Question: Please use this simulation link to fill in the 5 tables following the steps explained in the lab, no explanation needed. https://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulations/collision-lab Worksheet of Conservation
Please use this simulation link to fill in the 5 tables following the steps explained in the lab, no explanation needed.
https://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulations/collision-lab
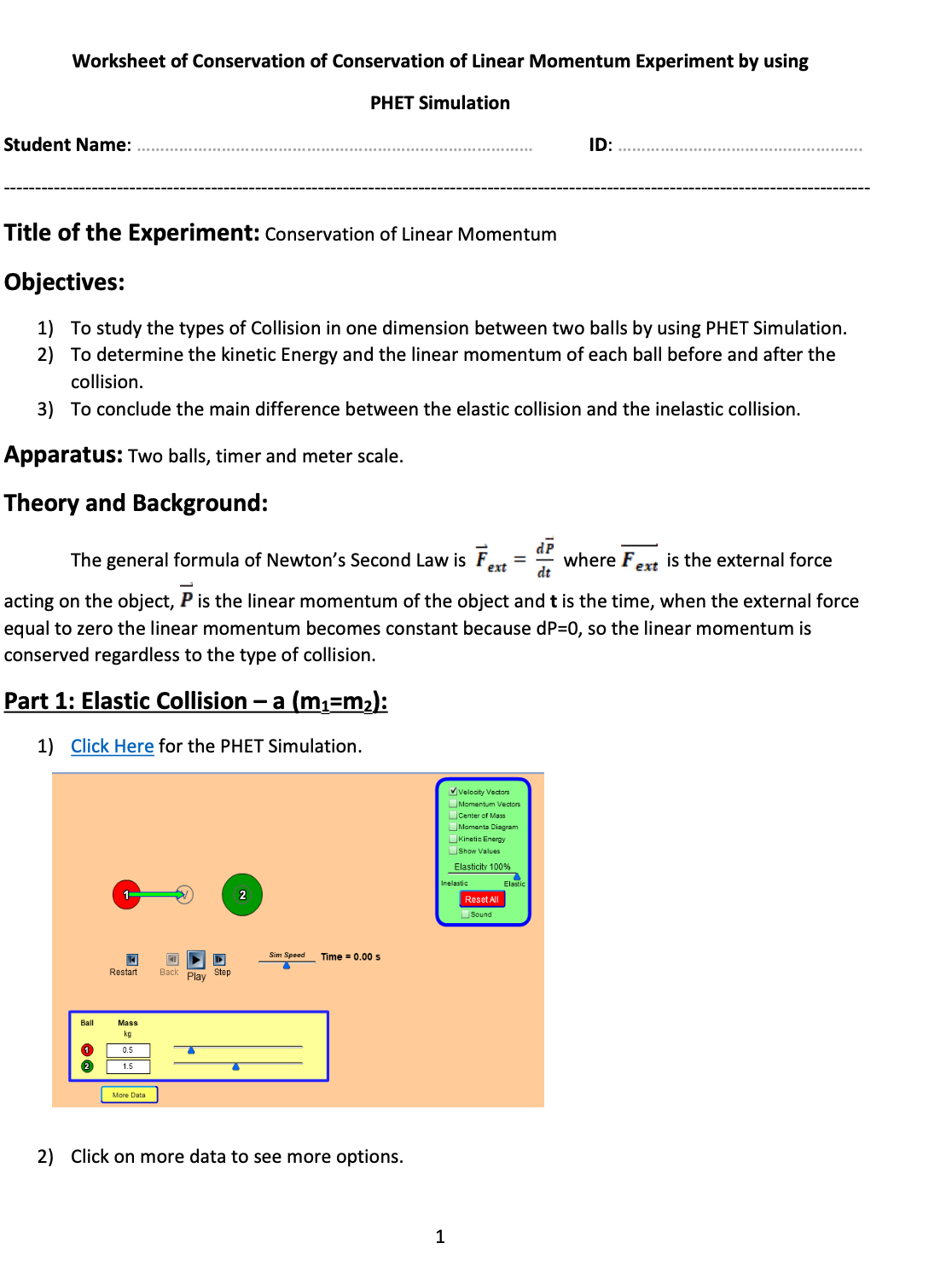
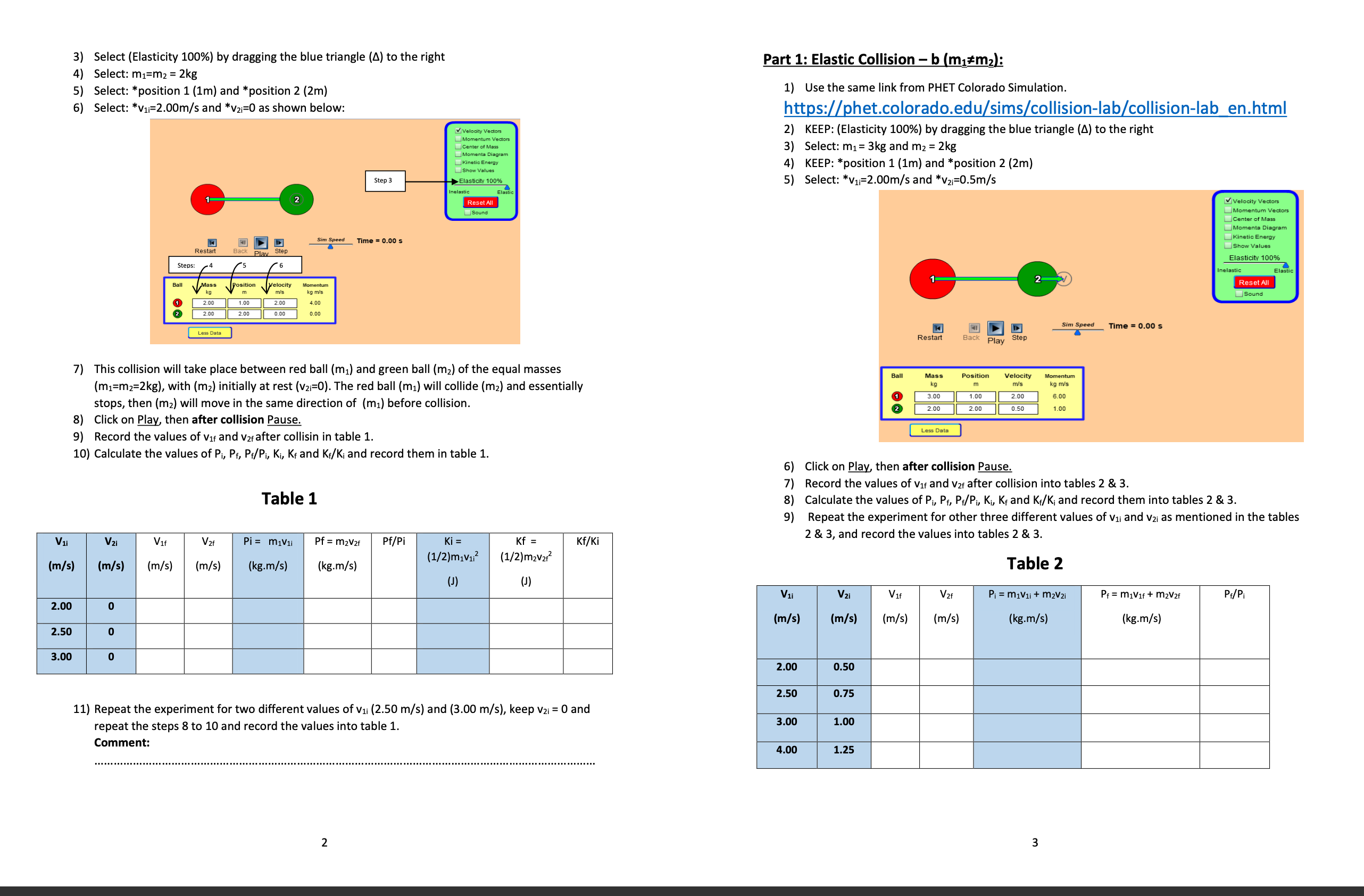
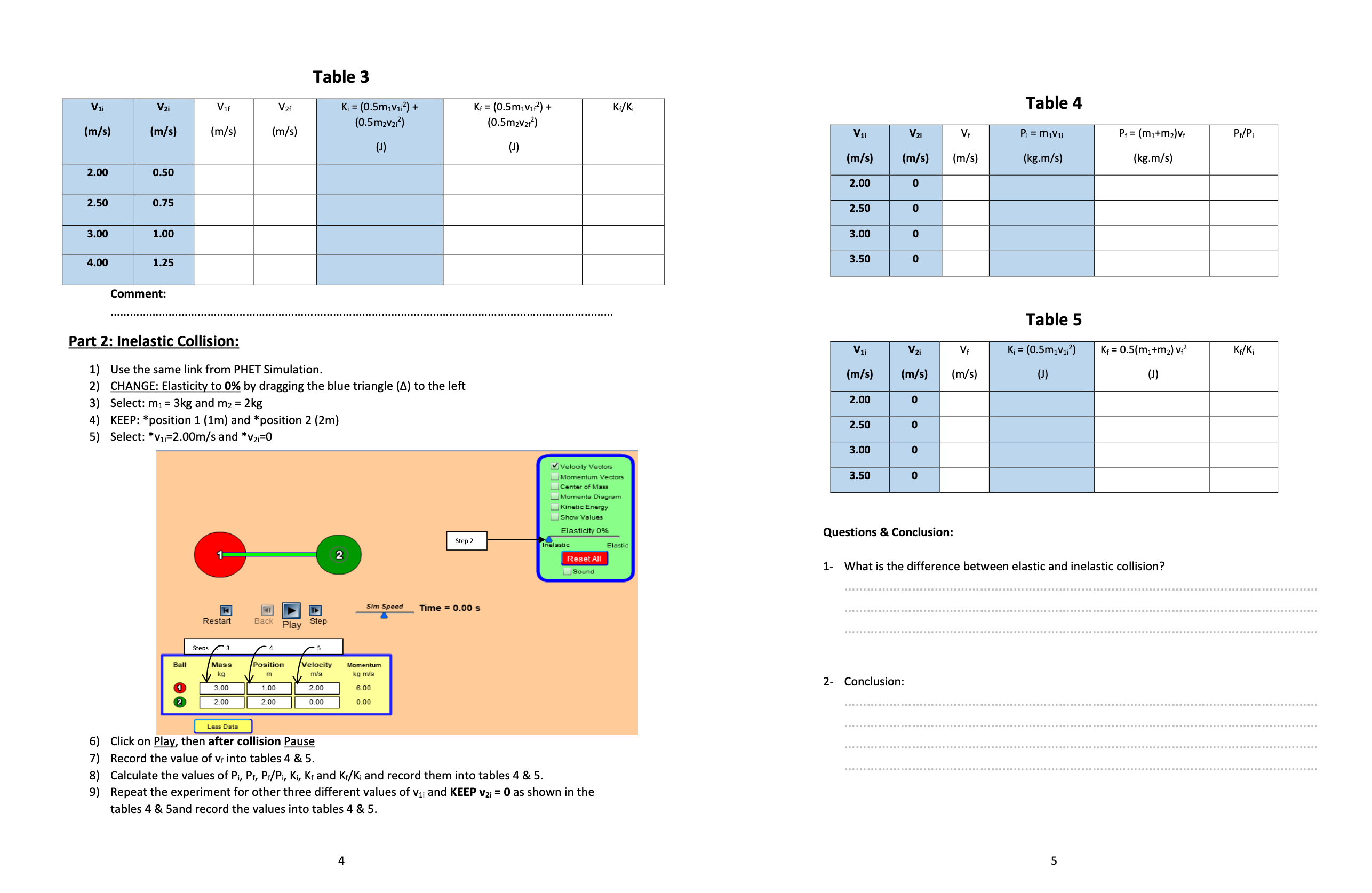
Worksheet of Conservation of Conservation of Linear Momentum Experiment by using PHET Simulation Student Name: ID: Title of the Experiment: Conservation of Linear Momentum Objectives: 1) To study the types of Collision in one dimension between two balls by using PHET Simulation. 2) To determine the kinetic Energy and the linear momentum of each ball before and after the collision. 3) To conclude the main difference between the elastic collision and the inelastic collision. Apparatus: Two balls, timer and meter scale. Theory and Background: The general formula of Newton's Second Law is Fent = # where Fext is the external force acting on the object, P is the linear momentum of the object and t is the time, when the external force equal to zero the linear momentum becomes constant because dP=0, so the linear momentum is conserved regardless to the type of collision. Part 1: Elastic Collision - a (m1=m2): 1) Click Here for the PHET Simulation. V Velocity Vectors Momentum Vectors center of Mass Moments Diagram Kinetic Energy Show Values Elasticity 100% elastic Reset All Sound 41 D Sim Speed Time = 0.00 s T Restar Back Play Step Ball Mass kg O 0.5 1.5 More Data 2) Click on more data to see more options. 13) Select (Elasticity 100%) by dragging the blue triangle (A) to the right Part 1: Elastic Collision - b (m1#m2): 4) Select: m1=m2 = 2kg 5) Select: *position 1 (1m) and * position 2 (2m) 1) Use the same link from PHET Colorado Simulation. Select: *V1=2.00m/s and *V21=0 as shown below: https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/collision-lab/collision-lab en.html MiVelocity Vectors 2) KEEP: (Elasticity 100%) by dragging the blue triangle (A) to the right Momentum Vectors Center of Mass Momenta Diagram 3 ) Select: m1= 3kg and mz = 2kg Kinetic Energy Show Values 4) KEEP: *position 1 (1m) and *position 2 (2m) Step 3 Elasticity 1009% 5) Select: *V1=2.00m/s and *V2i=0.5m/s lastic Reset All Velocity Vectors Sound Momentum Vector center of Mass Moments Diagram Sim Speed Time = 0.00 s Kinetic Ene Show Values Elasticity 100% Steps: Inelastic Elastic Ball Mass Position Velocity Reset All kg TV's Sound 2.00 1.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 0.00 0.00 Sim Speed Time = 0.00 s Less Data Restart Play 7) This collision will take place between red ball (m1) and green ball (m2) of the equal masses Ball Mass Velocity Momentum (m1=m2=2kg), with (m2) initially at rest (V21=0). The red ball (mi) will collide (m2) and essentially kg m m/'s kg m/'s 3.00 1.00 2.00 6.00 stops, then (mz) will move in the same direction of (mi) before collision. 2 2.00 2.00 0.50 1.00 8) Click on Play, then after collision Pause. 9) Record the values of Vir and var after collisin in table 1. Less Data 10) Calculate the values of Pi, Pf, Pf/Pi, Ki, Kf and K:/K; and record them in table 1. 6) Click on Play, then after collision Pause. 7) Record the values of Vir and var after collision into tables 2 & 3. Table 1 8) Calculate the values of Pi, Pf, P:/Pi, Ki, K, and K,/K; and record them into tables 2 & 3. 9) Repeat the experiment for other three different values of Vii and v2i as mentioned in the tables Pi = miVli Pf = m2V2f Pf/Pi Ki = Kf = Kf/Ki 2 & 3, and record the values into tables 2 & 3. V1i V2 Vif V2f (1/2)m1V12 (1/2)m2V212 (m/s) (m/s) (m/s) (m/s) (kg.m/s) (kg.m/s) Table 2 (J) (J) V1i Vzi Vif V 2f Pi = m1Vli + m2V2i Pf = m1Vif + m2V2f P./Pi 2.00 0 (m/s) (m/s) (m/s) (m/s) (kg.m/s) (kg.m/s) 2.50 0 3.00 2.00 0.50 2.50 0.75 11) Repeat the experiment for two different values of vii (2.50 m/s) and (3.00 m/s), keep v2i = 0 and repeat the steps 8 to 10 and record the values into table 1. 3.00 1.00 Comment: 4.00 1.25 2 3Table 3 Table 4 V1 V2 V16 V2 Ki = (0.5m1V12) + Kf = (0.5m1v172) + KF/Ki (0.5m2V212) (0.5m2V2f-) (m/s) (m/s) (m/s) (m/s) V1 V 2i Pi = m1Vli Pf = (mitm2) Vf P /P (J) (m/s) (m/s) (m/s) (kg.m/s) kg.m/s) 2.00 0.50 2.00 2.50 0.75 2.50 1.00 3.00 0 3.00 3.50 4.0 1.25 Comment: Table 5 Part 2: Inelastic Collision: V1i V 21 Vf Ki = (0.5m1V12) Kf = 0.5(m1+m2) V/2 KF/Ki 1) Use the same link from PHET Simulation. (m/s) (m/s (m/s) (J ) (J) 2) CHANGE: Elasticity to 0% by dragging the blue triangle (4) to the left 2.00 Select: m1= 3kg and mz = 2kg 4) KEEP: *position 1 (1m) and *position 2 (2m) 2.50 0 5) Select: *V1=2.00m/s and *V21=0 3.00 o Vi Velocity Vectors Momentum Vectors 3.50 0 Center of Mass Moments Diagram Kinetic Energy Show Values Elasticity 0% Questions & Conclusion: Step 2 Inelastic Elastic Reset All sound 1- What is the difference between elastic and inelastic collision? Sim Speed Time = 0.00 s Restart Back Play Step Stens 3 4 Ball Mass Position Velocity Momentum kg m m/'s kg m/'s 2- Conclusion: 3.00 1.00 2.00 6.00 NC 2.00 2.00 0.00 0.00 . .. ................. Less Data 6) Click on Play, then after collision Pause 7) Record the value of v into tables 4 & 5. 8 ) Calculate the values of Pi, Pf, Pf/Pi, Ki, Kf and Kf/K; and record them into tables 4 & 5. ) Repeat the experiment for other three different values of Vii and KEEP v2; = 0 as shown in the tables 4 & 5and record the values into tables 4 & 5. UT
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


