Question: Problem 1: In this exercise, we look at how software techniques can extract instruction-level parallelism (ILP) in a common vector loop. The following loop
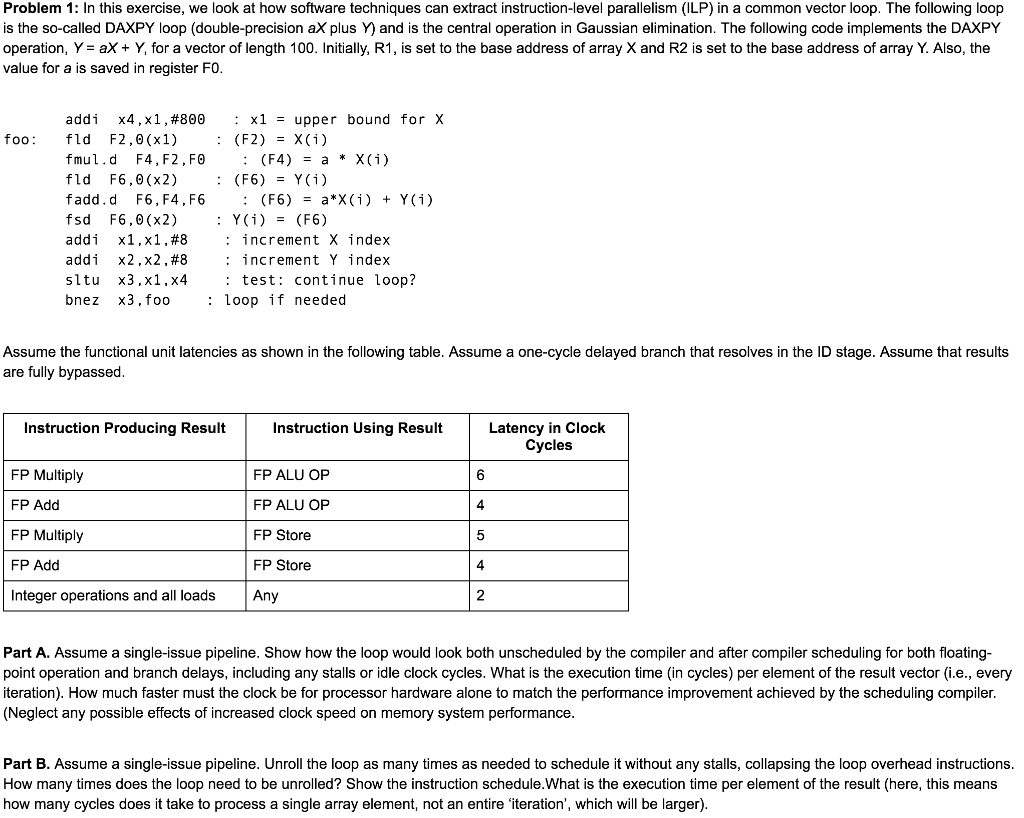
Problem 1: In this exercise, we look at how software techniques can extract instruction-level parallelism (ILP) in a common vector loop. The following loop is the so-called DAXPY loop (double-precision aX plus Y) and is the central operation in Gaussian elimination. The following code implements the DAXPY operation, Y = ax + Y, for a vector of length 100. Initially, R1, is set to the base address of array X and R2 is set to the base address of array Y. Also, the value for a is saved in register FO. addi x4,x1, # 800 x1 upper bound for X foo: fld F2,0(x1) : fmul.d F4, F2,F0 fld F6,0(x2) : (F6) = Y(i) fadd.d F6, F4, F6 fsd F6,0(x2) : Y(i) = (F6) addi x1,x1,#8 addi x2,x2,#8 sltu x3,x1,x4 bnez x3,foo (F2) = X(1) (F4) = a * X(i) : (F6) = a*X(i) + Y(i) increment X index increment Y index test: continue loop? loop if needed Assume the functional unit latencies as shown in the following table. Assume a one-cycle delayed branch that resolves in the ID stage. Assume that results are fully bypassed. Instruction Producing Result Instruction Using Result Latency in Clock Cycles FP Multiply FP ALU OP 6 FP Add FP ALU OP 4 FP Multiply FP Store 5 FP Add Integer operations and all loads FP Store Any 4 2 Part A. Assume a single-issue pipeline. Show how the loop would look both unscheduled by the compiler and after compiler scheduling for both floating- point operation and branch delays, including any stalls or idle clock cycles. What is the execution time (in cycles) per element of the result vector (i.e., every iteration). How much faster must the clock be for processor hardware alone to match the performance improvement achieved by the scheduling compiler. (Neglect any possible effects of increased clock speed on memory system performance. Part B. Assume a single-issue pipeline. Unroll the loop as many times as needed to schedule it without any stalls, collapsing the loop overhead instructions. How many times does the loop need to be unrolled? Show the instruction schedule. What is the execution time per element of the result (here, this means how many cycles does it take to process a single array element, not an entire 'iteration', which will be larger).
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
It seems there are still no ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


