run calculator(Calculator) Input Parameters A pointer to a Calculator Return Value None. Notes This function should perform all of the operations in order and print them to stdout. Requirement Conditions Function bool destroy calculator(Calculator) Input Parameters A pointer to a Calculator. Return value Return true if the calculator is successfully freed from memory. Otherwise false. Notes This function should deallocate all of the data from the calculator, then the calculator itself. Requirement Conditions Function double add calculator(int, int) double subcalculator(int, int) double mnl.calculator(int, int) double div calculator(int, int) double mod calculator(int, int) luput Parameters An integer and b. Return value A double vite representing the output of a opI Notes The functions should cach use their associated operator in %. 7.2.1 Problem You must create a struct for holding calculation operations and data, then write functions to load and run the calculation process. 7.2.2 Preconditions You are required to write an arithmetic calculator for handling add, subtract, multiply, divide, and mod (remainder) operations across a simple data set. You will create a struct for holding the math functions (as an array of function pointers), a selection of operation inputs (an array of integer arrays), as well as the lengths of those arrays. You will then write a series of functions for creating a calculator, loading the operation inputs, and then executing those inputs. The input files must be read into your program via file 1/0, where each file contains 100 lines of integers, with 3 integers on cach line. Each line's integers are represented as op a b, where op represents an index in the function pointer list (to select the math function to use), while a and b are the inputs to those functions, in order. Once your program reads in the input, it should also have the capability of performing all of the operations in order and printing them to stdout. Your calculator.h header file will contain forward definitions, struct definitions and typedefs, and any necessary library imports to ensure the proper operation of your functions. You must also write an accompanying calculator.c file containing all of the matching function implementations. When you compile, you will need to include the source file in your command in order to ensure the functions exist during the linking process. You may include any additional helper functions as you see fit, although they will likely not be necessary. Since you are dealing with pointers, you will need to check all of your pointers to crostire they are not null. Trying to perform operations on mill will lead to segmentation faults or other program crashes at run-time. Your calculator program must include the following structs (typedef-ed appropriately): Structure Name Fields Functionality Calculator double (operations) (int,int) Holds a list of function pointers to math operations, (typedef Calenator) int **data Holds the operational data from an input file. int operation Count Holes the total number of operations in the Caleulator int dataLength Holds the total number of data points from the input file. Your calculator program must include the following functions: Requirement Conditions Function Calculator* create calculator(double (*)(int,int), int) Input Parameters An array of function pointers representing math operations and the length of that array. Return Value An initialized Calculator. Notes An initialized Calculator has no data. The operations and operation count should be saved. Requirement Conditions Function bool load calculator data(Calculator*, char*) Input Parameters A pointer to a Calculator and a string representing a file name. Return value Return true if data is successfully read and stored in the calculator. Otherwise false. Notes This function should read the data from the provided file and store it in the Calculator. Requirement Conditions Function void run calculator(Calculator) Input Parameters A pointer to a Calculator Return Value None. Notes This function should perform all of the operations in order and print them to stdout. Requirement Conditions Function bool destroy calculator(Calculator) Input Parameters A pointer to a Calculator. Return value Return true if the calculator is successfully freed from memory. Otherwise false. Notes This function should deallocate all of the data from the calculator, then the calculator itself. Requirement Conditions Function double add calculator(int, int) double subcalculator(int, int) double mnl.calculator(int, int) double div calculator(int, int) double mod calculator(int, int) luput Parameters An integer and b. Return value A double vite representing the output of a opI Notes The functions should cach use their associated operator in %
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


