Question: Problem 7.18 (a) Solve the following problems by reducing to the original max-flow problem Algorithms [Dasgupta, Papadimitriou, Vazirani][DPV] 1st edition There are many common variations
Problem 7.18 (a) Solve the following problems by reducing to the original max-flow problem
Algorithms [Dasgupta, Papadimitriou, Vazirani][DPV] 1st edition
There are many common variations of the maximum flow problem. Here are four of them.
Solve the following problems by reducing to the original max-flow problem. In other words, explain how to solve the new flow variant problem using an algorithm for solving max-flow as a black-box. Explain how to take an input for the new problem and define an input for the original max-flow problem. Then given a max-flow F* to this input you just defined, explain how to get the solution to the new problem.
describe your algorithm in words; no pseudocode.
(a) There are many sources and many sinks, and we wish to maximize the total flow from all sources to all sinks
my answer: (not sure if #5 is enough to satisfy the multi Source/Sink and is the steps for max-flow are 100% correct in 1-4)
1. Start with a directed graph 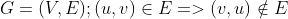
2. Find fe for all ![max-flow problem Algorithms [Dasgupta, Papadimitriou, Vazirani][DPV] 1st edition There are many common](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/08/66d1f1a7d2b1c_91966d1f1a786316.jpg) a valid flow of maximum capacity
a valid flow of maximum capacity
3. capacity constraint for all 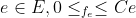 and flow-in to V = flow-out of V.
and flow-in to V = flow-out of V.
4. using BFS algorithm over a subset of the graph to find a valid flow of maximum capacity in 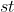 path
path 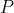
5. to compensate for the multiple sources and sinks we add and artificial Source s and an artificial Sink 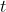 which connects to all sources and sinks.
which connects to all sources and sinks.
running time: this is reduced to the max-flow problem therefore the run time is O(|E|) for all edges explored and O(|V|) for all vertices explored so the total run time is O(|V|+|E|).
st st
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


