Question: Programming language: C++ input file1: Expected output file1: input file2: expected output file 2: Clarification: 1. After you delete a node from tree, maintain that
Programming language: C++

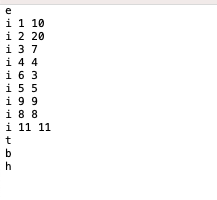
input file1:
Expected output file1:

input file2:

expected output file 2:

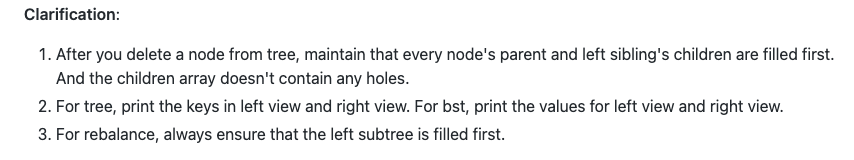
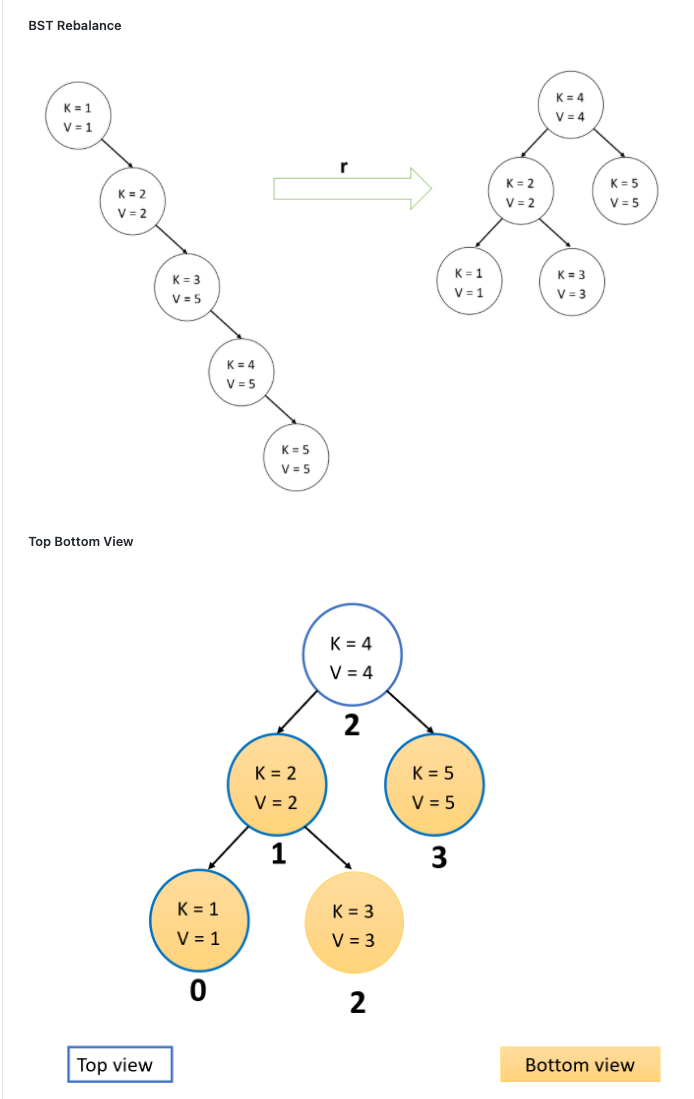
Clarification: 1. After you delete a node from tree, maintain that every node's parent and left sibling's children are filled first. And the children array doesn't contain any holes. 2. For tree, print the keys in left view and right view. For bst, print the values for left view and right view. 3. For rebalance, always ensure that the left subtree is filled first. Binary Search Tree (RBT) For binary search tree, compare by values instead of keys Always insert the value greater or equal to the root on the right subtree. You will find the input file for stack in [PROJ_ROOT]/input/rbt/[num].txt. For each line in the input file for binary search tree: 1. C COMMENTS All comments will begin with c. 2. e Create an empty tree. Note there will be only one t for every file and t will always proceed other non- comment commands. 3. ik v Create a tree node with key = k and value = v insert the new node into the tree. 4. d k Delete the TreeNode with the key = k 5. t Print the top view of the tree [See Example Below] (#Top Bottoml Views) 6. b Print the bottom view of the tree (See Example Below](#Top Bottom Views) 7. r Rebalance the tree using the left leaning red black tree technique. (See Example Below] (#BST| Rebalance) 8. h Print the height of the tree BST Rebalance K = 1 V = 1 K = 4 V=4 r K = 2 V = 2 K = 2 V = 2 K = 5 V = 5 K = 3 V=5 K = 1 V = 1 K = 3 V=3 K=4 V = 5 K = 5 V = 5 Top Bottom View K = 4 V = 4 2 K = 2 V = 2 K = 5 V = 5 1 3 K = 1 V = 1 K = 3 V = 3 0 2 Top view Bottom view 00 OWNP COLOUW i 88 i 11 11 3 4 7 10 20 3 4 5 8 9 11 20 4 2 2 Clarification: 1. After you delete a node from tree, maintain that every node's parent and left sibling's children are filled first. And the children array doesn't contain any holes. 2. For tree, print the keys in left view and right view. For bst, print the values for left view and right view. 3. For rebalance, always ensure that the left subtree is filled first. Binary Search Tree (RBT) For binary search tree, compare by values instead of keys Always insert the value greater or equal to the root on the right subtree. You will find the input file for stack in [PROJ_ROOT]/input/rbt/[num].txt. For each line in the input file for binary search tree: 1. C COMMENTS All comments will begin with c. 2. e Create an empty tree. Note there will be only one t for every file and t will always proceed other non- comment commands. 3. ik v Create a tree node with key = k and value = v insert the new node into the tree. 4. d k Delete the TreeNode with the key = k 5. t Print the top view of the tree [See Example Below] (#Top Bottoml Views) 6. b Print the bottom view of the tree (See Example Below](#Top Bottom Views) 7. r Rebalance the tree using the left leaning red black tree technique. (See Example Below] (#BST| Rebalance) 8. h Print the height of the tree BST Rebalance K = 1 V = 1 K = 4 V=4 r K = 2 V = 2 K = 2 V = 2 K = 5 V = 5 K = 3 V=5 K = 1 V = 1 K = 3 V=3 K=4 V = 5 K = 5 V = 5 Top Bottom View K = 4 V = 4 2 K = 2 V = 2 K = 5 V = 5 1 3 K = 1 V = 1 K = 3 V = 3 0 2 Top view Bottom view 00 OWNP COLOUW i 88 i 11 11 3 4 7 10 20 3 4 5 8 9 11 20 4 2 2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


