Question: Prior to beginning work on this assignment, read Chapter 4 and review Case 4 - 1 Jaguar Land Rover PLC in your course text. Complete
Prior to beginning work on this assignment, read Chapter and review Case Jaguar Land Rover PLC in your course text.
Complete Requirements and of the case. Summarize your results and conclusions supporting your conclusions with key concepts from the weekly reading including:
Comparison of the capitalization ratios of JLR with those of German automakers profiled in Exhibit in the textbook.
Evaluation of capitalized product development costs including an analysis of the accounting policy footnote disclosures.
Discussion of key financial statements figures presented under the requirements of US GAAP compared with the figures presented using IFRS.
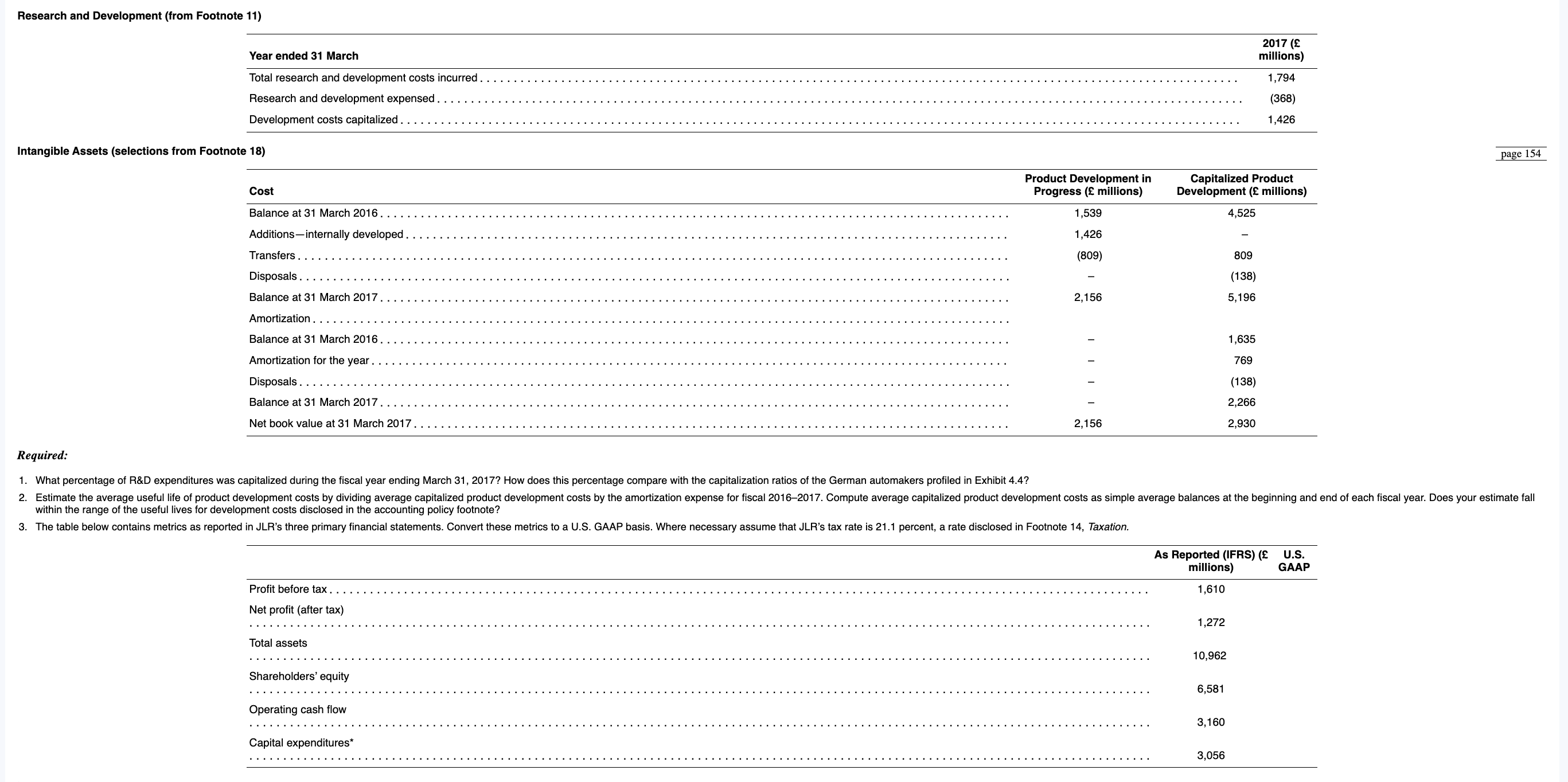
Requirement : What percentage of R&D expenditures was capitalized during the fiscal year ending March How does this percentage compare with the capitalization ratios of the German automakers profiled in Exhibit
Requirement : Estimate the average useful life of product development costs by dividing average capitalized product development costs by the amortization expense for fiscal Compute average capitalized product development costs as simple average balances at the beginning and end of each fiscal year. Does your estimate fall within the range of the useful lives for development costs disclosed in the accounting policy footnote?
Requirement ; The table below contains metrics as reported in JLRs three primary financial statements. Convert these metrics to a US GAAP basis. Where necessary assume that JLRs tax rate is percent, a rate disclosed in Footnote Taxation.
Case
Jaguar Land Rover Automotive PLC JLR is a maker of luxury autos based in Coventry, United Kingdom. JLR uses IFRS and has a fiscal yearend of March You have been asked to use your knowledge of IFRS to convert key metrics for the company to a US GAAP basis. For simplicity, you may assume that the only material differences between JLRs asreported numbers and those it would report under US GAAP are traceable to its policy of capitalizing development costs.
Internally Generated Intangible Assets from Footnote Accounting Policies
Research costs are charged to the consolidated income statement in the year in which they are incurred. Product development costs incurred on new vehicle platforms, engines, transmission and new products are recognised as intangible assetswhen feasibility has been established, the Group has committed technical, financial and other resources to complete the development and it is probable that the asset will generate future economic benefits. The costs capitalised include the cost of materials, direct labour and directly attributable overhead expenditure incurred up to the date the asset is available for use. Interest cost incurred is capitalised up to the date the asset is ready for its intended use, based on borrowings incurred specifically for financing the asset or the weighted average rate of all other borrowings, if no specific borrowings have been incurred for the asset. Product development cost is amortised over a period of between two and ten years. Capitalised development expenditure is measured at cost less accumulated amortisation and accumulated impairment loss, if any. Amortisation is not recorded on product development in progress until development is complete.Research and Development from Footnote
Intangible Assets selections from Footnote
Required:
What percentage of R&D expenditures was capitalized during the fiscal year ending March How does this percentage compare with the capitalization ratios of the German automakers profiled in Exhibit
within the range of the useful lives for development costs disclosed in the accounting policy footnote?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


