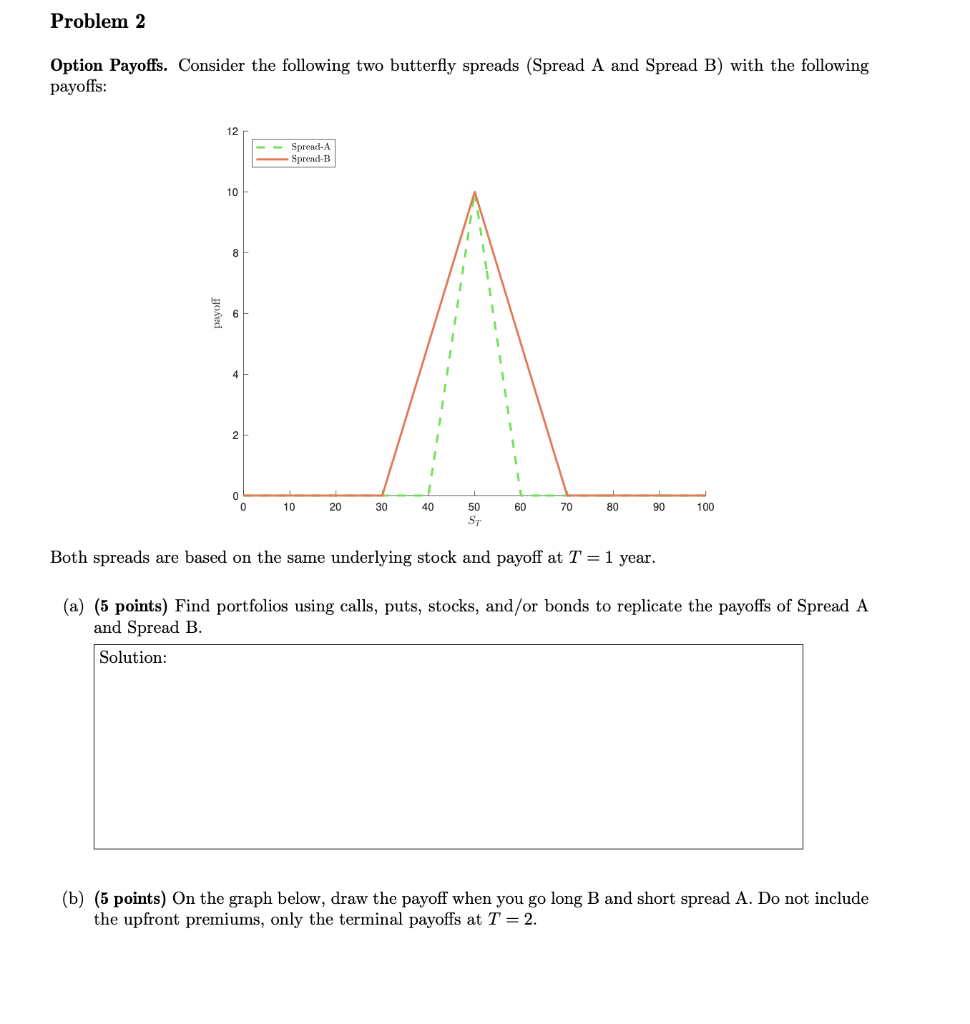
Question: Problem 2 has no other given details Problem 2 Option Payoffs. Consider the following two butterfly spreads (Spread A and Spread B) with the following
Problem 2 has no other given details
Problem 2 Option Payoffs. Consider the following two butterfly spreads (Spread A and Spread B) with the following payoffs: 12 Spread-A Spread-B 10 8 1 6 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4 2 1 0 0 10 20 30 40 60 70 80 90 100 50 ST Both spreads are based on the same underlying stock and payoff at T = 1 year. (a) (5 points) Find portfolios using calls, puts, stocks, and/or bonds to replicate the payoffs of Spread A and Spread B. Solution: (b) (5 points) On the graph below, draw the payoff when you go long B and short spread A. Do not include the upfront premiums, only the terminal payoffs at T = 2. Solution: 20 15 10 payoffr -10 0 10 20 30 40 60 70 80 90 100 50 ST (c) (5 points) Suppose that the price of spread B is lower than the price of spread A. Explain how you can construct an arbitrage. Solution: Problem 3 Binomial Pricing Model. Suppose that a a stock is currently selling for So = $150 and next year will either rise to Su = $220 or fall to Sa = $120. So = 150 - Su = 220 Sd = 120 The one year interest rate is 5%/year (EAR). The cost of capital of the stock is 10%. Problem 2 Option Payoffs. Consider the following two butterfly spreads (Spread A and Spread B) with the following payoffs: 12 Spread-A Spread-B 10 8 1 6 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4 2 1 0 0 10 20 30 40 60 70 80 90 100 50 ST Both spreads are based on the same underlying stock and payoff at T = 1 year. (a) (5 points) Find portfolios using calls, puts, stocks, and/or bonds to replicate the payoffs of Spread A and Spread B. Solution: (b) (5 points) On the graph below, draw the payoff when you go long B and short spread A. Do not include the upfront premiums, only the terminal payoffs at T = 2. Solution: 20 15 10 payoffr -10 0 10 20 30 40 60 70 80 90 100 50 ST (c) (5 points) Suppose that the price of spread B is lower than the price of spread A. Explain how you can construct an arbitrage. Solution: Problem 3 Binomial Pricing Model. Suppose that a a stock is currently selling for So = $150 and next year will either rise to Su = $220 or fall to Sa = $120. So = 150 - Su = 220 Sd = 120 The one year interest rate is 5%/year (EAR). The cost of capital of the stock is 10%
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


