Question: Please use Ubuntu, Linux, and Virtual Box to solve the problem below(this is an operating systems question): Write a kernel module that create an entry
Please use Ubuntu, Linux, and Virtual Box to solve the problem below(this is an operating systems question):
Write a kernel module that create an entry in the /proc file system. The new entry cannot be directly read or written using cat and echo commands. Instead, map the new entry to a user space memory area so that user-level processes can read from and write to the kernel space via mmap. The skeleton of the kernel module is given below:
#include
static struct proc_dir_entry *tempdir, *tempinfo; static unsigned char *buffer; static unsigned char array[12]={0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11};
static void allocate_memory(void); static void clear_memory(void); static int my_map(struct file *filp, struct vm_area_struct *vma);
static const struct file_operations myproc_fops = { .mmap = my_map, };
static int my_map(struct file *filp, struct vm_area_struct *vma) { // map vma of user space to a continuous physical space return 0; }
static int init_myproc_module(void) { tempdir=proc_mkdir("mydir", NULL); if(tempdir == NULL) { printk("mydir is NULL "); return -ENOMEM; }
tempinfo = proc_create("myinfo", 0, tempdir, &myproc_fops); if(tempinfo == NULL) { printk("myinfo is NULL "); remove_proc_entry("mydir",NULL); return -ENOMEM; } printk("init myproc module successfully ");
allocate_memory();
return 0; }
static void allocate_memory(void) { /* allocation memory */ buffer = (unsigned char *)kmalloc(PAGE_SIZE,GFP_KERNEL); /* set the memory as reserved */ SetPageReserved(virt_to_page(buffer)); }
static void clear_memory(void) { /* clear reserved memory */ ClearPageReserved(virt_to_page(buffer)); /* free memory */ kfree(buffer); }
static void exit_myproc_module(void) { clear_memory(); remove_proc_entry("myinfo", tempdir); remove_proc_entry("mydir", NULL); printk("remove myproc module successfully "); }
module_init(init_myproc_module); module_exit(exit_myproc_module); MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
The above code will create an entry /proc/mydir/myinfo under the proc file system. You are required to implement the my_map function to map one piece of memory (char array[12]) into user space. Then write a user space program using mmap to visit the memory space of the proc file and print the data in that memory area. You can use the following skeleton:
#include
#define PAGE_SIZE 4096
int main(int argc , char *argv[]) { int fd; int i; unsigned char *p_map;
/* open proc file */ fd = open("/proc/mydir/myinfo", O_RDWR); if(fd
// map p_map to the proc file and grant read & write privilege // read data from p_map // unmap p_map from the proc file
return 0; }
Please show source code, output screenshot of your parallel code and a report describe your code logic. Please show your modification (file diff1.txt, diff2.txt, ) and the screenshot of output
Please use diff command to highlight your modification: $ diff -u original_file.c modified_file.c. > diff.txt
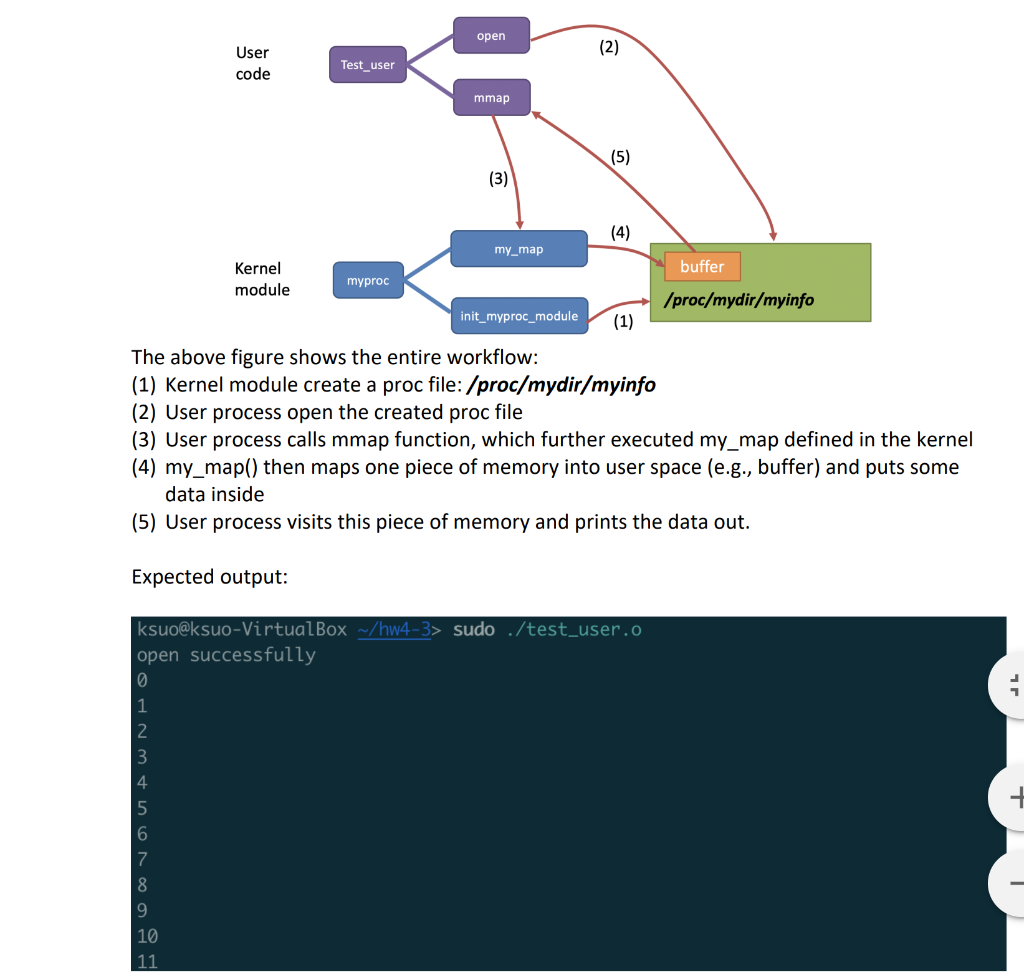
open User code Test_user mmap my_map buffer Kernel module myproc /proc/mydir/myinfo init_myproc_module (1) The above figure shows the entire workflow: (1) Kernel module create a proc file: /proc/mydir/myinfo (2) User process open the created proc file (3) User process calls mmap function, which further executed my_map defined in the kernel (4) my_map() then maps one piece of memory into user space (e.g., buffer) and puts some data inside (5) User process visits this piece of memory and prints the data out. Expected output: ksuo@ksuo-VirtualBox ~/hw4-3> sudo ./test_user.o open successfully open User code Test_user mmap my_map buffer Kernel module myproc /proc/mydir/myinfo init_myproc_module (1) The above figure shows the entire workflow: (1) Kernel module create a proc file: /proc/mydir/myinfo (2) User process open the created proc file (3) User process calls mmap function, which further executed my_map defined in the kernel (4) my_map() then maps one piece of memory into user space (e.g., buffer) and puts some data inside (5) User process visits this piece of memory and prints the data out. Expected output: ksuo@ksuo-VirtualBox ~/hw4-3> sudo ./test_user.o open successfully
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


