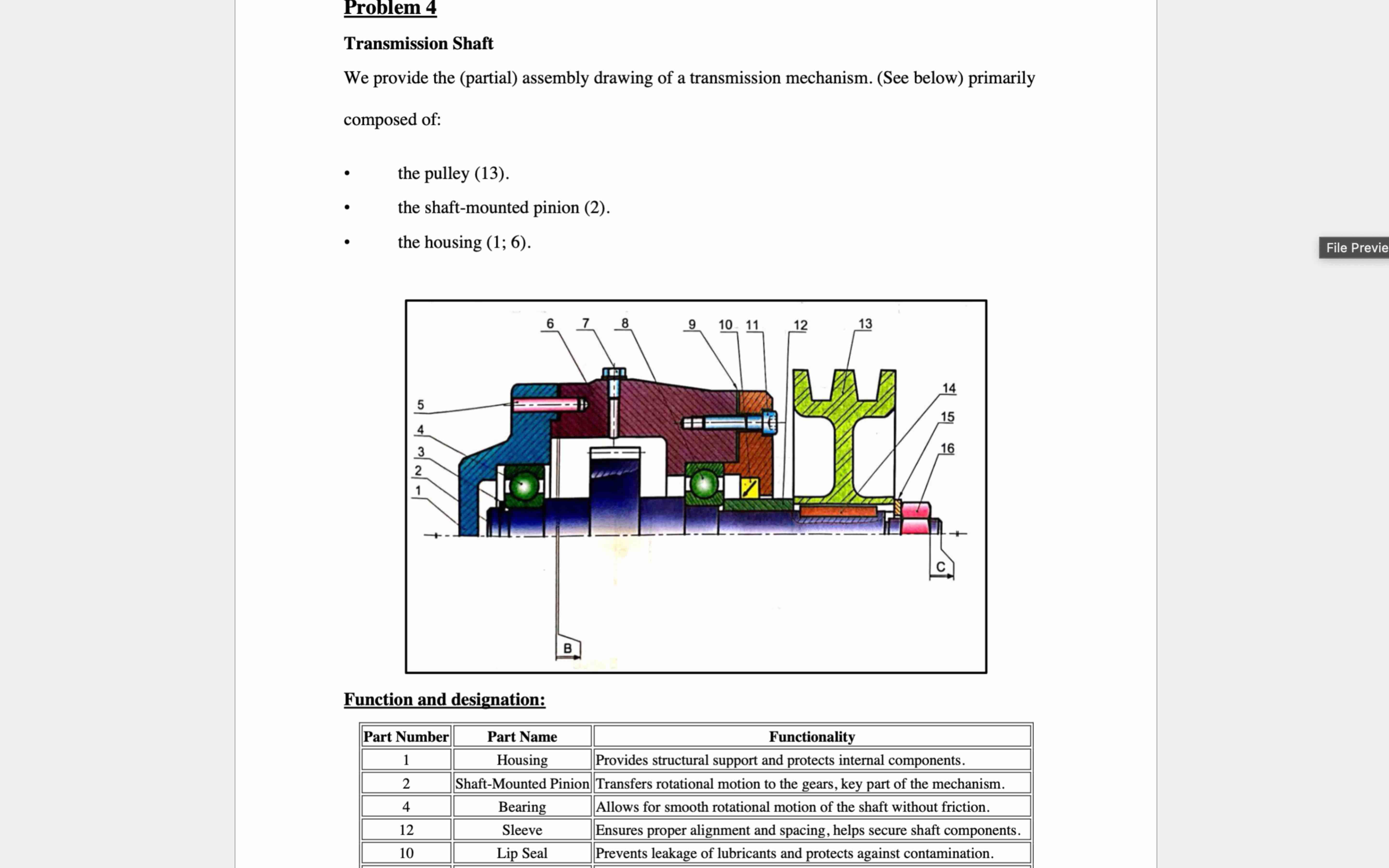
Question: Problem 4 Transmission Shaft We provide the ( partial ) assembly drawing of a transmission mechanism. ( See below ) primarily composed of: - the
Problem
Transmission Shaft
We provide the partial assembly drawing of a transmission mechanism. See below primarily
composed of:
the pulley
quad the shaftmounted pinion
quad the housing ;
File Previe
Function and designation:
begintabularccl
hline Part Number & Part Name & multicolumnc Functionality
hline hline & Housing & Provides structural support and protects internal components.
hline hline & ShaftMounted Pinion & Transfers rotational motion to the gears, key part of the mechanism.
hline hline & Bearing & Allows for smooth rotational motion of the shaft without friction.
hline hline & Sleeve & Ensures proper alignment and spacing, helps secure shaft components.
hline hline & Lip Seal & Prevents leakage of lubricants and protects against contamination.
hline hline
endtabular
Detail drawinos cdot
Explain the presence of Condition B see assembly drawing
Hint: Condition B involves preventing direct contact between the housing and the other components. Think about which components need a clearance or precise fit to avoid wear or misalignment. Focus on how the housing interacts with the bearing and what it is protecting.
Explain the presence of Condition C see assembly drawing:
Hint: Condition C involves the clamping force or tightening mechanism that holds certain parts together.
Consider what parts might need to be securely fastened to avoid movement during operation. Focus on the pinion and how the sleeve must remain stable in operation. Think about what elements need to be held firmly in place to avoid shifting or loosening.
Referring to the partial assembly drawing of the transmission shaft, complete the table below.
Hint: When determining assembly tolerances, think about whether the part requires:
A tight fit to ensure no movement between parts, like bearings and shafts
A neutral fit to allow easy assembly while still supporting functionality, like sleeves and seals
A loose fit for parts that need flexibility or adjustments, like seals
Use engineering handbooks or lecture slide tables to find the appropriate tolerance positions like H k g and grades eg for each part. Consider how the type of fit tight neutral, loose affects the tolerance you choose.
You can follow this link to access a useful engineering handbook:
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


