Question: Principle 1: A value not in the confidence interval can be rejected as a possible value of the population parameter. A value in the confidence

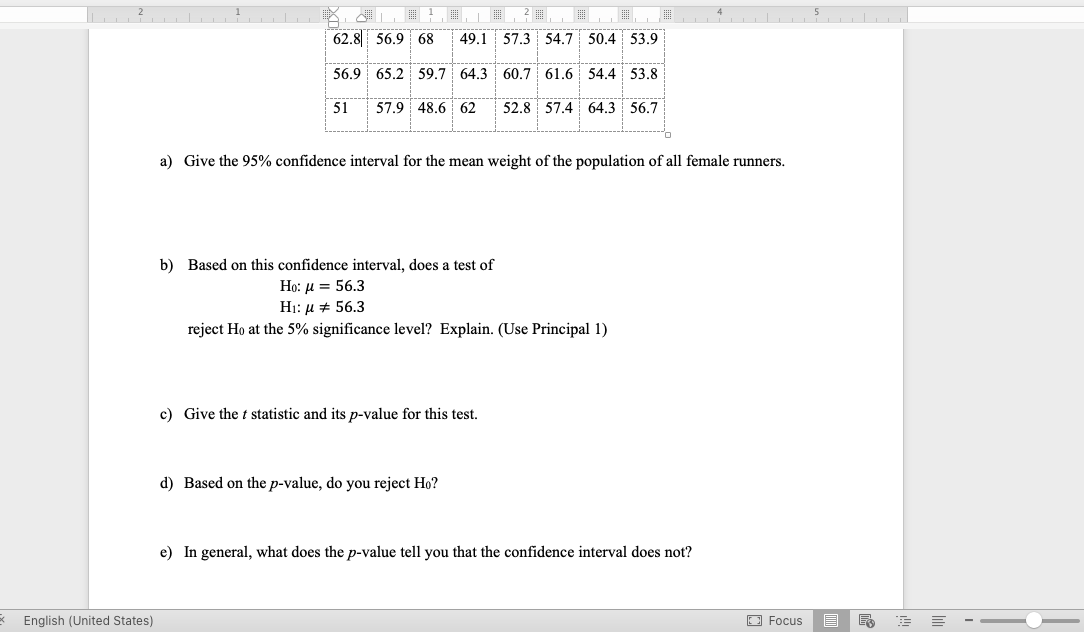
Principle 1: A value not in the confidence interval can be rejected as a possible value of the population parameter. A value in the confidence interval is an "acceptable" possibility for the value of a population parameter. Principle 2: When the confidence intervals in two different populations do not overlap, it is reasonable to conclude that the two populations are different. 1. Exercise Gear. A company sells exercise clothing and equipment on the Internet. To design clothing, data on physical characteristics of different types of customers is collected. The weight, in kilograms, of 24 female randomly selected runners are recorded: 62.8 56.9 6 49.1 57.3 54.7 50.4 53.9 56.9 65.2 59.7 64.3 60.7 61.6 6 54.4 53.8 51 57.9 48.6 62 52.8 57.4 1 64.3 56.7 a) Give the 95% confidence interval for the mean weight of the population of all female runners. b) Based on this confidence interval, does a test of Ho: H = 56.3 HI: M # 56.3 reject Ho at the 5% significance level? Explain. (Use Principal 1) English (United States) Focus E -62.8 56.9 68 49.1 57.3 54.7 : 50.4 53.9 56.9 65.2 59.7 64.3 60.7 61.6 54.4 53.8 51 57.9 48.6 62 52.8 57.4 64.3 56.7 a) Give the 95% confidence interval for the mean weight of the population of all female runners. b) Based on this confidence interval, does a test of Ho: / = 56.3 Hi: u # 56.3 reject Ho at the 5% significance level? Explain. (Use Principal 1) c) Give the t statistic and its p-value for this test. d) Based on the p-value, do you reject Ho? e) In general, what does the p-value tell you that the confidence interval does not? English (United States) Focus E
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


