Question: Problem I ( old exam problem ) For a chemical process, species A must be added to a stream of inert carrier gas B .
Problem I old exam problem
For a chemical process, species A must be added to a stream of inert carrier gas B To do
this in a controlled manner, liquid is evaporated from a round pan into a flowing stream of
see right figure below Unfortunately, little is known about the mass transfer coefficients for
the round pan and the diffusion coefficient of A in air, which prevents the process engineer
from optimizing the conditions.
In order to quantify the relative importance of convection and diffusion for the evaporation of
A from the pan, two laboratory experiments are performed see Figures below under
identical conditions atm :
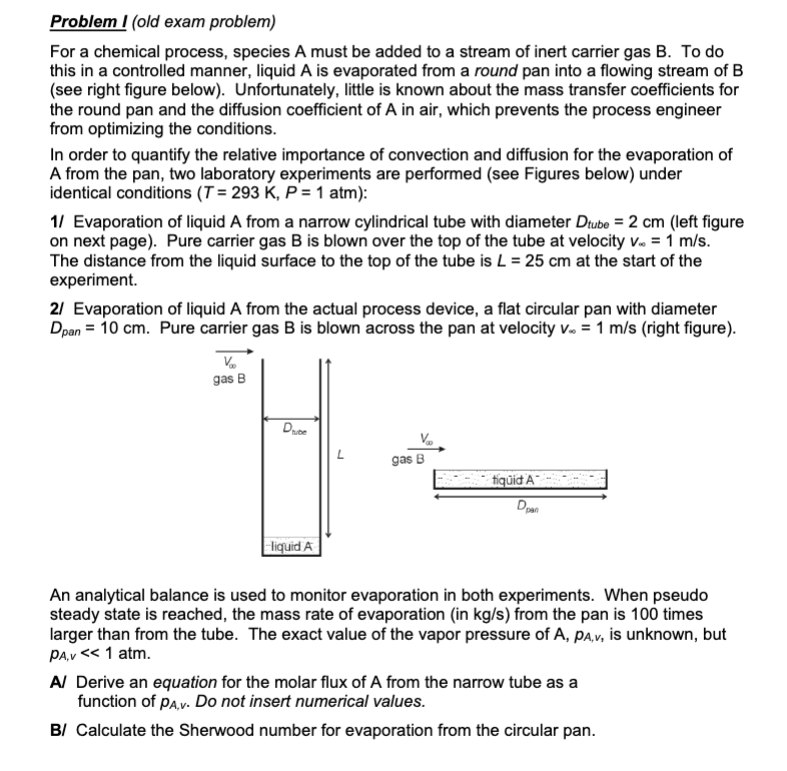
Evaporation of liquid A from a narrow cylindrical tube with diameter left figure
on next page Pure carrier gas is blown over the top of the tube at velocity
The distance from the liquid surface to the top of the tube is at the start of the
experiment.
Evaporation of liquid A from the actual process device, a flat circular pan with diameter
Pure carrier gas is blown across the pan at velocity right figure
An analytical balance is used to monitor evaporation in both experiments. When pseudo
steady state is reached, the mass rate of evaporation in from the pan is times
larger than from the tube. The exact value of the vapor pressure of is unknown, but
atm.
A Derive an equation for the molar flux of A from the narrow tube as a
function of Do not insert numerical values.
B Calculate the Sherwood number for evaporation from the circular pan.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


