Question: Problem A: Consider the following graph. A 6 5 10 7 H G 11 3 B 1 A F 8 D 2 9 (a).
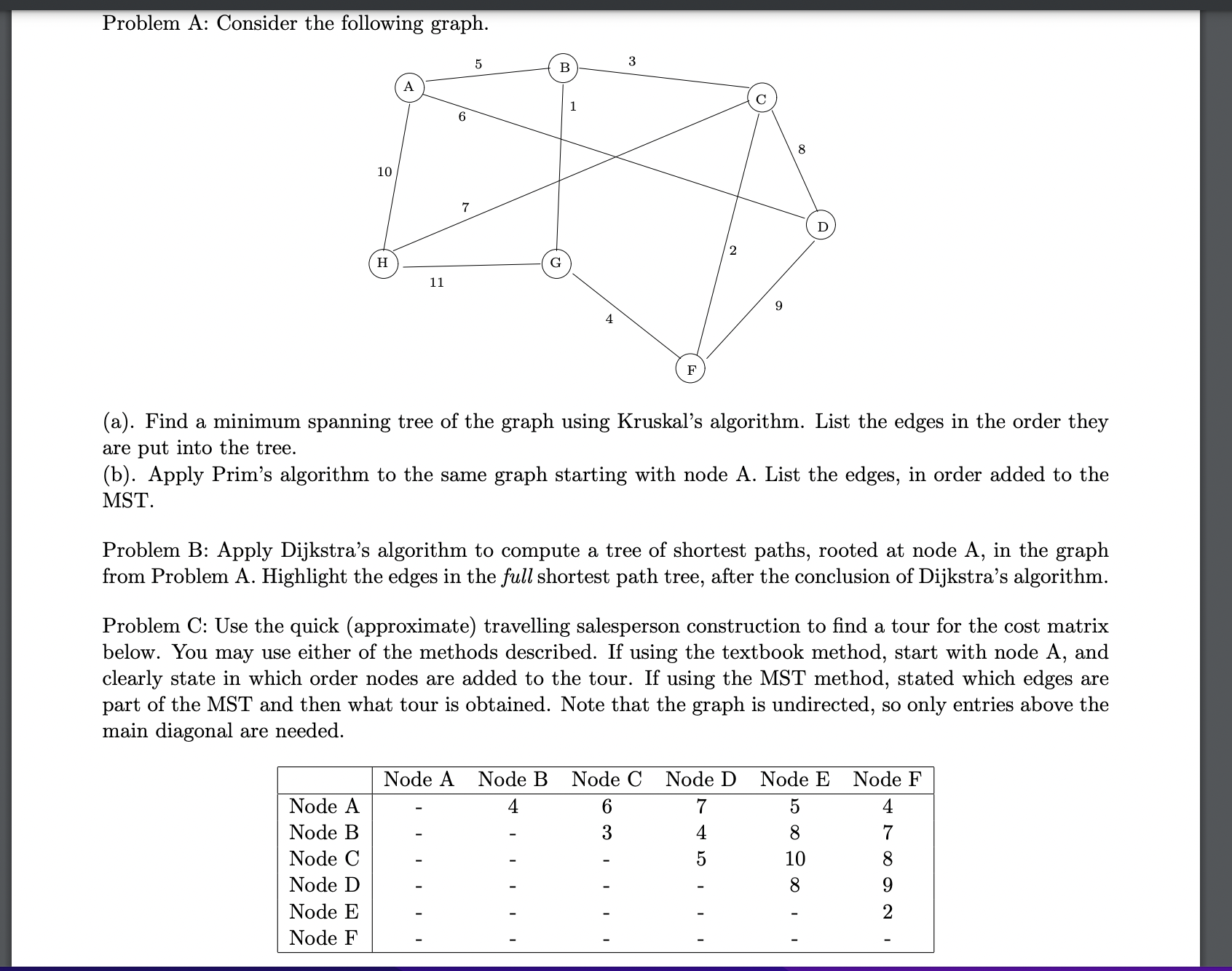

Problem A: Consider the following graph. A 6 5 10 7 H G 11 3 B 1 A F 8 D 2 9 (a). Find a minimum spanning tree of the graph using Kruskal's algorithm. List the edges in the order they are put into the tree. (b). Apply Prim's algorithm to the same graph starting with node A. List the edges, in order added to the MST. Problem B: Apply Dijkstra's algorithm to compute a tree of shortest paths, rooted at node A, in the graph from Problem A. Highlight the edges in the full shortest path tree, after the conclusion of Dijkstra's algorithm. Problem C: Use the quick (approximate) travelling salesperson construction to find a tour for the cost matrix below. You may use either of the methods described. If using the textbook method, start with node A, and clearly state in which order nodes are added to the tour. If using the MST method, stated which edges are part of the MST and then what tour is obtained. Note that the graph is undirected, so only entries above the main diagonal are needed. Node A Node B Node C Node D Node E Node F Node A 4 6 7 5 Node B 3 4 8 Node C 10 Node D 8 Node E 47812 9 Node F I Problem D: For each of the following parts, state True or False. If true, give a short proof. If false, giver a counterexample: (1). Using Kruskal's algorithm, edges are (always) inserted into the MST in the same order as using Prim's algorithm. (2). If an edge e is part of a Shortest Path Tree rooted at A then it must also be part of a Shortest Path Tree rooted at B. (3). If all edge costs are increased by 2 the Shortest Path Tree rooted at A remains the same tree. (4). If all edge costs of all edges touching node A are increased by 2, the shortest path tree rooted at A remains the same. (5). If all edge costs of all edges touching node A are increased by 2, the minimum spanning tree rooted at A remains the same. Problem E: In class we stated that Dijkstra's algorithm may give a wrong shortest path from a node s to a node d if one or more of the edges has a negative cost. (a) Draw one such example. Make sure to clearly show the costs on each edge. (b) Draw the correct shortest path from s to d. (c) Draw the path (from s to d) that would be obtained using Dijkstra's algorithm
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


