Question: Problem 2.5. Assume your wavefunction is defined by a sum of N sine waves, called a Fourier series, e.g. (x)=n=0NAncos(n2cx+n) where An is the amplitude
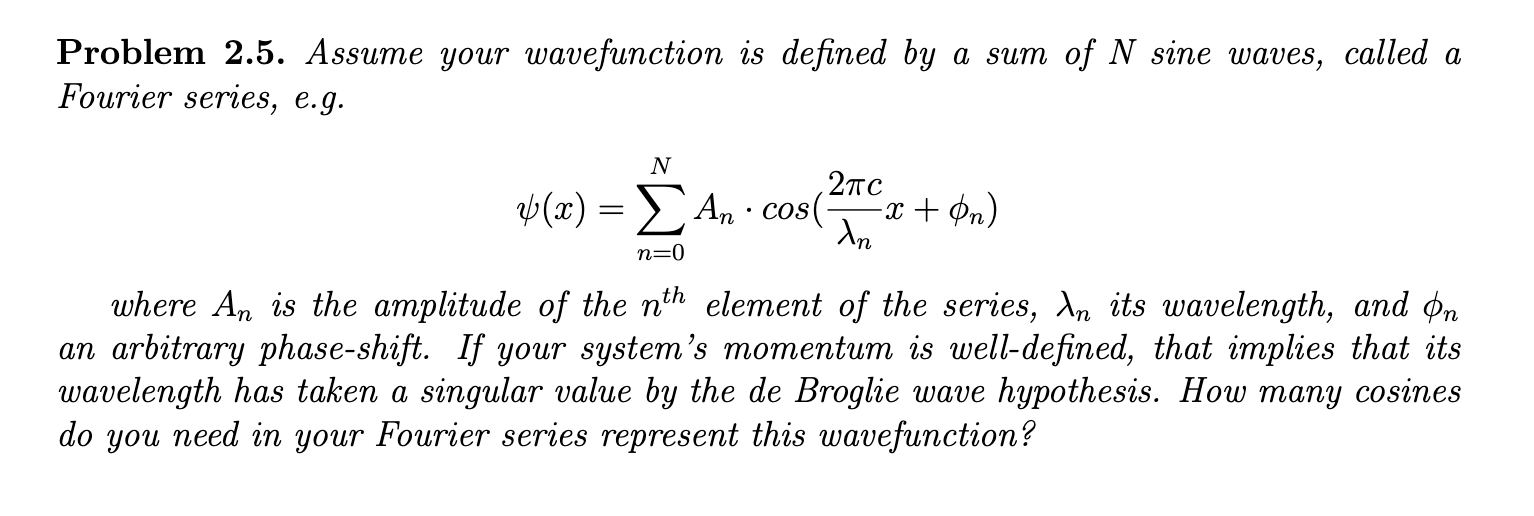
Problem 2.5. Assume your wavefunction is defined by a sum of N sine waves, called a Fourier series, e.g. (x)=n=0NAncos(n2cx+n) where An is the amplitude of the nth element of the series, n its wavelength, and n an arbitrary phase-shift. If your system's momentum is well-defined, that implies that its wavelength has taken a singular value by the de Broglie wave hypothesis. How many cosines do you need in your Fourier series represent this wavefunction
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


