Question: Project description: The TCP/IP stack has five layers, namely application, transport, network, link, and physical. In Phase 1, each student implemented the standard user datagram
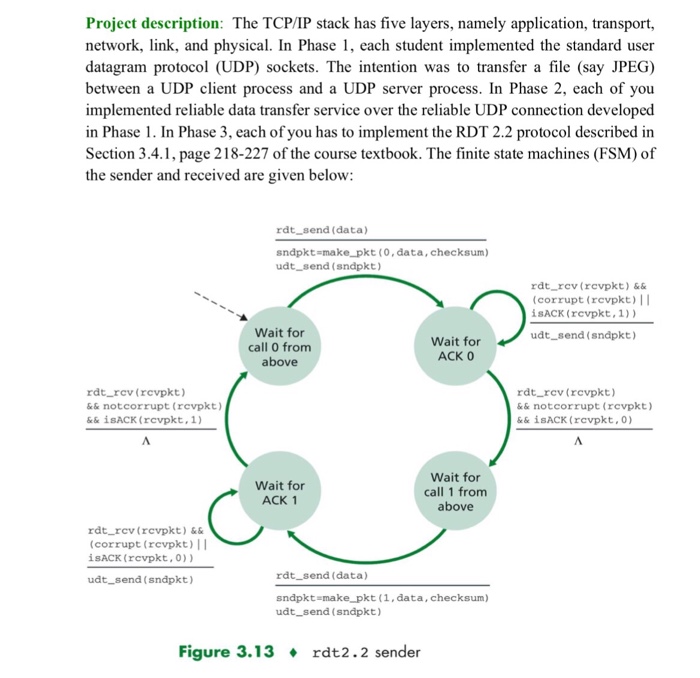



Project description: The TCP/IP stack has five layers, namely application, transport, network, link, and physical. In Phase 1, each student implemented the standard user datagram protocol (UDP) sockets. The intention was to transfer a file (say JPEG) between a UDP client process and a UDP server process. In Phase 2, each of you implemented reliable data transfer service over the reliable UDP connection developed in Phase 1. In Phase 3, each ofyou has to implement the RDT 2.2 protocol described in Section 3.4.1, page 218-227 of the course textbook. The finite state machines (FSM)of the sender and received are given below: rdt send (data) sndpkt make pkt. (0,data, checksum) udt send (sndpkt) rat rev (rcvpkt) && (corrupt (rcvpkt) II isACK (rcvpkt, 1)) Wait for udt send (sndpkt) Wait for call 0 from ACK 0 above rdt rcv (rcvpkt) && not corrupt (rcvpkt) && not corrupt (rcvpkt) && isACK (rcvpkt, 1) && isACK (rcvpkt, 0) Wait for Wait for call 1 from ACK 1 above rdt_rcv (rcvpkt) && (corrupt (rcvpkt) II SACK (rcvpkt., 0)) rdt send (data) udt-send (sndpkt) sndpkt make pkt (1, data, checksum) udt send (sndpkt) Figure 3.13 rdt2.2 sender
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


