Question: Problem 1 (10 points) Calculate Fg for a 1-2 exchanger with z =1 and nu = 0.5, then check your answer with the value from

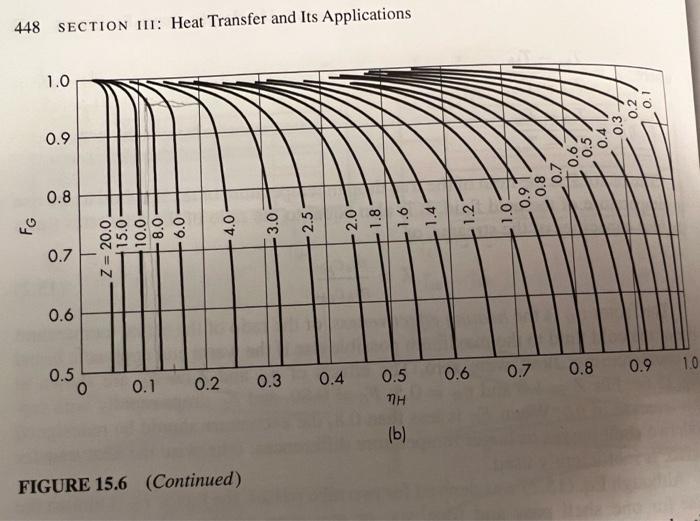

Problem 1 (10 points) Calculate Fg for a 1-2 exchanger with z =1 and nu = 0.5, then check your answer with the value from Fig. 15.6. Using Eq. (15.1), you will have zero in the denominator that your value will be indeterminate. Therefore, calculate FG at z = 0.99 and at z=1.01, then interpolate. 448 SECTION IT: Heat Transfer and Its Applications 1.0 0.9 0.8 1.0 FG 0.7 15.0 10.0 - 8.0 - 6.0 Z = 20.0 0.6 0.5 0.9 1.0 0.3 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.1 0.2 0.4 0.5 0 TH (b) FIGURE 15.6 (Continued) FIGURE 15.5 Temperature-length curves: (a) passes. shell. The hotter pass of the shell-side fluid is in thermal contact with the two hottest tube-side passes and the cooler shell-side pass with the two coolest tube-side The exchanger as a whole approximates a true countercurrent unit more closely than is possible with a 1-2 exchanger. Correction of LMTD in multipass exchangers The LMTD as given by Eq. (11.15) does not apply to the exchanger as a whole, LMTD. The reason is that the AT for each tube pass is not a linear function of the heat transferred, as was assumed in the derivation of Eq. (11.15). It is customary to define a correction factor Fg by which the LMTD must be multiplied to get a com rect average driving force. If the overall heat transfer coefficient and the specific heats are constant, and all elements of a given fluid have the same thermal history in passing through the exchanger, Fg can be calculated from the equationsa a Fo 1- (Z2 + 1)12 In 1 - 2 - (Z +1-(Z2 + 1)/2) (Z - 1) In 2-N (+ 1 + (Z2 + 1)1/2) (15.1)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


