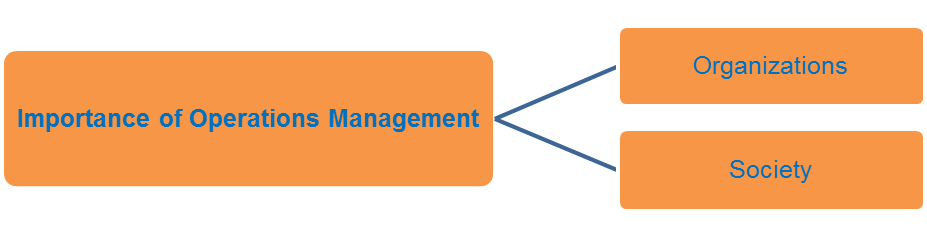
Question: PLSSS HELP ME Can you explain why do we study Operations Management? Can you explain the Figure one presented below. How does the framework work?
PLSSS HELP ME
- Can you explain why do we study Operations Management?
- Can you explain the Figure one presented below. How does the framework work?
PLS REFER HERE:
Introduction to Operations Management
This introductory lesson focuses on activating your prior knowledge on Management. It may sound repetitive on your part as you might have studied this already in Senor High School, however, we would like you to have a smooth transition from high school lesson to college lessons. Afterall, it is just practical to start our discussion with something you are familiar with, so that you may not find it difficult to adjust to the more complicated topics.
So, when you hear the word Management, what comes into our mind? Perhaps you think of - a business, people, managers, and the like. Several ideas might be running in your head now, and slowly you are able to recall what you have learned in high school.
Management, as a distinct field of study, encompasses what we call"The Managerial Functions"ofPlanning, Organizing, Staffing/Directing, Actuating, and Controlling. Now, our course,Operations Management or Production and Operations Management (as previously known),is just one of the areas of concern in management. However, we will still be talking about the Managerial Functions here as we study this course.
NOTE: In the past, the termProductionwas considered to connote only themanufacture of tangible items. Later, the termOperationswas added to include references tonon-manufacturing operations.That's whyProduction and Operations ManagementandOperations Managementare just the same. But we stick with our course description that is,Operations Management (OM).
Lesson Proper:
Basic Concepts on Operations Management (OM)
Operations as a competitive weapon is important to...
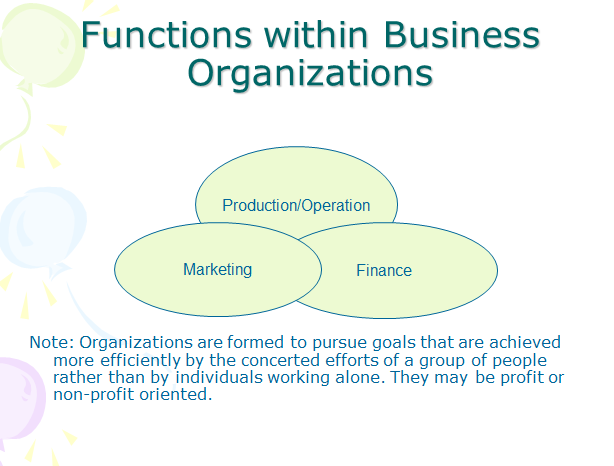
Accounting, which prepares financial and cost accounting information that aids operations managers in designing and operatingproduction systems.
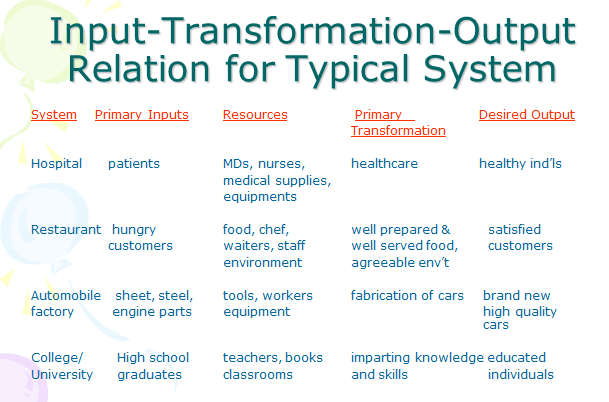
Theproduction systemconsists ofinputs, processes, outputs, and information flowsthat connect with customers and the external environment. It uses operation resources to transform inputs into desired outputs. It is considered as the heart of Operations Management.
Inputs - includes human resources( workers, managers ), capital (equipment, facilities), purchased materials and services, land, and energy
- It may also be raw materials, a customer, or a finished product from another system
Process - any activity or group of activities that takes one or more inputs,transformsand adds value to them, and provides output for a customer
Finance, which manages the cash flows and capital investment requirements that are created by the operations function.
Human Resources, which hires and trains employees to match process needs, location decisions, and planned production levels.
Management Information Systems, which develops information systems and decision support systems for operations managers.
Marketing, which helps create the demand that operations must satisfy, link customer demand with staffing and production plans, and keep the operations function focused on satisfying customer's needs.
Operations, which designs and operates production systems to give the firm a sustainable competitive advantage.
Let's take into consideration these terms, for us to have a clear understanding of our course description.
1.Production - creation of goods and/or services
- Management -denotes both FUNCTION and PEOPLE who discharge the functions
- A distinct process of planning, organizing, staffing, directing (actuating)and controlling for the achievement of stated objectives efficiently and effectively by the use of human beings and other business resources.
- Operations - encompasses the overall activities within the organization
- Organization - a business, an entity, a private school, a government office, a hospital, a restaurant, a religious organization, etc. that is composed of people
- Manufacturing firms - those companies/businesses engaged in the manufacture/creation/production of tangible items. Tangible items are those that we could see and touch, like your smartphones,laptops, house, buildings, etc.
- Non-Manufacturing firms - those companies/business engaged offering non-tangible items. Non-tangible items are those that we could experience or feel. It includes services of a hospital, a beautician, an artist, a chef, a hotel, a school, and many others.
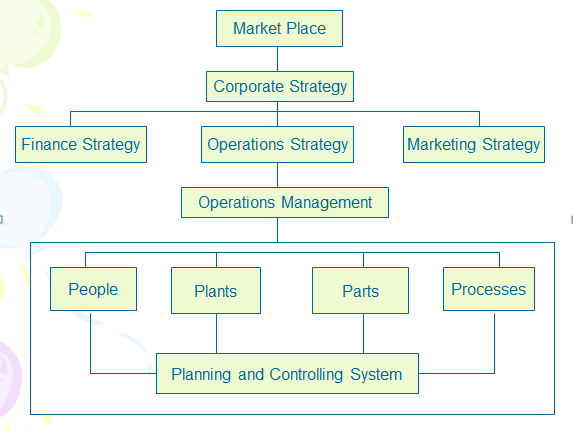
What is Production/Operations Management?
- Set of activities that creates goods and services by transforming inputs into outputs involving planning, coordinating, and executing of all activities
- The management of systems or processes that creates goods and/or services
- The design, operation and movement of the production systems that create the firm's primary product or service.
Figure 1. OM Framework

\fInput-Transformation-Output Relation for Typical System System Primary Inputs Resources Primary Desired Output Transformation Hospital patients MDs, nurses, healthcare healthy ind'ls medical supplies, equipments Restaurant hungry food, chef, well prepared & satisfied customers waiters, staff well served food, customers environment agreeable env't Automobile sheet, steel, tools, workers fabrication of cars brand new factory engine parts equipment high quality cars College/ High school teachers, books imparting knowledge educated University graduates classrooms and skills individualsFunctions within Business Organizations Production/Operation Marketing Finance Note: Organizations are formed to pursue goals that are achieved more efficiently by the concerted efforts of a group of people rather than by individuals working alone. They may be profit or non-profit oriented.Market Place Corporate Strategy Finance Strategy Operations Strategy Marketing Strategy Operations Management People Plants Parts Processes Planning and Controlling SystemTen Decision . Issues Areas Service and Product . What product or service should we offer? Design . How should we design these products and services? Quality Management .Who is responsible for quality? . How do we define the quality we want in our product or service? Process and Capacity What process will these products require and in what order? . What equipment and technology is necessary for these Design processes? Location . Where should we put the facility? . On what criteria should we base location decisions? Layout Design . How large must the facility be to meet our plan? . How should we arrange the facility? Human Resource and . How do we provide a reasonable work environment? Job Design . How much can we expect our employees to produce? Supply Chain Who are our supplier and who can integrate into our e- commerce program? Management .Should we make or buy this component? Inventory, Material, Equipment, Planning and JIT . How much inventory of each item should we have? .When do we reorder? (just in time) Intermediate, Short-term, Is subcontracting production a good idea? and Project Scheduling . Are we better of keeping people on payroll during slowdowns? Maintenance .Who is responsible for maintenance
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


