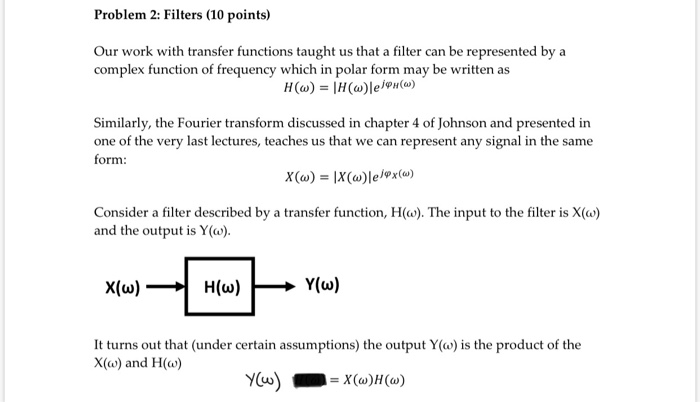
Question: Problem 2: Filters (10 points) Our work with transfer functions taught us that a filter can be represented by a complex function of frequency which

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


