Question: Project 13-The Caesar Cipher In cryptography, a Caesar cipher, also known as a Caesar's cipher, or the shift cipher, is one of the simplest and

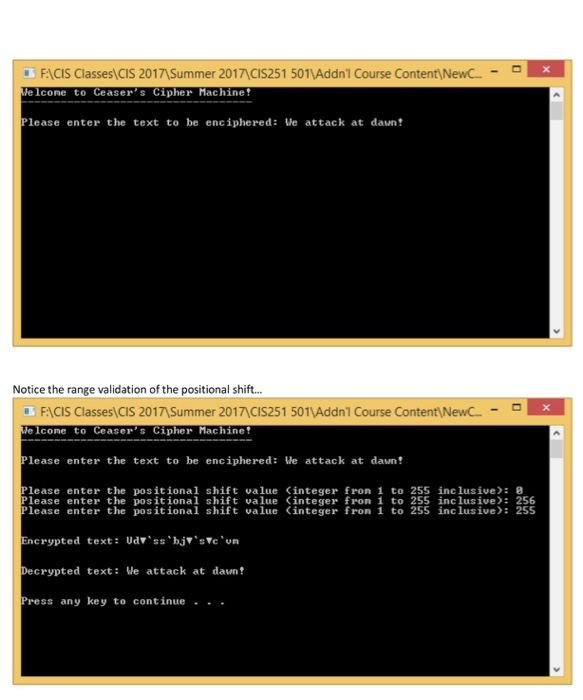
Project 13-The Caesar Cipher In cryptography, a Caesar cipher, also known as a Caesar's cipher, or the shift cipher, is one of the simplest and most widely known encryption techniques. It is a type of substitution cipher in which each letter in the plaintext is replaced by a letter some fixed number of positions down the alphabet. For example, with a shift of 3, A would be replaced by D, B would become E, and so on. The method is named after Julius Caesar, who used it to communicate with his generals. Caesar cipher ABICIDIEIF The action of a Caesar cipher is to replace each plaintext letter with one foxed number of places down the alphabet. This example s with a shift of three, so that a B in the plaintext becomes in the cipherted Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Caesar_cipher Code a Ct+ program based upon the following constraints: Get the plain text to be enciphered from the user, storing it in a variable of type string. Get the positional shift value from the user and validate that the value is an integer who's value falls in the range of 1 to 255 inclusive (truncate any digits to the right of the decimal point). Create a value returning function that will both encipher and decipher the text. This function will accept two arguments-the plain text and the positional shift value. Call this function from main() twice- once to encipher the plain text and once to decipher the previously enciphered text. Do NOT store the original plain text to display after the last function call. Your program must both encipher and decipher. After each function call you shall output the resultant string returned from your cypher engine. Show all prompts per the screens shots below: 1. 2. 3. 5
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


