Question: Problem 2: Decision Analysis -- Comparing Automobile Leases You are interested in leasing a Honda Accord. There are three local car dealers that are offering
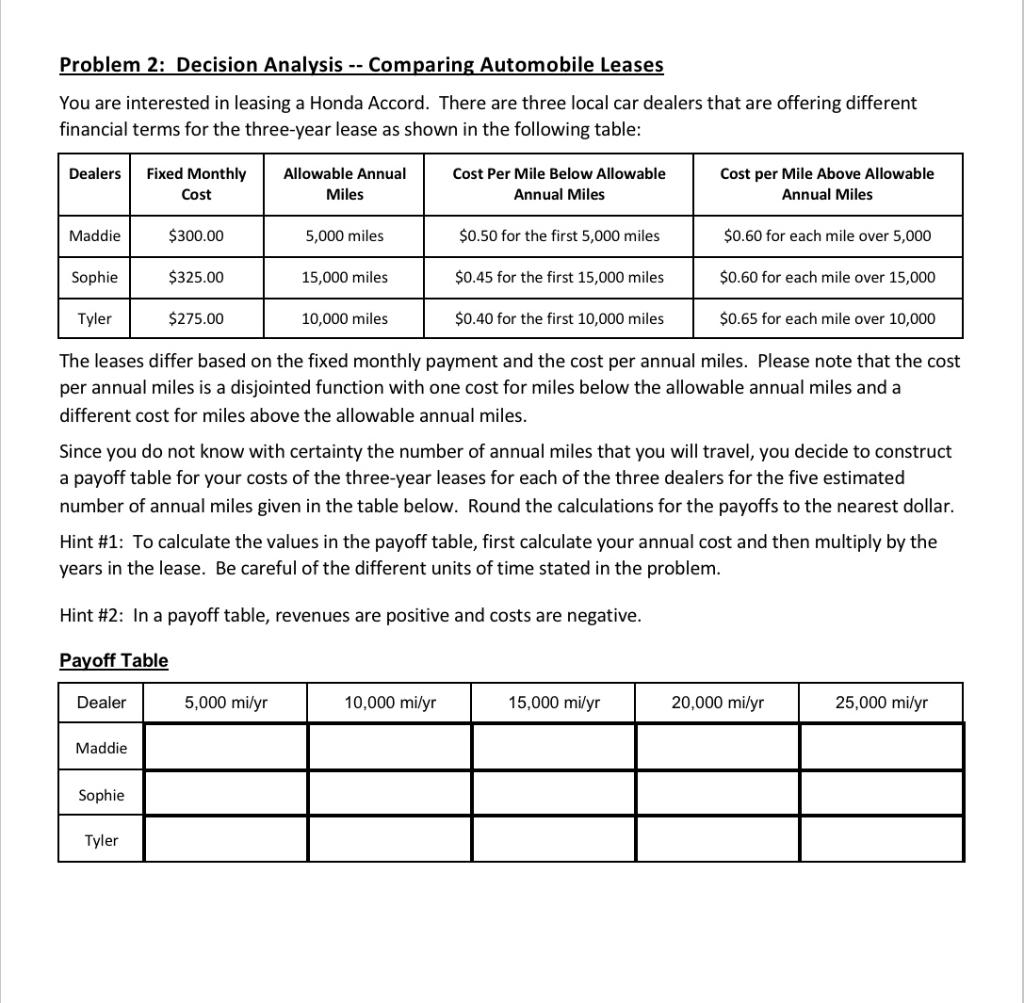
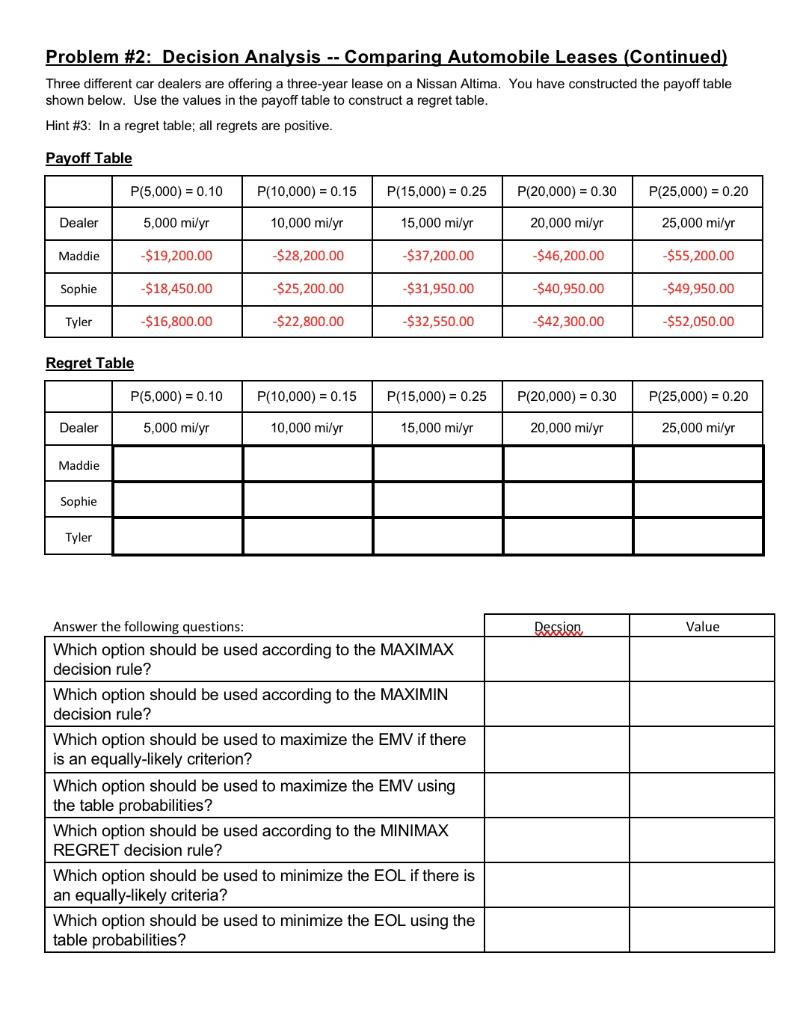
Problem 2: Decision Analysis -- Comparing Automobile Leases You are interested in leasing a Honda Accord. There are three local car dealers that are offering different financial terms for the three-year lease as shown in the following table: Dealers Fixed Monthly Cost Allowable Annual Miles Cost Per Mile Below Allowable Annual Miles Cost per Mile Above Allowable Annual Miles Maddie $300.00 5,000 miles $0.50 for the first 5,000 miles $0.60 for each mile over 5,000 Sophie $325.00 15,000 miles $0.45 for the first 15,000 miles $0.60 for each mile over 15,000 Tyler $275.00 10,000 miles $0.40 for the first 10,000 miles $0.65 for each mile over 10,000 The leases differ based on the fixed monthly payment and the cost per annual miles. Please note that the cost per annual miles is a disjointed function with one cost for miles below the allowable annual miles and a different cost for miles above the allowable annual miles. Since you do not know with certainty the number of annual miles that you will travel, you decide to construct a payoff table for your costs of the three-year leases for each of the three dealers for the five estimated number of annual miles given in the table below. Round the calculations for the payoffs to the nearest dollar. Hint #1: To calculate the values in the payoff table, first calculate your annual cost and then multiply by the years in the lease. Be careful of the different units of time stated in the problem. Hint #2: In a payoff table, revenues are positive and costs are negative. Payoff Table Dealer 5,000 mi/yr 10,000 mi/yr 15,000 mi/yr 20,000 mi/yr 25,000 mi/yr Maddie Sophie Tyler Problem #2: Decision Analysis -- Comparing Automobile Leases (Continued) Three different car dealers are offering a three-year lease on a Nissan Altima. You have constructed the payoff table shown below. Use the values in the payoff table to construct a regret table. Hint #3: In a regret table; all regrets are positive. Payoff Table P(5,000) = 0.10 P(10,000) = 0.15 P(15,000) = 0.25 P(20,000) = 0.30 P(25,000) = 0.20 Dealer 5,000 mily 10,000 mi/yr 15,000 mi/yr 20,000 mi/yr 25,000 mily Maddie $19,200.00 $28,200.00 $37,200.00 $46,200.00 -$55,200.00 Sophie -$18,450.00 $25,200.00 $31,950.00 $40,950.00 $49,950.00 Tyler $16,800.00 -$22,800.00 $32,550.00 -$42,300.00 -$52,050.00 Regret Table P(5,000) = 0.10 P(10,000) = 0.15 P(15,000) = 0.25 P(20,000) = 0.30 P(25,000) = 0.20 Dealer 5,000 mi/yr 10,000 mi/yr 15,000 mi/yr 20,000 mi/yr 25,000 mi/yr Maddie Sophie Tyler Dession Value Answer the following questions: Which option should be used according to the MAXIMAX decision rule? Which option should be used according to the MAXIMIN decision rule? Which option should be used to maximize the EMV if there is an equally-likely criterion? Which option should be used to maximize the EMV using the table probabilities? Which option should be used according to the MINIMAX REGRET decision rule? Which option should be used to minimize the EOL if there is an equally-likely criteria? Which option should be used to minimize the EOL using the table probabilities






