Question: Problem 4-6 (Level 2) The catalytic cracking reaction A + B + C +D is taking place in a fluidized-bed reactor. At reaction conditions, the
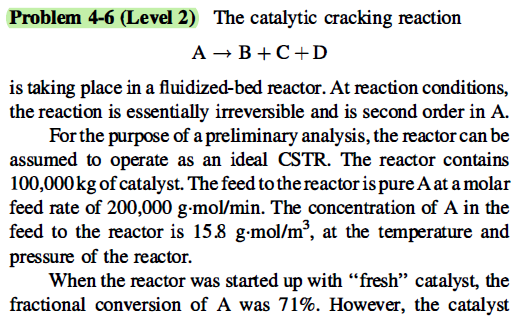
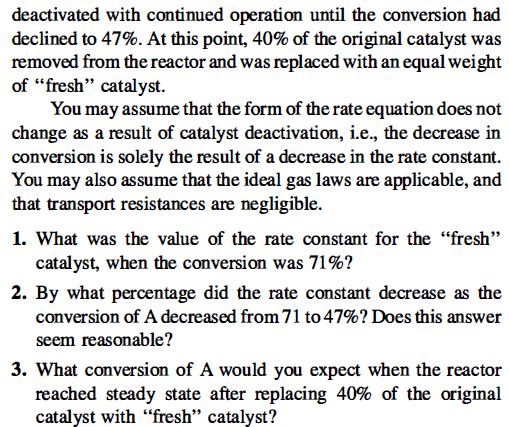
Problem 4-6 (Level 2) The catalytic cracking reaction A + B + C +D is taking place in a fluidized-bed reactor. At reaction conditions, the reaction is essentially irreversible and is second order in A. For the purpose of a preliminary analysis, the reactor can be assumed to operate as an ideal CSTR. The reactor contains 100,000kg of catalyst. The feed to the reactor is pure A at a molar feed rate of 200,000 g.mol/min. The concentration of A in the feed to the reactor is 15.8 g.mol/m, at the temperature and pressure of the reactor. When the reactor was started up with fresh" catalyst, the fractional conversion of A was 71%. However, the catalyst deactivated with continued operation until the conversion had declined to 47%. At this point, 40% of the original catalyst was removed from the reactor and was replaced with an equal weight of "fresh" catalyst. You may assume that the form of the rate equation does not change as a result of catalyst deactivation, i.e., the decrease in conversion is solely the result of a decrease in the rate constant. You may also assume that the ideal gas laws are applicable, and that transport resistances are negligible. 1. What was the value of the rate constant for the "fresh" catalyst, when the conversion was 71%? 2. By what percentage did the rate constant decrease as the conversion of A decreased from 71 to 47%? Does this answer seem reasonable? 3. What conversion of A would you expect when the reactor reached steady state after replacing 40% of the original catalyst with "fresh" catalyst
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


