Question: Previous Problem Problem List Next Problem A first order linear differential equation is one that can be put in the form dy dz +
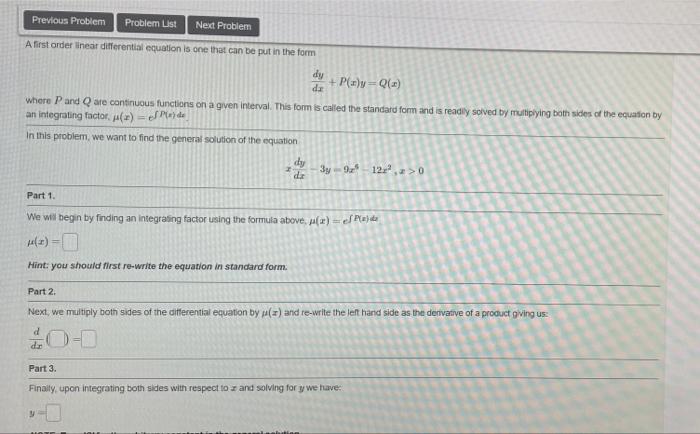
Previous Problem Problem List Next Problem A first order linear differential equation is one that can be put in the form dy dz + P(x)y-Q(2) where P and Q are continuous functions on a given interval. This form is called the standard form and is readily solved by multiplying both sides of the equation by an integrating factor, (x)=ef Pede In this problem, we want to find the general solution of the equation dy 3y-9 122,2>0 dz Part 1. We will begin by finding an integrating factor using the formula above, pa(z) = elada (2)- Hint: you should first re-write the equation in standard form. Part 2. Next, we multiply both sides of the differential equation by p() and re-write the left hand side as the derivative of a product giving us: d 0-0 Part 3. Finally, upon integrating both sides with respect to and solving for y we have: HOTE
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


