Question: Problem 1: Assume planar motion, a disk with radius R is spinning about an axis passing through point A. Point P acts as a pendulum
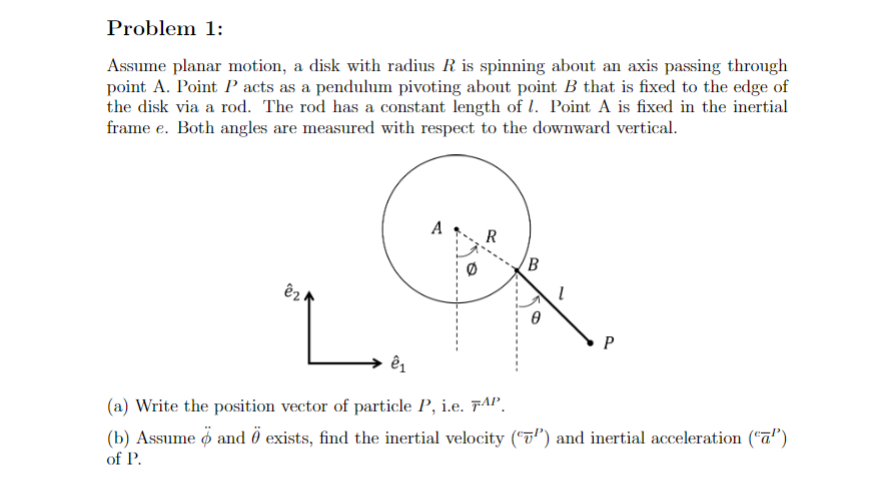
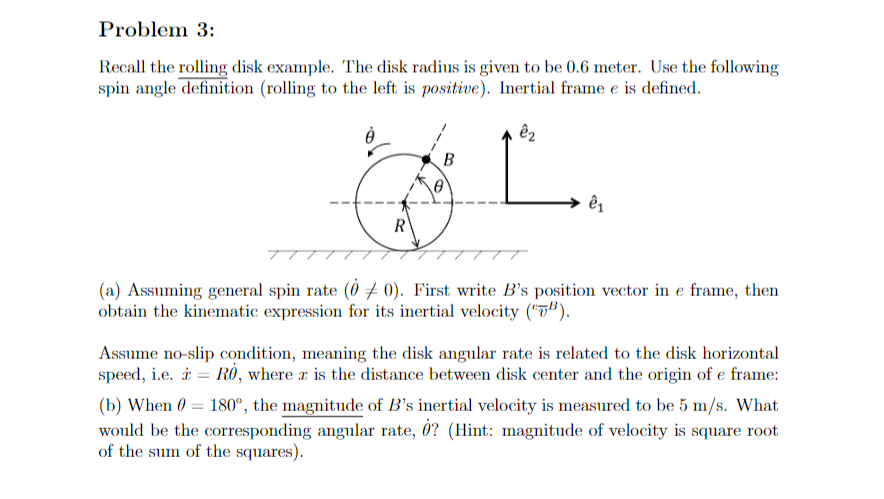
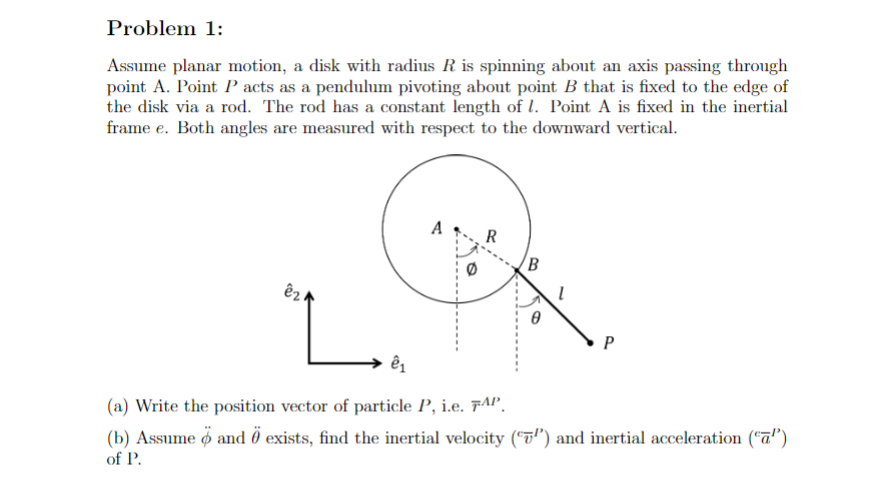
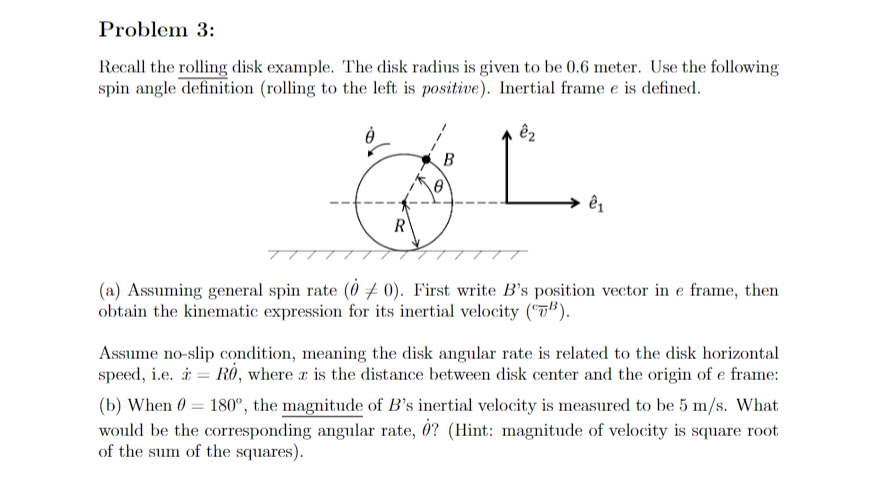
Problem 1: Assume planar motion, a disk with radius R is spinning about an axis passing through point A. Point P acts as a pendulum pivoting about point B that is fixed to the edge of the disk via a rod. The rod has a constant length of . Point A is fixed in the inertial frame e. Both angles are measured with respect to the downward vertical. A R B eza P 21 (a) Write the position vector of particle P, i.e. FAP. (b) Assume o and 0 exists, find the inertial velocity (") and inertial acceleration ("a") of P.Problem 3: Recall the rolling disk example. The disk radius is given to be 0.6 meter. Use the following spin angle definition (rolling to the left is positive). Inertial frame e is defined. B R (a) Assuming general spin rate (0 / 0). First write B's position vector in e frame, then obtain the kinematic expression for its inertial velocity (7"). Assume no-slip condition, meaning the disk angular rate is related to the disk horizontal speed, i.e. x = R0, where a is the distance between disk center and the origin of e frame: (b) When 0 = 180", the magnitude of B's inertial velocity is measured to be 5 m/s. What would be the corresponding angular rate, 0? (Hint: magnitude of velocity is square root of the sum of the squares)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


