Question: Problem 6-35 Financial Break-Even Analysis The technique for calculating a bid price can be extended to many other types of problems. Answer the following questions



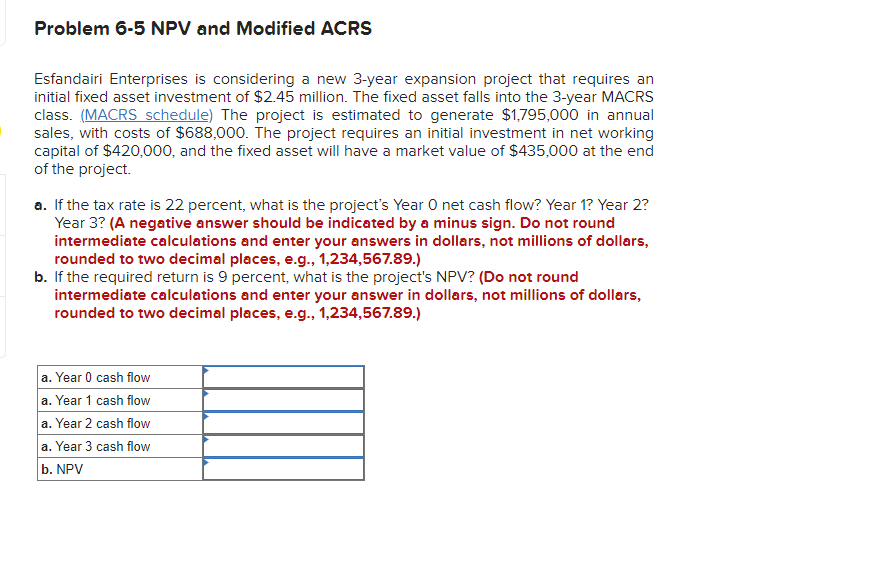
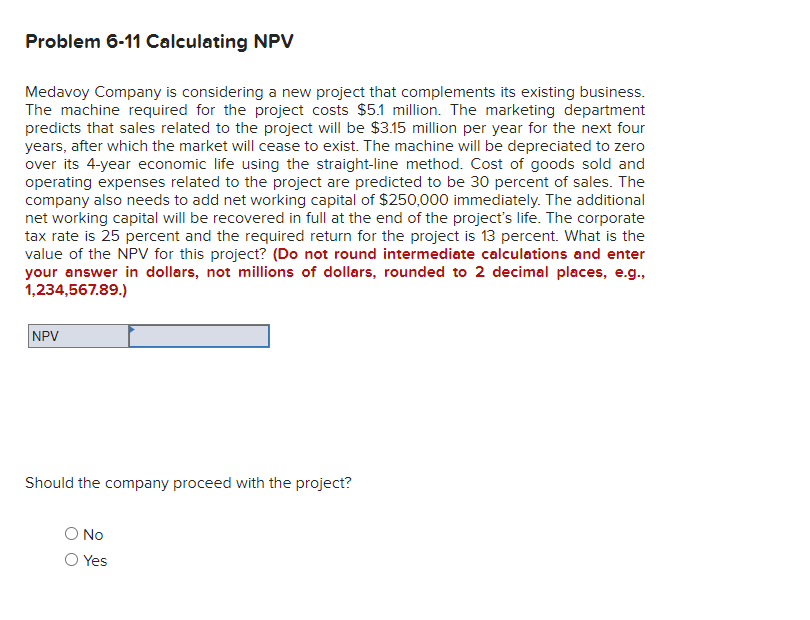
Problem 6-35 Financial Break-Even Analysis The technique for calculating a bid price can be extended to many other types of problems. Answer the following questions using the same technique as setting a bid price; that is, set the project NPV to zero and solve for the variable in question. Martin Enterprises needs someone to supply it with 156,000 cartons of machine screws per year to support its manufacturing needs over the next five years, and you've decided to bid on the contract. It will cost $1,960,000 to install the equipment necessary to start production, you'll depreciate this cost straight-line to zero over the project's life. You estimate that, in five years, this equipment can be salvaged for $166,000. Your fixed production costs will be $281,000 per year, and your variable production costs should be $11.00 per carton. You also need an initial investment in net working capital of $146,000. The tax rate is 21 percent and you require a return of 10 percent on your investment. Assume that the price per carton is $17.60. a. Calculate the project NPV. (Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.) b. What is the minimum number of cartons per year that can be supplied and still break even? (Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to the nearest whole number, e.g., 32.) c. What are the highest fixed costs that could be incurred and still break even? (Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16.) a. NPV b. Minimum cartons c. Highest fixed costs Problem 6-30 Calculating Project NPV Calligraphy Pens is deciding when to replace its old machine. The machine's current salvage value is $2,400,000. Its current book value is $1,475,000. If not sold, the old machine will require maintenance costs of $645,000 at the end of the year for the next five years. Depreciation on the old machine is $295,000 per year. At the end of five years, it will have a salvage value of $90,000 and a book value of $0. A replacement machine costs $4,000,000 now and requires maintenance costs of $315,000 at the end of each year during its economic life of five years. At the end of the five years, the new machine will have a salvage value of $680,000. It will be fully depreciated by the straight-line method. In five years, a replacement machine will cost $3,000,000. The company will need to purchase this machine regardless of what choice it makes today. The corporate tax rate is 22 percent and the appropriate discount rate is 7 percent. The company is assumed to earn sufficient revenues to generate tax shields from depreciation. Calculate the NPV for the new and old machines. (Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answers in dollars, not millions of dollars, rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 1,234,567.89.) New machine Old machine Problem 6-20 Inflation and Company Value Sparkling Water, Incorporated, expects to sell 3.7 million bottles of drinking water each year in perpetuity. This year each bottle will sell for $1.46 in real terms and will cost $.82 in real terms. Sales income and costs occur at year-end. Revenues will rise at a real rate of 1.7 percent annually, while real costs will rise at a real rate of 1.2 percent annually. The real discount rate is 8 percent. The corporate tax rate is 22 percent. What is the company worth today? (Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer in dollars, not millions of dollars, rounded to the nearest whole number, e.g., 1,234,567.) Value of the firm $ 27,006,914 Problem 6-5 NPV and Modified ACRS Esfandairi Enterprises is considering a new 3-year expansion project that requires an initial fixed asset investment of $2.45 million. The fixed asset falls into the 3-year MACRS class. (MACRS schedule) The project is estimated to generate $1,795,000 in annual sales, with costs of $688,000. The project requires an initial investment in net working capital of $420,000, and the fixed asset will have a market value of $435,000 at the end of the project a. If the tax rate is 22 percent, what is the project's Year Onet cash flow? Year 1? Year 2? Year 3? (A negative answer should be indicated by a minus sign. Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answers in dollars, not millions of dollars, rounded to two decimal places, e.g., 1,234,567.89.) b. If the required return is 9 percent, what is the project's NPV? (Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer in dollars, not millions of dollars, rounded to two decimal places, e.g., 1,234,567.89.) a. Year 0 cash flow a. Year 1 cash flow a. Year 2 cash flow a. Year 3 cash flow b. NPV Problem 6-11 Calculating NPV Medavoy Company is considering a new project that complements its existing business. The machine required for the project costs $5.1 million. The marketing department predicts that sales related to the project will be $3.15 million per year for the next four years, after which the market will cease to exist. The machine will be depreciated to zero over its 4-year economic life using the straight-line method. Cost of goods sold and operating expenses related to the project are predicted to be 30 percent of sales. The company also needs to add net working capital of $250,000 immediately. The additional net working capital will be recovered in full at the end of the project's life. The corporate tax rate is 25 percent and the required return for the project is 13 percent. What is the value of the NPV for this project? (Do not round intermediate calculations and enter your answer in dollars, not millions of dollars, rounded to 2 decimal places, e.g., 1,234,567.89.) NPV Should the company proceed with the project? Yes
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


