Question: Population parameter, hypothesis test, sample statistic, randomized experiment, random, normal, quantitative, confidence interval, central limit theorem, statistical inference, standard error, statistical, biased, categorical variable versus
Population parameter, hypothesis test, sample statistic, randomized experiment, random, normal, quantitative, confidence interval, central limit theorem, statistical inference, standard error, statistical, biased, categorical variable versus a categorical, P value, large, representative, quantitative variable versus a quantitative, categorical, categorical variable versus a quantitative variable
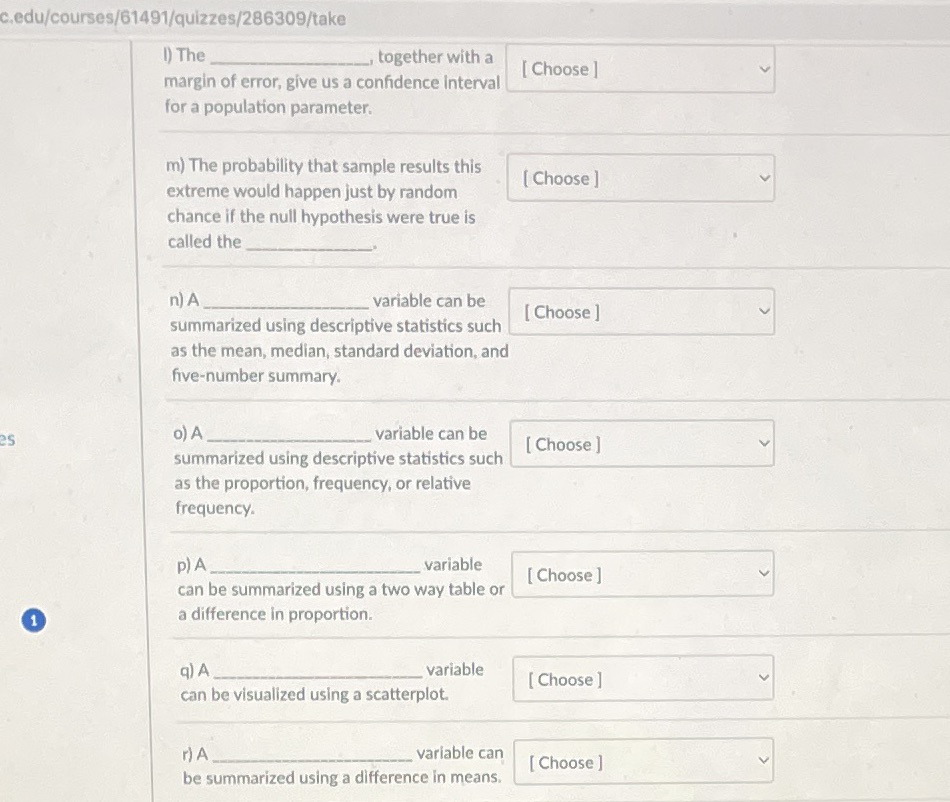
c.edu/courses/61491/quizzes/286309/take 1) The together with a margin of error, give us a confidence interval [ Choose ] for a population parameter. m) The probability that sample results this extreme would happen just by random [ Choose ] chance if the null hypothesis were true is called the n) A variable can be summarized using descriptive statistics such [ Choose ] as the mean, median, standard deviation, and five-number summary. O) A variable can be summarized using descriptive statistics such [ Choose ] as the proportion, frequency, or relative frequency. P) A variable [ Choose ] can be summarized using a two way table or 1 a difference in proportion. q) A _variable [ Choose ] can be visualized using a scatterplot. r) A variable can [ Choose ] be summarized using a difference in means
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


