Question: Problem 3 A random walk is a stochastic process that describes the path of successive random steps on some mathematical space (we'll use integers for
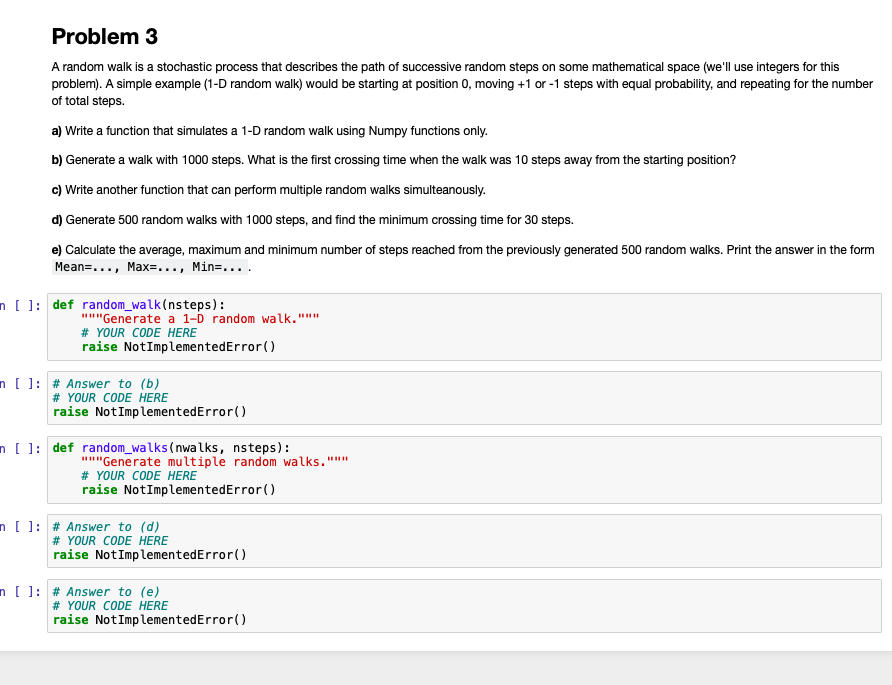
Problem 3 A random walk is a stochastic process that describes the path of successive random steps on some mathematical space (we'll use integers for this problem). A simple example (1-D random walk) would be starting at position 0, moving +1 or -1 steps with equal probability, and repeating for the number of total steps. a) Write a function that simulates a 1-D random walk using Numpy functions only. b) Generate a walk with 1000 steps. What is the first crossing time when the walk was 10 steps away from the starting position? c) Write another function that can perform multiple random walks simulteanously. d) Generate 500 random walks with 1000 steps, and find the minimum crossing time for 30 steps. e) Calculate the average, maximum and minimum number of steps reached from the previously generated 500 random walks. Print the answer in the form Mean=..., Max=..., Min=.... n[ ]: def random_walk(nsteps): "Generate a 1-D random walk." # YOUR CODE HERE raise NotImplementedError() n[ ]: # Answer to (b) # YOUR CODE HERE raise Not ImplementedError() n[ ]: def random_walks (nwalks, nsteps): "11"Generate multiple random walks." # YOUR CODE HERE raise NotImplementedError() n[ ]: # Answer to (d) # YOUR CODE HERE raise NotImplementedError() n [ ]: # Answer to (e) # YOUR CODE HERE raise NotImplementedError() Problem 3 A random walk is a stochastic process that describes the path of successive random steps on some mathematical space (we'll use integers for this problem). A simple example (1-D random walk) would be starting at position 0, moving +1 or -1 steps with equal probability, and repeating for the number of total steps. a) Write a function that simulates a 1-D random walk using Numpy functions only. b) Generate a walk with 1000 steps. What is the first crossing time when the walk was 10 steps away from the starting position? c) Write another function that can perform multiple random walks simulteanously. d) Generate 500 random walks with 1000 steps, and find the minimum crossing time for 30 steps. e) Calculate the average, maximum and minimum number of steps reached from the previously generated 500 random walks. Print the answer in the form Mean=..., Max=..., Min=.... n[ ]: def random_walk(nsteps): "Generate a 1-D random walk." # YOUR CODE HERE raise NotImplementedError() n[ ]: # Answer to (b) # YOUR CODE HERE raise Not ImplementedError() n[ ]: def random_walks (nwalks, nsteps): "11"Generate multiple random walks." # YOUR CODE HERE raise NotImplementedError() n[ ]: # Answer to (d) # YOUR CODE HERE raise NotImplementedError() n [ ]: # Answer to (e) # YOUR CODE HERE raise NotImplementedError()
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


