Question: Problem 5-18 Interpreting a Report-Weighted-Average Method [LO5-2, LO5-3, LO5-4] Cooperative San Jos of southern Sonora state in Mexico makes a unique syrup using cane sugar
![Problem 5-18 Interpreting a Report-Weighted-Average Method [LO5-2, LO5-3, LO5-4] Cooperative San](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66e6cf3a1f282_36166e6cf39925c2.jpg)
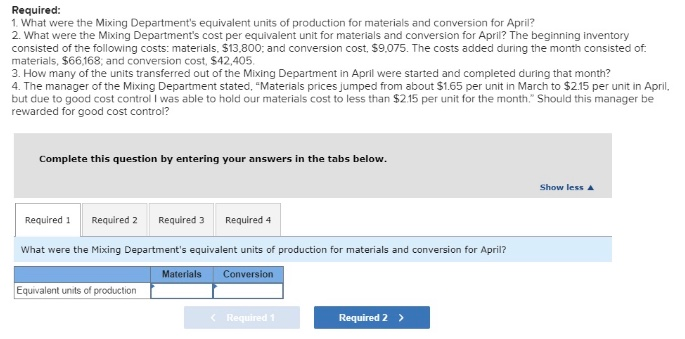
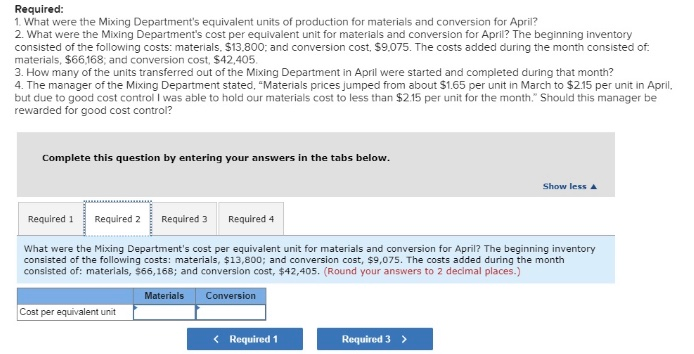
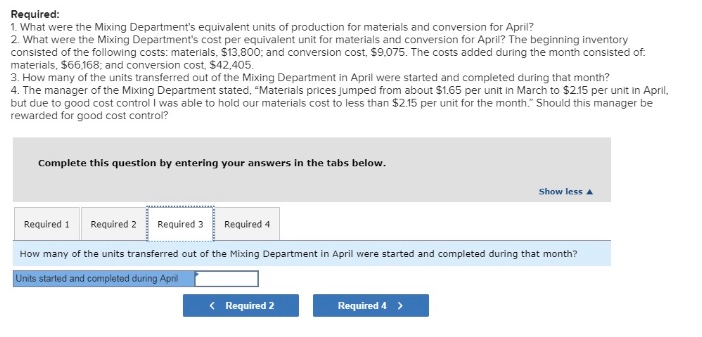
Problem 5-18 Interpreting a Report-Weighted-Average Method [LO5-2, LO5-3, LO5-4] Cooperative San Jos of southern Sonora state in Mexico makes a unique syrup using cane sugar and local herbs. The syrup is sold in small bottles and is prized as a flavoring for drinks and for use in desserts. The bottles are sold for $12 each. The first stage in the production process is carried out in the Mixing Department, which removes foreign matter from the raw materials and mixes them in the proper proportions in large vats. The company uses the weighted-average method in its process costing system. A hastily prepared report for the Mixing Department for April appears below: Units to be accounted for: Work in process, April 1 (materials 90% complete; 7,566 34,980 42,408 sion 88s complete) Started into production Total units to be accounted for Units accounted for as follows Transferred to next department Work in process, April 30 (materials 75% complete; 29,600 12,800 42,488 conversion 5e% complete) Total units accounted for Cost Reconciliation Cost to be accounted for: Work in process, April1 Cost added during the month 22,875 188,573 131,448 Total cost to be accounted for Cost accounted for as follows work in process, April 3e Transferred to next department $ 28,736 182,712 Total cost accounted for 131,448 Required: 1. What were the Mixing Department's equivalent units of production for materials and conversion for April? 2. What were the Mixing Department's cost per equivalent unit for materials and conversion for April? The beginning inventory consisted of the following costs: materials, $13.800 and conversion cost. $9.075. The costs added during the month consisted of. materials, $66,168, and conversion cost, $42,405 3. How many of the units transferred out of the Mixing Department in April were started and completed during that month? 4. The manager of the Mixing Department stated, "Materials prices jumped from about $1.65 per unit in March to $2.15 per unit in April, but due to good cost control I was able to hold our materials cost to less than $2.15 per unit for the month." Should this manager be rewarded for good cost control? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Show less Required 1 Required 2 Required 3 Required 4 What were the Mixing Department's equivalent units of production for materials and conversion for April? Materials Conversion Equivalent units of production Required 1 Required 2 > Required: 1. What were the Mixing Department's equivalent units of production for materials and conversion for April? 2. What were the Mixing Department's cost per equivalent unit for materials and conversion for Apri? The beginning inventory consisted of the following costs: materials. $13.800: and conversion cost, $9.075. The costs added during the month consisted of materials, $66,168, and conversion cost, $42,405 3. How many of the units transferred out of the Mixing Department in April were started and completed during that month? 4. The manager of the Mixing Department stated, "Materials prices jumped from about $1.65 per unit in March to $2.15 per unit in April, but due to good cost control I was able to hold our materials cost to less than $2.15 per unit for the month." Should this manager be rewarded for good cost control: Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Show less Required 1 Required 2Required 3 Required 4 What were the Mixing Department's cost per equivalent unit for materials and conversion for April? The beginning inventory consisted of the following costs: materials, $13,800; and conversion cost, $9,075. The costs added during the month consisted of: materlals, $66,168; and conversion cost, $42,405. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) Materials Conversion Cos t per equivalent unit Required 1 Required 3 > Required 1. What were the Mixing Department's equivalent units of production for materials and conversion for April? 2. What were the Mixing Department's cost per equivalent unit for materials and conversion for April? The beginning inventory consisted of the following costs: materials, $13,800: and conversion cost, $9,075. The costs added during the month consisted of. materials, $66,168: and conversion cost, $42.405 3. How many of the units transferred out of the Mixing Department in April were started and completed during that month? 4. The manager of the Mixing Department stated, "Materials prices jumped from about $1.65 per unit in March to $2.15 per unit in Apri but due to good cost control I was able to hold our materials cost to less than $2.15 per unit for the month. Should this manager be rewarded for good cost control? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below Show less Required 1 Required 2 Required 3 Required 4 How many of the units transferred out of the Mixing Department in April were started and completed during that month? Units started and completed during Apn Required 2 Required 4>
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


