Question: Problem 2 : Species A diffuses into a cylindrical pore where it reacts at the cylindrical surface to produce B(AB) according to a zero order
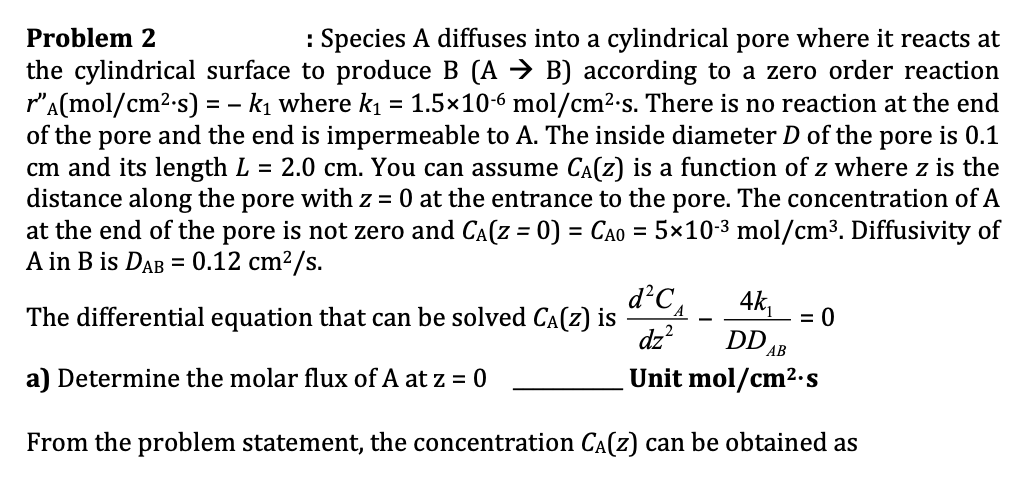

Problem 2 : Species A diffuses into a cylindrical pore where it reacts at the cylindrical surface to produce B(AB) according to a zero order reaction rA(mol/cm2s)=k1 where k1=1.5106mol/cm2s. There is no reaction at the end of the pore and the end is impermeable to A. The inside diameter D of the pore is 0.1 cm and its length L=2.0cm. You can assume CA(z) is a function of z where z is the distance along the pore with z=0 at the entrance to the pore. The concentration of A at the end of the pore is not zero and CA(z=0)=CA0=5103mol/cm3. Diffusivity of A in B is DAB=0.12cm2/s. The differential equation that can be solved CA(z) is dz2d2CADDAB4k1=0 a) Determine the molar flux of A at z=0 Unit mol/cm.s From the problem statement, the concentration CA(z) can be obtained as CA(z)=Cz2+C1z+C2 where z is in cm b) C (numerical value with units) = c) C1 (numerical value with units) = d) C2 (numerical value with units) =
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


