Question: Please use the MACRS Table that has been provided. Rounded Depreciation Percentages by Recovery Year Using MACRS for First Four Property Classes Percentage by recovery
 Please use the MACRS Table that has been provided.
Please use the MACRS Table that has been provided.
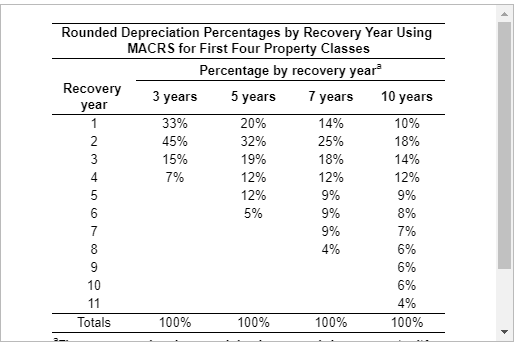
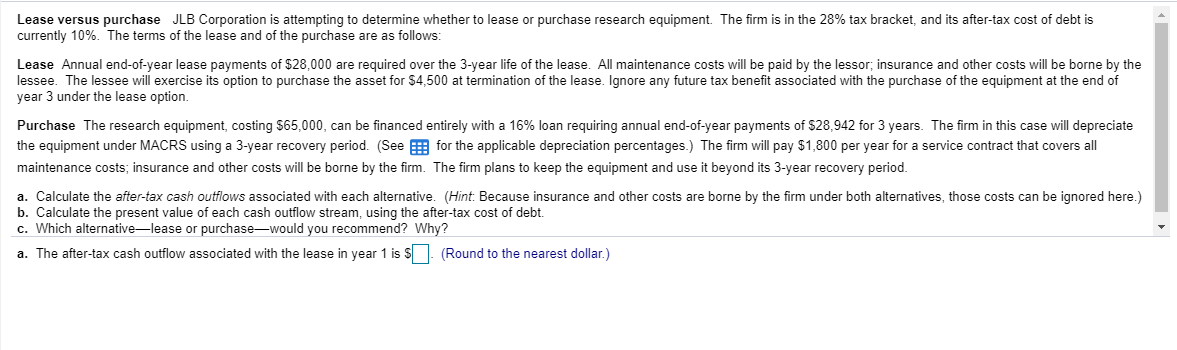
Rounded Depreciation Percentages by Recovery Year Using MACRS for First Four Property Classes Percentage by recovery year Recovery 3 years 5 years 7 years 10 years year 33% 20% 14% 10% 45% 32% 25% 18% 15% 19% 18% 14% 7% 12% 12% 9% covo AWN- 9% 8% 9% 4% 6% 6% 4% 100% Totals 100% 100% 100% Lease versus purchase JLB Corporation is attempting to determine whether to lease or purchase research equipment. The firm is in the 28% tax bracket, and its after-tax cost of debt is currently 10%. The terms of the lease and of the purchase are as follows: Lease Annual end-of-year lease payments of $28,000 are required over the 3-year life of the lease. All maintenance costs will be paid by the lessor; insurance and other costs will be borne by the lessee. The lessee will exercise its option to purchase the asset for $4,500 at termination of the lease. Ignore any future tax benefit associated with the purchase of the equipment at the end of year 3 under the lease option. Purchase The research equipment, costing $65,000, can be financed entirely with a 16% loan requiring annual end-of-year payments of $28,942 for 3 years. The firm in this case will depreciate the equipment under MACRS using a 3-year recovery period. (See for the applicable depreciation percentages.) The firm will pay $1,800 per year for a service contract that covers all maintenance costs, insurance and other costs will be borne by the firm. The firm plans to keep the equipment and use it beyond its 3-year recovery period. a. Calculate the after-tax cash outflows associated with each alternative. (Hint: Because insurance and other costs are borne by the firm under both alternatives, those costs can be ignored here.) b. Calculate the present value of each cash outflow stream, using the after-tax cost of debt. c. Which alternativelease or purchasewould you recommend? Why? a. The after-tax cash outflow associated with the lease in year 1 is $ (Round to the nearest dollar.) Rounded Depreciation Percentages by Recovery Year Using MACRS for First Four Property Classes Percentage by recovery year Recovery 3 years 5 years 7 years 10 years year 33% 20% 14% 10% 45% 32% 25% 18% 15% 19% 18% 14% 7% 12% 12% 9% covo AWN- 9% 8% 9% 4% 6% 6% 4% 100% Totals 100% 100% 100% Lease versus purchase JLB Corporation is attempting to determine whether to lease or purchase research equipment. The firm is in the 28% tax bracket, and its after-tax cost of debt is currently 10%. The terms of the lease and of the purchase are as follows: Lease Annual end-of-year lease payments of $28,000 are required over the 3-year life of the lease. All maintenance costs will be paid by the lessor; insurance and other costs will be borne by the lessee. The lessee will exercise its option to purchase the asset for $4,500 at termination of the lease. Ignore any future tax benefit associated with the purchase of the equipment at the end of year 3 under the lease option. Purchase The research equipment, costing $65,000, can be financed entirely with a 16% loan requiring annual end-of-year payments of $28,942 for 3 years. The firm in this case will depreciate the equipment under MACRS using a 3-year recovery period. (See for the applicable depreciation percentages.) The firm will pay $1,800 per year for a service contract that covers all maintenance costs, insurance and other costs will be borne by the firm. The firm plans to keep the equipment and use it beyond its 3-year recovery period. a. Calculate the after-tax cash outflows associated with each alternative. (Hint: Because insurance and other costs are borne by the firm under both alternatives, those costs can be ignored here.) b. Calculate the present value of each cash outflow stream, using the after-tax cost of debt. c. Which alternativelease or purchasewould you recommend? Why? a. The after-tax cash outflow associated with the lease in year 1 is $ (Round to the nearest dollar.)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


