Question: Project Description: Implement the Backtracking Algorithm in Figure 3 below to solve the Kropki Sudoku puzzle. The rules of the game are: - The game
Project Description: Implement the Backtracking Algorithm in Figure below to solve the Kropki Sudoku puzzle. The rules of the game are:
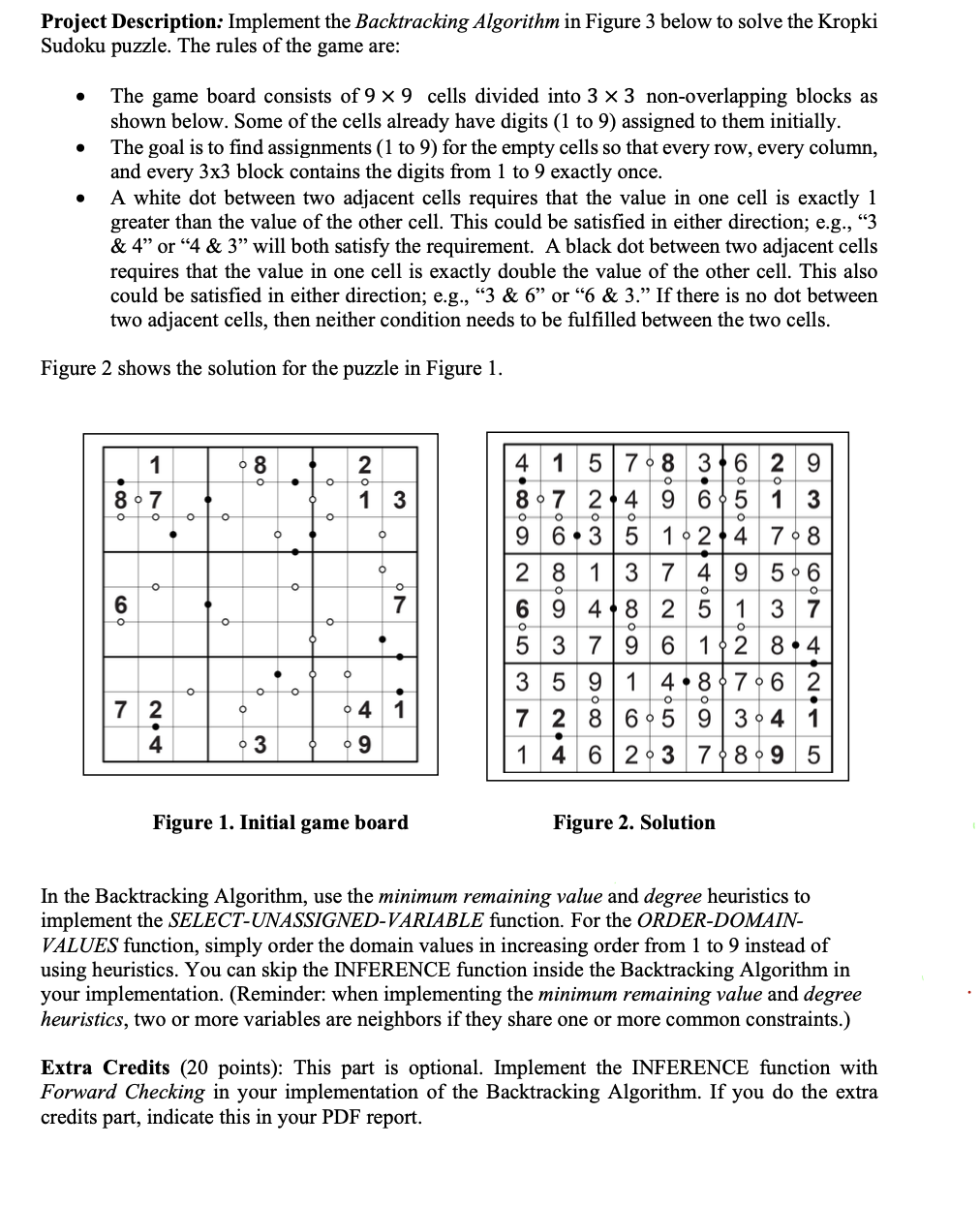
The game board consists of times cells divided into times nonoverlapping blocks as shown below. Some of the cells already have digits to assigned to them initially.
The goal is to find assignments to for the empty cells so that every row, every column, and every times block contains the digits from to exactly once.
A white dot between two adjacent cells requires that the value in one cell is exactly greater than the value of the other cell. This could be satisfied in either direction; eg& or & will both satisfy the requirement. A black dot between two adjacent cells requires that the value in one cell is exactly double the value of the other cell. This also could be satisfied in either direction; eg& or & If there is no dot between two adjacent cells, then neither condition needs to be fulfilled between the two cells.
Figure shows the solution for the puzzle in Figure
Figure Initial game board
Figure Solution
In the Backtracking Algorithm, use the minimum remaining value and degree heuristics to implement the SELECTUNASSIGNEDVARIABLE function. For the ORDERDOMAINVALUES function, simply order the domain values in increasing order from to instead of using heuristics. You can skip the INFERENCE function inside the Backtracking Algorithm in your implementation. Reminder: when implementing the minimum remaining value and degree heuristics, two or more variables are neighbors if they share one or more common constraints.
Extra Credits points: This part is optional. Implement the INFERENCE function with Forward Checking in your implementation of the Backtracking Algorithm. If you do the extra credits part, indicate this in your PDF report. n n n n n n n n
n n n n n n n n
n nnnnnnn
nnnnnnnn
nnnnnnnn
nnnnnnnn
n n n n n n n n
n n n n n n n n
n n n n n n n n
dddddddd
dddddddd
dddddddd
d d d d d d d
dddddddd
dddddddd
dddddddd
dddddddd
d d d d d d d
dddddddd
ddddddddd
ddddddddd
ddddddddd
ddddddddd
ddddddddd
ddddddddd
d d d d d d d
Figure Input file format: boldsymboln is an integer between and boldsymbold is an integer between and The digits are separated by blanks.
n n n n n n n n
n n n n n n n n
nnnnnnnn
n n n n n n n n
n nnnnnnn
nnnnnnnn
nnnnnnnn
n nnnnnnn
n n n n n n n n
Figure Output file format: boldsymboln is an integer between and The digits are separated by blanks.
Figure The Backtracking Algorithm for CSPs Input and output files: Your program will read in the initial game board values from an input text file and then produce an output text file that contains the solution. The format of the input file is as shown in Figure below. The first rows contain the initial cell values of the game board, separated by blanks. The cell values range from to with indicating a blank cell. This is followed by a blank line. The next rows contain the locations of dots between horizontallyadjacent cells. Row # contains the locations of dots for horizontallyadjacent cells in row # of the game board, and similarly for the other rows. A value of means there is no dot between two adjacent cells, a value of means there is a white dot between two adjacent cells, and a value of means there is a black dot between two adjacent cells. This is then followed by another blank line. The next rows contain the locations of dots between verticallyadjacent cells. Row # contains the locations of dots between verticallyadjacent cells in the first and second rows of the game board, and similarly for the other rows. Again, a value of means there is no dot between two adjacent cells, a value of means there is a white dot between two adjacent cells, and a value of means there is a black dot between two adjacent cells. The format of the output file is as shown in Figure below. The output file contains rows of integers ranging from to separated by blanks.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


