Question: Pricing SECTION 2: PROBLEM SOLVING (3 QUESTIONS, 25 POINTS) Do not use Excel for this section Question 1 - Customers (5 points) Lang Lang is
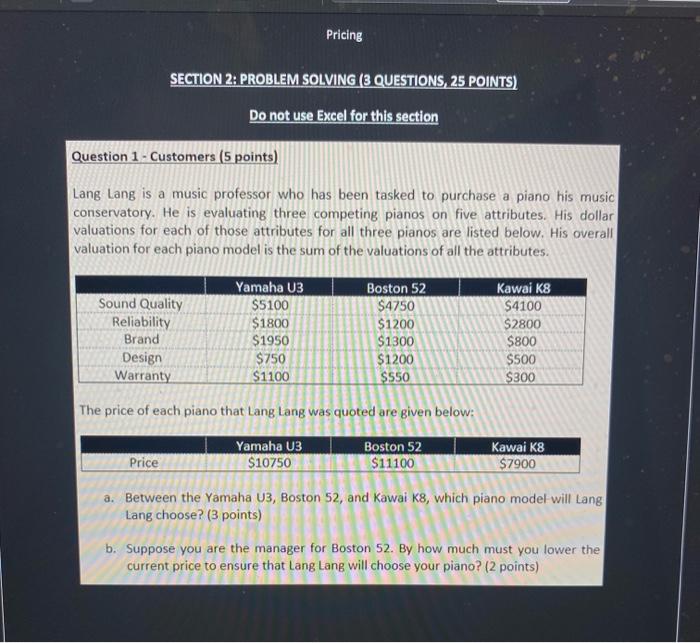
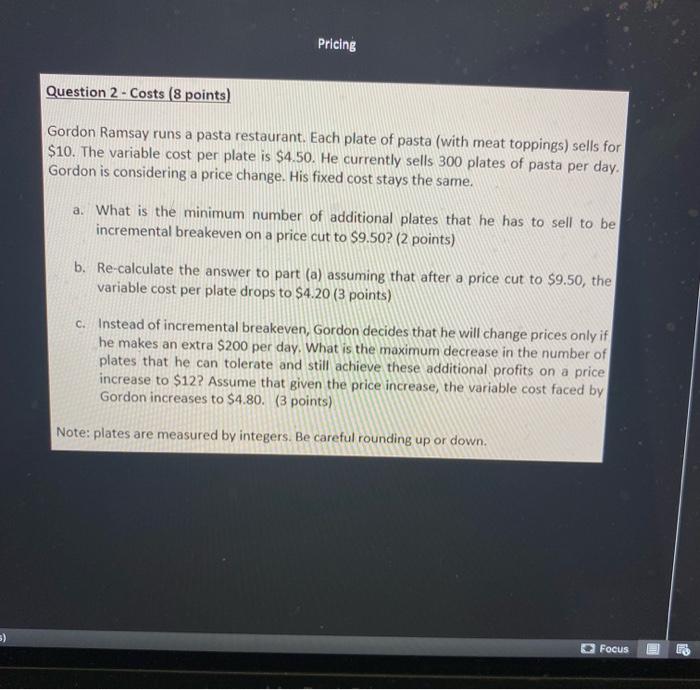
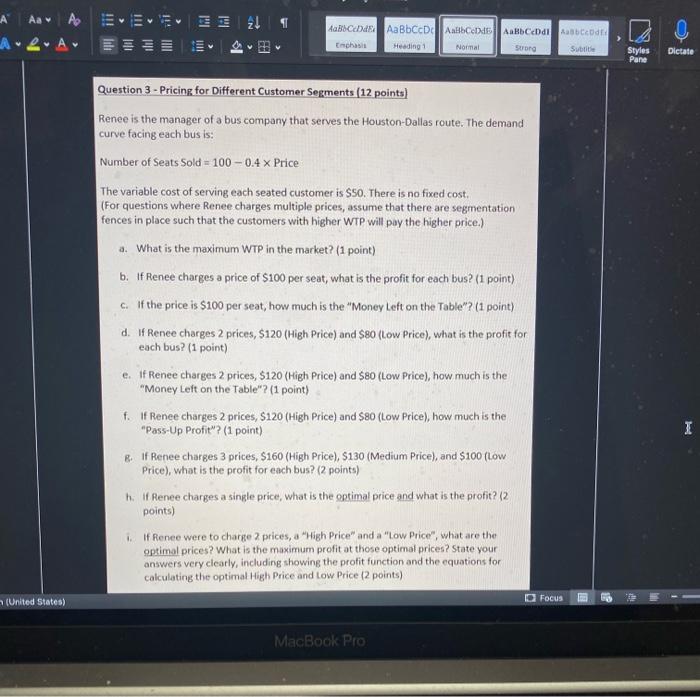
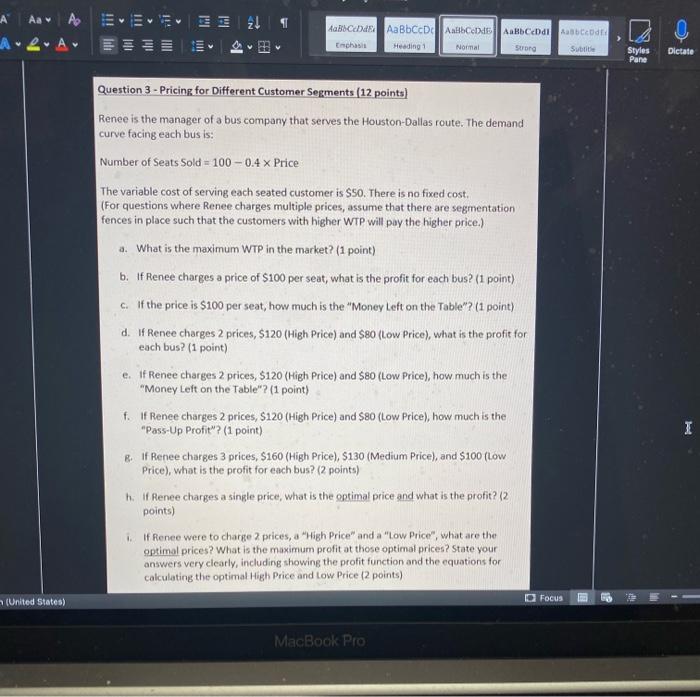
Pricing SECTION 2: PROBLEM SOLVING (3 QUESTIONS, 25 POINTS) Do not use Excel for this section Question 1 - Customers (5 points) Lang Lang is a music professor who has been tasked to purchase a piano his music conservatory. He is evaluating three competing pianos on five attributes. His dollar valuations for each of those attributes for all three pianos are listed below. His overall valuation for each piano model is the sum of the valuations of all the attributes. Sound Quality Reliability Brand Design Warranty Yamaha U3 $S100 $1800 $1950 $750 $1100 Boston 52 $4750 $1200 $1300 $1200 $550 Kawai K8 $4100 $2800 $800 $500 $300 The price of each piano that Lang Lang was quoted are given below: Yamaha U3 $10750 Boston 52 $11100 Kawai K8 $7900 Price a. Between the Yamaha 13, Boston 52, and Kawai K8, which piano model will Lang Lang choose? (3 points) b. Suppose you are the manager for Boston 52. By how much must you lower the current price to ensure that Lang Lang will choose your piano? (2 points) Pricing Question 2 - Costs (8 points) Gordon Ramsay runs a pasta restaurant. Each plate of pasta (with meat toppings) sells for $10. The variable cost per plate is $4.50. He currently sells 300 plates of pasta per day. Gordon is considering a price change. His fixed cost stays the same. a. What is the minimum number of additional plates that he has to sell to be incremental breakeven on a price cut to $9.50? (2 points) b. Re-calculate the answer to part (a) assuming that after a price cut to $9.50, the variable cost per plate drops to $4.20 (3 points) C. Instead of incremental breakeven, Gordon decides that he will change prices only if he makes an extra $200 per day. What is the maximum decrease in the number of plates that he can tolerate and still achieve these additional profits on a price increase to $12? Assume that given the price increase, the variable cost faced by Gordon increases to $4.80. (3 points) Note: plates are measured by integers. Be careful rounding up or down. 5) Focus 2! Aa A ARA OIL Iili ABCD AaBbCcDc Albed | ABCDdl Enchas Heading 1 Normal Strong aber Q > Subtitle Styles Pane Dictate Question 3 - Pricing for Different Customer Segments (12 points) Renee is the manager of a bus company that serves the Houston Dallas route. The demand curve facing each bus is: Number of Seats Sold - 100 -0.4 x Price The variable cost of serving each seated customer is $50. There is no fixed cost. (For questions where Renee charges multiple prices, assume that there are segmentation fences in place such that the customers with higher WTP will pay the higher price.) a. What is the maximum WTP in the market? (1 point) b. If Renee charges a price of $100 per seat, what is the profit for each bus? (1 point) c. If the price is $100 per seat, how much is the "Money Left on the Table"? (1 point) d. If Renee charges 2 prices, $120 (High Price) and $80 (Low Price), what is the profit for each bus? (1 point) e. if Renee charges 2 prices, $120 (High Price) and $80 (Low Price), how much is the "Money Left on the Table"? (1 point) f. If Renee charges 2 prices, $120 (High Price) and $80 (Low Price), how much is the "Pass-Up Profit"? (1 point) B. If Renee charges 3 prices, $160 (High Price), 5130 (Medium Price), and $100 (Low Price), what is the profit for each bus? (2 points) t: If Renee charges a single price, what is the optimal price and what is the profit? (2 points) If Renee were to charge 2 prices, a "High Price and a "Low Price", what are the optimal prices? What is the maximum profit at those optimal prices? State your answers very clearly, including showing the profit function and the equations for calculating the optimal High Price and Low Price (2 points) I (United States) Focus MacBook Pro 2! Aa A ARA OIL Iili ABCD AaBbCcDc Albed | ABCDdl Enchas Heading 1 Normal Strong aber Q > Subtitle Styles Pane Dictate Question 3 - Pricing for Different Customer Segments (12 points) Renee is the manager of a bus company that serves the Houston Dallas route. The demand curve facing each bus is: Number of Seats Sold - 100 -0.4 x Price The variable cost of serving each seated customer is $50. There is no fixed cost. (For questions where Renee charges multiple prices, assume that there are segmentation fences in place such that the customers with higher WTP will pay the higher price.) a. What is the maximum WTP in the market? (1 point) b. If Renee charges a price of $100 per seat, what is the profit for each bus? (1 point) c. If the price is $100 per seat, how much is the "Money Left on the Table"? (1 point) d. If Renee charges 2 prices, $120 (High Price) and $80 (Low Price), what is the profit for each bus? (1 point) e. if Renee charges 2 prices, $120 (High Price) and $80 (Low Price), how much is the "Money Left on the Table"? (1 point) f. If Renee charges 2 prices, $120 (High Price) and $80 (Low Price), how much is the "Pass-Up Profit"? (1 point) B. If Renee charges 3 prices, $160 (High Price), 5130 (Medium Price), and $100 (Low Price), what is the profit for each bus? (2 points) t: If Renee charges a single price, what is the optimal price and what is the profit? (2 points) If Renee were to charge 2 prices, a "High Price and a "Low Price", what are the optimal prices? What is the maximum profit at those optimal prices? State your answers very clearly, including showing the profit function and the equations for calculating the optimal High Price and Low Price (2 points) I (United States) Focus MacBook Pro Pricing SECTION 2: PROBLEM SOLVING (3 QUESTIONS, 25 POINTS) Do not use Excel for this section Question 1 - Customers (5 points) Lang Lang is a music professor who has been tasked to purchase a piano his music conservatory. He is evaluating three competing pianos on five attributes. His dollar valuations for each of those attributes for all three pianos are listed below. His overall valuation for each piano model is the sum of the valuations of all the attributes. Sound Quality Reliability Brand Design Warranty Yamaha U3 $S100 $1800 $1950 $750 $1100 Boston 52 $4750 $1200 $1300 $1200 $550 Kawai K8 $4100 $2800 $800 $500 $300 The price of each piano that Lang Lang was quoted are given below: Yamaha U3 $10750 Boston 52 $11100 Kawai K8 $7900 Price a. Between the Yamaha 13, Boston 52, and Kawai K8, which piano model will Lang Lang choose? (3 points) b. Suppose you are the manager for Boston 52. By how much must you lower the current price to ensure that Lang Lang will choose your piano? (2 points) Pricing Question 2 - Costs (8 points) Gordon Ramsay runs a pasta restaurant. Each plate of pasta (with meat toppings) sells for $10. The variable cost per plate is $4.50. He currently sells 300 plates of pasta per day. Gordon is considering a price change. His fixed cost stays the same. a. What is the minimum number of additional plates that he has to sell to be incremental breakeven on a price cut to $9.50? (2 points) b. Re-calculate the answer to part (a) assuming that after a price cut to $9.50, the variable cost per plate drops to $4.20 (3 points) C. Instead of incremental breakeven, Gordon decides that he will change prices only if he makes an extra $200 per day. What is the maximum decrease in the number of plates that he can tolerate and still achieve these additional profits on a price increase to $12? Assume that given the price increase, the variable cost faced by Gordon increases to $4.80. (3 points) Note: plates are measured by integers. Be careful rounding up or down. 5) Focus 2! Aa A ARA OIL Iili ABCD AaBbCcDc Albed | ABCDdl Enchas Heading 1 Normal Strong aber Q > Subtitle Styles Pane Dictate Question 3 - Pricing for Different Customer Segments (12 points) Renee is the manager of a bus company that serves the Houston Dallas route. The demand curve facing each bus is: Number of Seats Sold - 100 -0.4 x Price The variable cost of serving each seated customer is $50. There is no fixed cost. (For questions where Renee charges multiple prices, assume that there are segmentation fences in place such that the customers with higher WTP will pay the higher price.) a. What is the maximum WTP in the market? (1 point) b. If Renee charges a price of $100 per seat, what is the profit for each bus? (1 point) c. If the price is $100 per seat, how much is the "Money Left on the Table"? (1 point) d. If Renee charges 2 prices, $120 (High Price) and $80 (Low Price), what is the profit for each bus? (1 point) e. if Renee charges 2 prices, $120 (High Price) and $80 (Low Price), how much is the "Money Left on the Table"? (1 point) f. If Renee charges 2 prices, $120 (High Price) and $80 (Low Price), how much is the "Pass-Up Profit"? (1 point) B. If Renee charges 3 prices, $160 (High Price), 5130 (Medium Price), and $100 (Low Price), what is the profit for each bus? (2 points) t: If Renee charges a single price, what is the optimal price and what is the profit? (2 points) If Renee were to charge 2 prices, a "High Price and a "Low Price", what are the optimal prices? What is the maximum profit at those optimal prices? State your answers very clearly, including showing the profit function and the equations for calculating the optimal High Price and Low Price (2 points) I (United States) Focus MacBook Pro 2! Aa A ARA OIL Iili ABCD AaBbCcDc Albed | ABCDdl Enchas Heading 1 Normal Strong aber Q > Subtitle Styles Pane Dictate Question 3 - Pricing for Different Customer Segments (12 points) Renee is the manager of a bus company that serves the Houston Dallas route. The demand curve facing each bus is: Number of Seats Sold - 100 -0.4 x Price The variable cost of serving each seated customer is $50. There is no fixed cost. (For questions where Renee charges multiple prices, assume that there are segmentation fences in place such that the customers with higher WTP will pay the higher price.) a. What is the maximum WTP in the market? (1 point) b. If Renee charges a price of $100 per seat, what is the profit for each bus? (1 point) c. If the price is $100 per seat, how much is the "Money Left on the Table"? (1 point) d. If Renee charges 2 prices, $120 (High Price) and $80 (Low Price), what is the profit for each bus? (1 point) e. if Renee charges 2 prices, $120 (High Price) and $80 (Low Price), how much is the "Money Left on the Table"? (1 point) f. If Renee charges 2 prices, $120 (High Price) and $80 (Low Price), how much is the "Pass-Up Profit"? (1 point) B. If Renee charges 3 prices, $160 (High Price), 5130 (Medium Price), and $100 (Low Price), what is the profit for each bus? (2 points) t: If Renee charges a single price, what is the optimal price and what is the profit? (2 points) If Renee were to charge 2 prices, a "High Price and a "Low Price", what are the optimal prices? What is the maximum profit at those optimal prices? State your answers very clearly, including showing the profit function and the equations for calculating the optimal High Price and Low Price (2 points) I (United States) Focus MacBook Pro
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


