Question: Problem 3. (1D Interval) Define a data type Interval in interval.py that represents a closed 1D interval. The data type must support the following API:

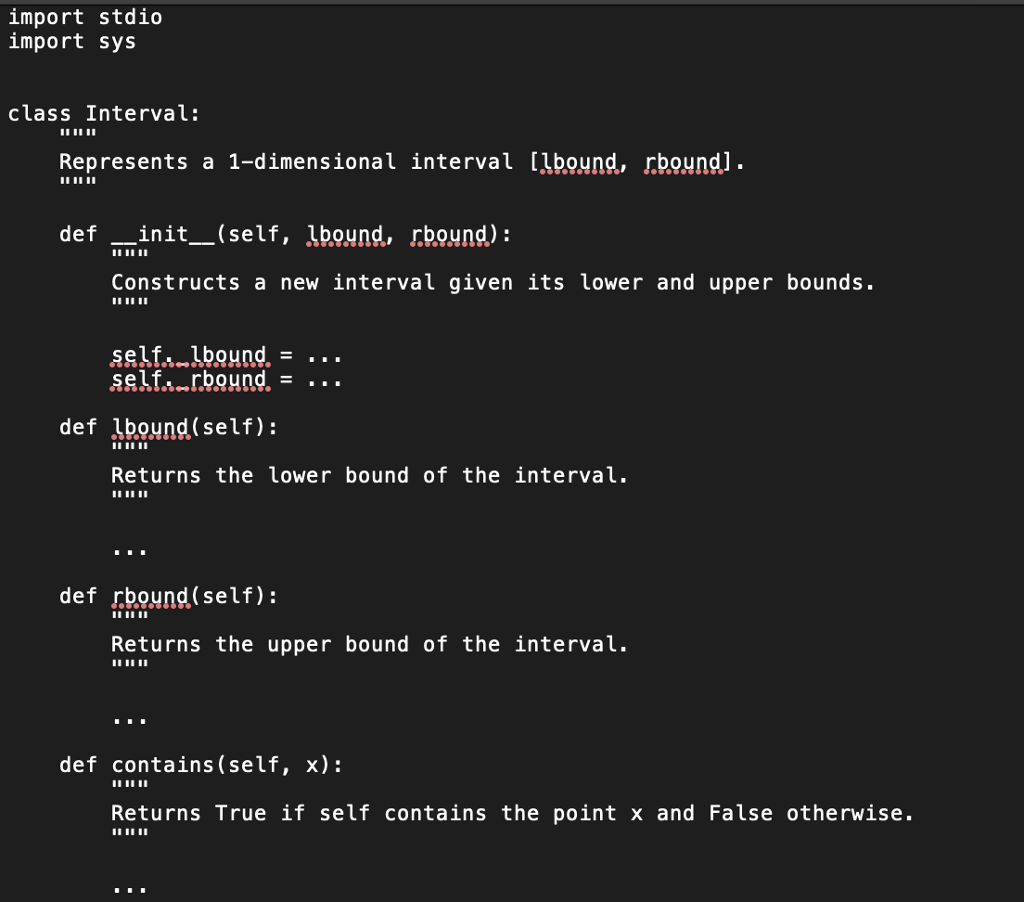
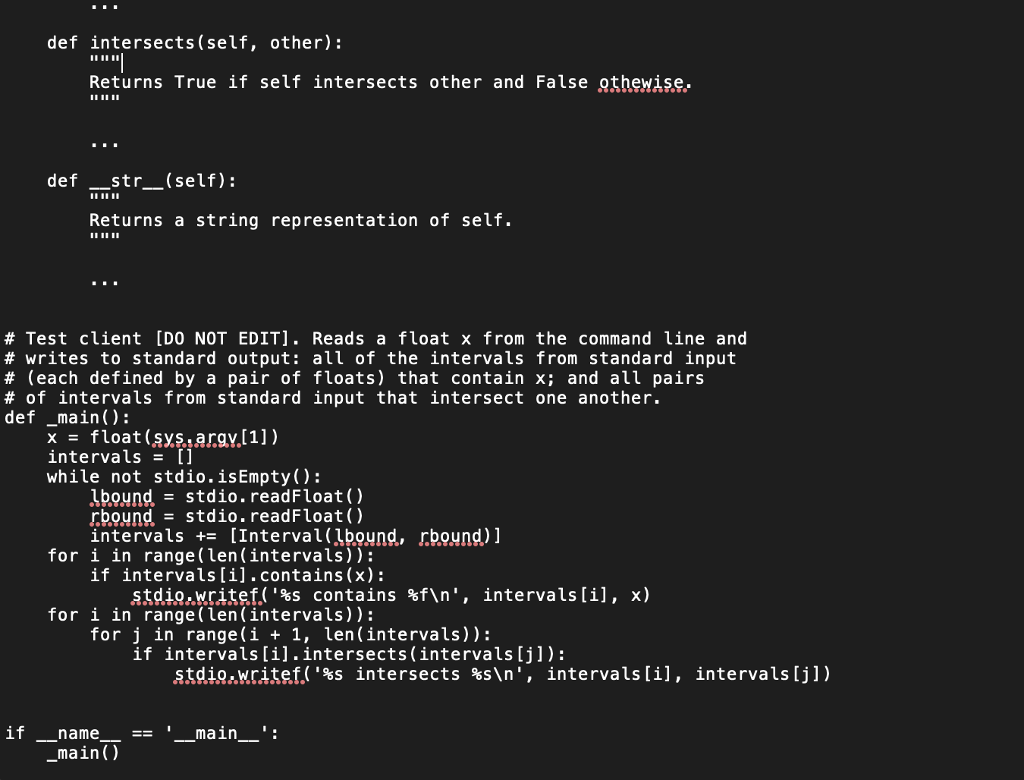
Problem 3. (1D Interval) Define a data type Interval in interval.py that represents a closed 1D interval. The data type must support the following API: method Interval(lbound, rbound) i.1boundO i .ubound) i.contains (x) i.intersects (j) str(i) description a new interval i from the given lower and upper bounds for the interval lower bound of i upper bound of i does i contain the point ? does i intersect the interval i? the string representation of i as [1bound, rbound] $ python3 interval.py 3.14 0 1 0.5 1.5 1 2 1.5 2.5 2.5 3.5 3 4 [2.5, 3.5] contains 3.140000 [3.0, 4.0] contains 3.140000 [0.0, 1.0] intersects [0.5, 1.5] [0.0, 1.0] intersects [1.0, 2.0] [0.5, 1.5] intersects [1.0, 2.0] [0.5, 1.5] intersects [1.5, 2.5.] [1.0, 2.0] intersects [1.5, 2.5.] [1.5, 2.5] intersects [2.5, 3.5.] [2.5, 3.5] intersects [3.0, 4.0] import stdio import sys class Interval: Represents a 1-dimensional interval [bound, rboundl def init-_(self, lbound, rbound): Constructs a new interval given its lower and upper bounds. self. .tbqund.-. def lbound(self): Returns the lower bound of the interval. def rbound( self): Returns the upper bound of the interval. def contains(self, x); Returns True if self contains the point x and False otherwise. def intersects (self, other): Returns True if self intersects other and False othewise. def str_(self): Returns a string representation of self. # Test client [DO NOT EDIT]. Reads a float x from the command line and # writes to standard output: all of the intervals from standard input # (each defined by a pair of floats) that contain x; and all pairs # of intervals from standard input that intersect one another. def main): x = float (SysArgy11]) intervals[] while not stdio.isEmpty(): Lbound. stdio.readFloat() rbound= stdio, readFloat () intervals += [Interval(pound, rbound)] for i in range(len (intervals)): if intervals [i].contains (x): stdiQmWratet('%s for i in range(len (intervals)): contains %f ", intervals [1], x) for j in range(i + 1, len(intervals)): intervals [i].intersects(intervals [j]): std49.writet('8s intersects %s ", if intervals [i], intervals [j]) if name__ main() Problem 3. (1D Interval) Define a data type Interval in interval.py that represents a closed 1D interval. The data type must support the following API: method Interval(lbound, rbound) i.1boundO i .ubound) i.contains (x) i.intersects (j) str(i) description a new interval i from the given lower and upper bounds for the interval lower bound of i upper bound of i does i contain the point ? does i intersect the interval i? the string representation of i as [1bound, rbound] $ python3 interval.py 3.14 0 1 0.5 1.5 1 2 1.5 2.5 2.5 3.5 3 4 [2.5, 3.5] contains 3.140000 [3.0, 4.0] contains 3.140000 [0.0, 1.0] intersects [0.5, 1.5] [0.0, 1.0] intersects [1.0, 2.0] [0.5, 1.5] intersects [1.0, 2.0] [0.5, 1.5] intersects [1.5, 2.5.] [1.0, 2.0] intersects [1.5, 2.5.] [1.5, 2.5] intersects [2.5, 3.5.] [2.5, 3.5] intersects [3.0, 4.0] import stdio import sys class Interval: Represents a 1-dimensional interval [bound, rboundl def init-_(self, lbound, rbound): Constructs a new interval given its lower and upper bounds. self. .tbqund.-. def lbound(self): Returns the lower bound of the interval. def rbound( self): Returns the upper bound of the interval. def contains(self, x); Returns True if self contains the point x and False otherwise. def intersects (self, other): Returns True if self intersects other and False othewise. def str_(self): Returns a string representation of self. # Test client [DO NOT EDIT]. Reads a float x from the command line and # writes to standard output: all of the intervals from standard input # (each defined by a pair of floats) that contain x; and all pairs # of intervals from standard input that intersect one another. def main): x = float (SysArgy11]) intervals[] while not stdio.isEmpty(): Lbound. stdio.readFloat() rbound= stdio, readFloat () intervals += [Interval(pound, rbound)] for i in range(len (intervals)): if intervals [i].contains (x): stdiQmWratet('%s for i in range(len (intervals)): contains %f ", intervals [1], x) for j in range(i + 1, len(intervals)): intervals [i].intersects(intervals [j]): std49.writet('8s intersects %s ", if intervals [i], intervals [j]) if name__ main()






