Question: Problem 4 . The rotating solid steel shaft is simply supported by bearings at points B and C and is driven by a gear (
Problem
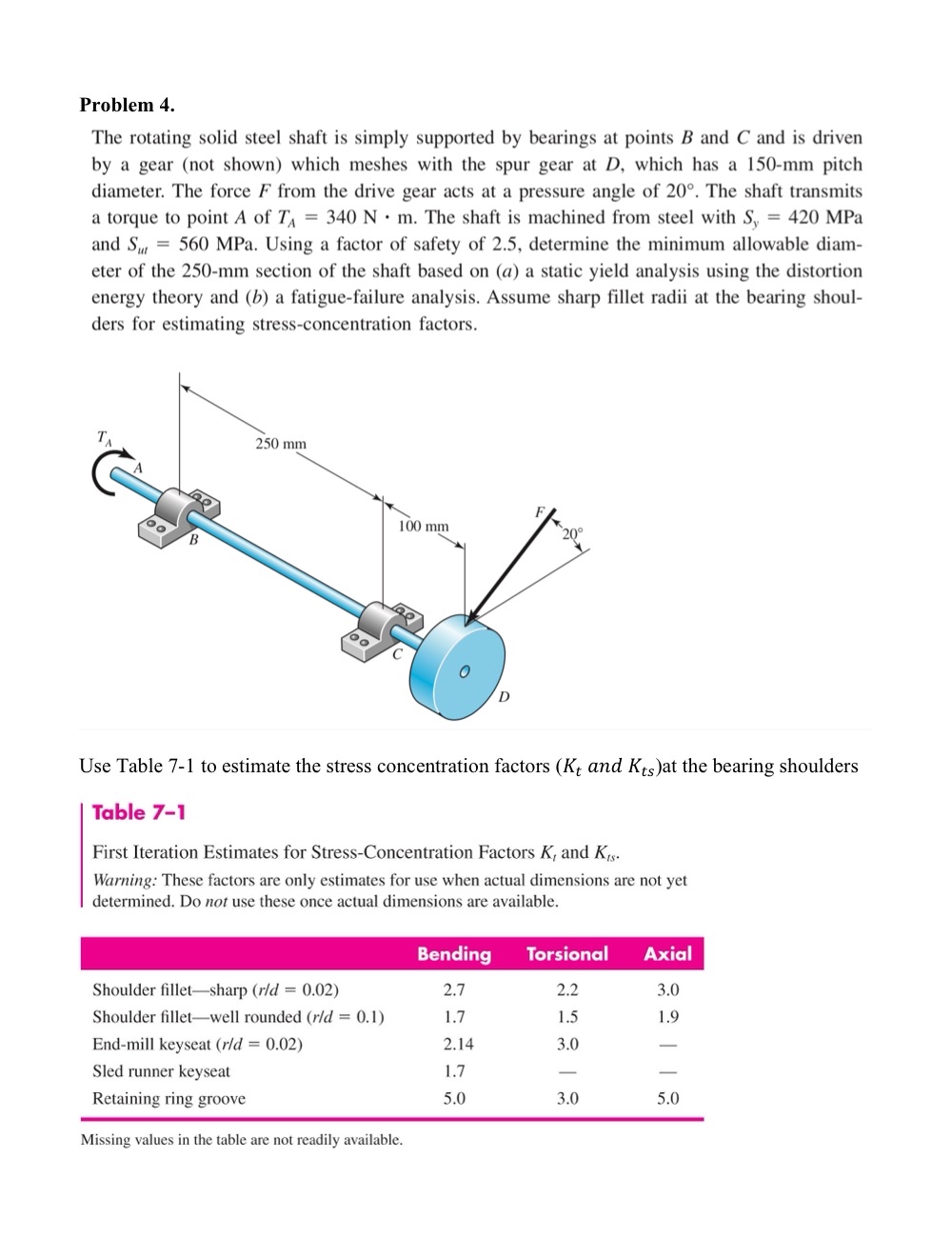
The rotating solid steel shaft is simply supported by bearings at points and and is driven by a gear not shown which meshes with the spur gear at which has a pitch diameter. The force from the drive gear acts at a pressure angle of The shaft transmits a torque to point of The shaft is machined from steel with MPa and MPa. Using a factor of safety of determine the minimum allowable diameter of the section of the shaft based on a a static yield analysis using the distortion energy theory and a fatiguefailure analysis. Assume sharp fillet radii at the bearing shoulders for estimating stressconcentration factors.
Use Table to estimate the stress concentration factors and at the bearing shoulders
Table
First Iteration Estimates for StressConcentration Factors and
Warning: These factors are only estimates for use when actual dimensions are not yet determined. Do not use these once actual dimensions are available.
tableBending,Torsional,AxialShoulder filletsharp
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


