Question: Pointers and Bubbles (A2) s Due Friday by 11:59pm Points 100 Overview C-style pointers are important to understand, because they live on in higher level
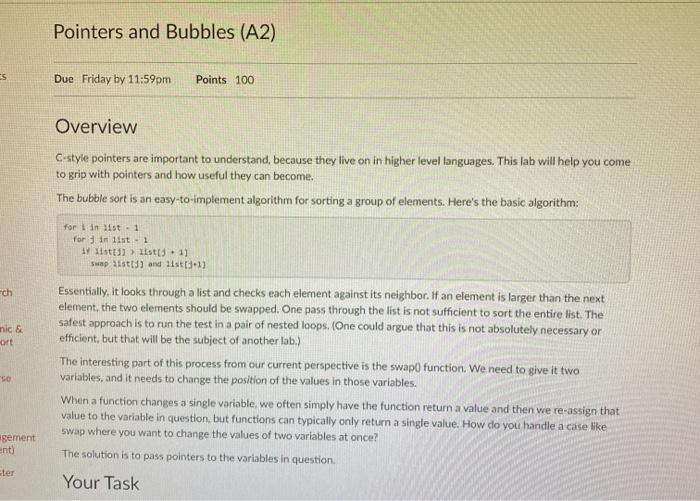
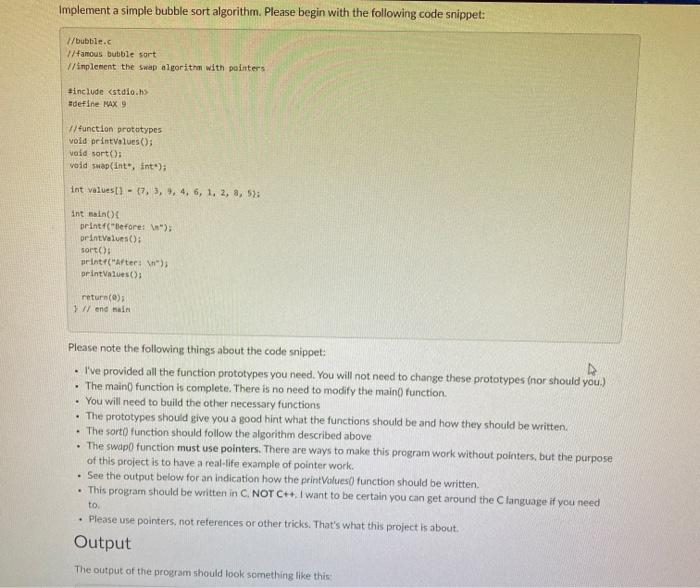
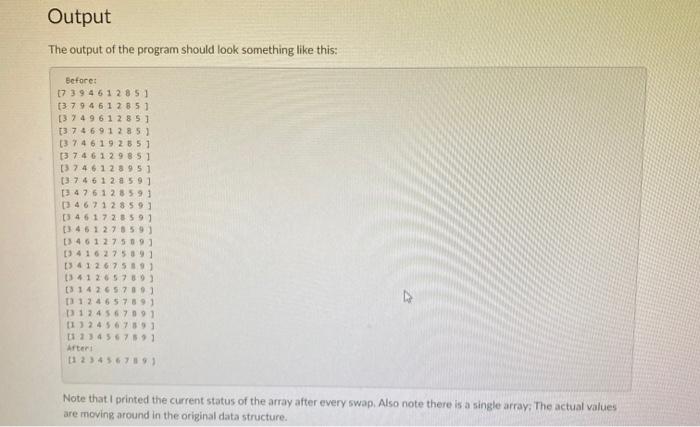
Pointers and Bubbles (A2) s Due Friday by 11:59pm Points 100 Overview C-style pointers are important to understand, because they live on in higher level languages. This lab will help you come to grip with pointers and how useful they can become The bubble sort is an easy-to-implement algorithm for sorting a group of elements. Here's the basic algorithm: for in list - 1 for sin list - 1 1 list ist 11 Swap ist) and list[d.1) ch nic & wort "SO Essentially, it looks through a list and checks each element against its neighbor. If an element is larger than the next element, the two elements should be swapped. One pass through the list is not sufficient to sort the entire list. The safest approach is to run the test in a pair of nested loops. One could argue that this is not absolutely necessary or efficient, but that will be the subject of another lab.) The interesting part of this process from our current perspective is the swap function. We need to give it two variables, and it needs to change the position of the values in those variables. When a function changes a single variable, we often simply have the function return a value and then we re-assign that value to the variable in question, but functions can typically only return a single value. How do you handle a case like swap where you want to change the values of two variables at once? The solution is to pass pointers to the variables in question. Your Task sement ent) ter Implement a simple bubble sort algorithm. Please begin with the following code snippet: /bubble.c / famous bubble sort 1/implement the Swap algorithm with pointers Sinclude
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


