Question: Prefer clear handwriting. 1. For the case where diffusion to the pellet surface is infinitely fast (i.e., the surface concentration is equal to the bulk
Prefer clear handwriting.
1. For the case where diffusion to the pellet surface is infinitely fast (i.e., the surface concentration is equal to the bulk concentration, calculate the mass of catalyst required to achieve 90% conversion of A)
2. For the case where the mass transfer coefficient to the external particle surface is 3.75 cm/s, calculate the mass of catalyst required to achieve 90% conversion of A. For this example, you may either apply the flux boundary condition at the catalyst surface or solve the external mass transfer problem separately to find the surface concentration as a function of bulk concentration and apply that surface concentration as your boundary condition.
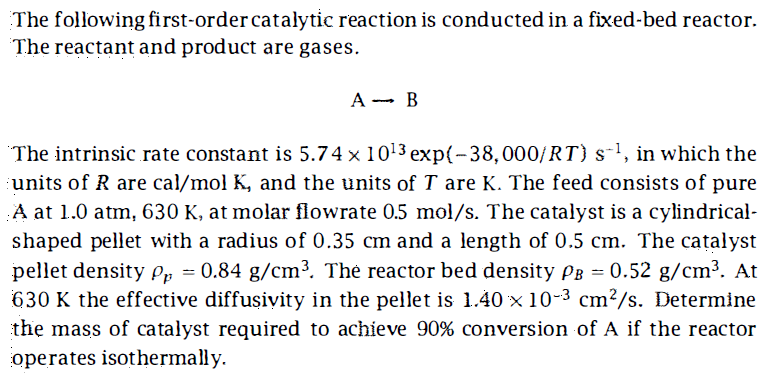
The following first-order catalytic reaction is conducted in a fixed-bed reactor. The reactant and product are gases. AB The intrinsic rate constant is 5.741013exp(38,000/RT)s1, in which the units of R are cal/molK, and the units of T are K. The feed consists of pure A at 1.0atm,630K, at molar flowrate 0.5mol/s. The catalyst is a cylindricalshaped pellet with a radius of 0.35cm and a length of 0.5cm. The catalyst pellet density p=0.84g/cm3. The reactor bed density B=0.52g/cm3. At 630K the effective diffusivity in the pellet is 1.40103cm2/s. Determine the mass of catalyst required to achieve 90% conversion of A if the reactor operates isothermally
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


